Embed presentation
Download to read offline

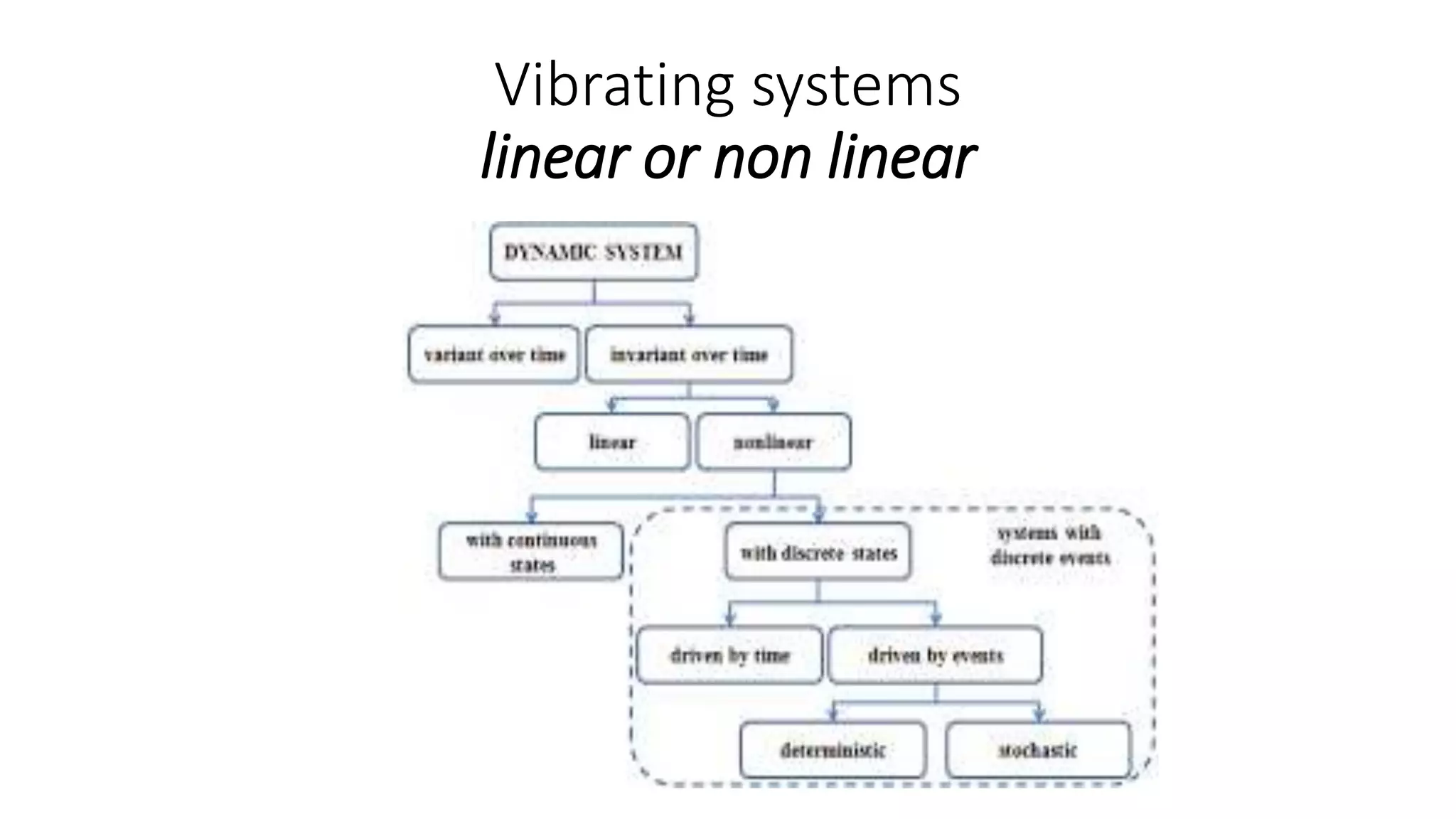



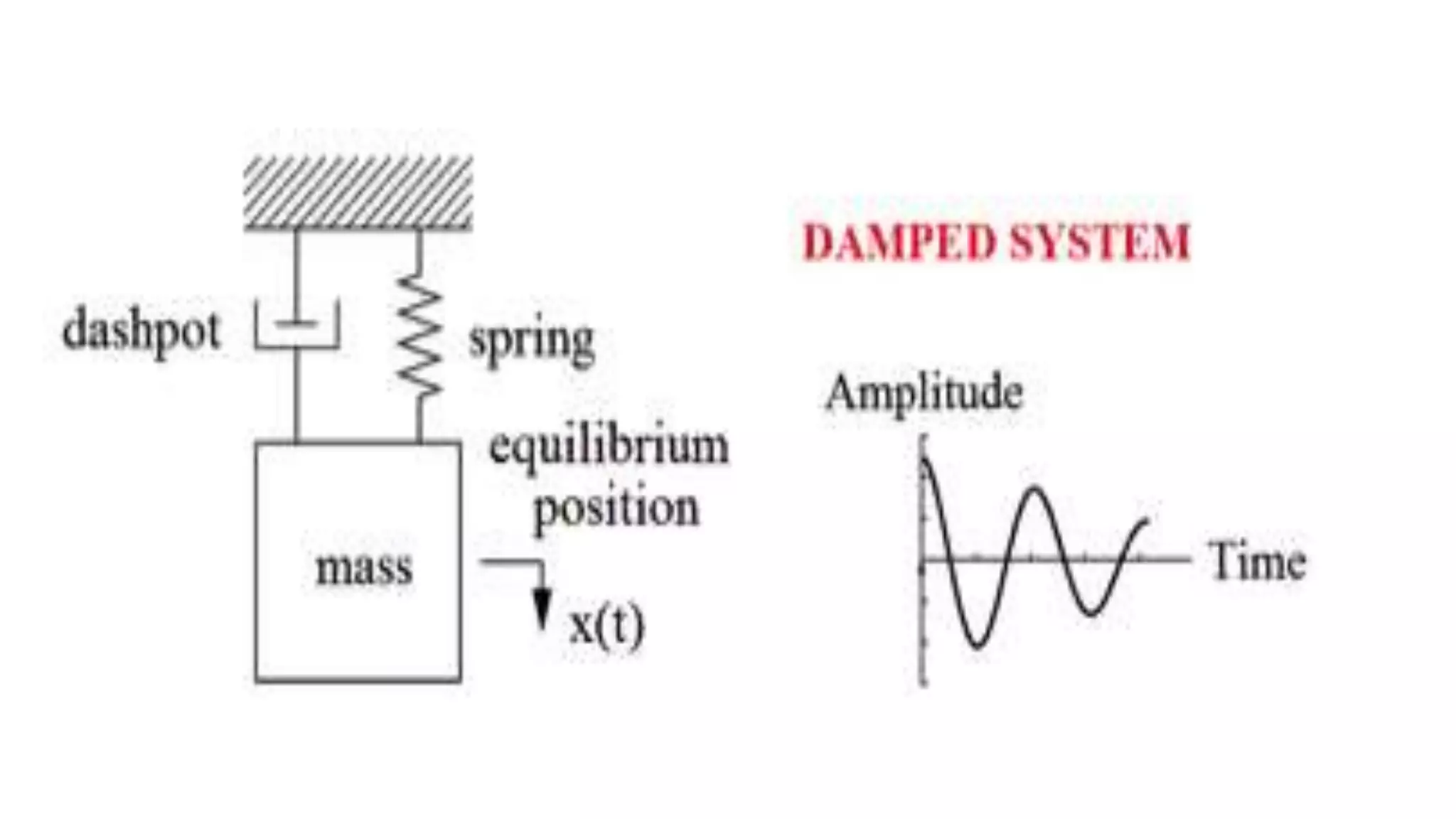


The document discusses the theory of vibration systems, covering concepts like static and dynamic behavior, as well as lumped and continuous models. It explains degrees of freedom, detailing the six types related to both rotational and translational movements. Additionally, it differentiates between forced vibrations, influenced by continuous external forces, and free vibrations, which occur when a system vibrates at its natural frequency after an initial input.









