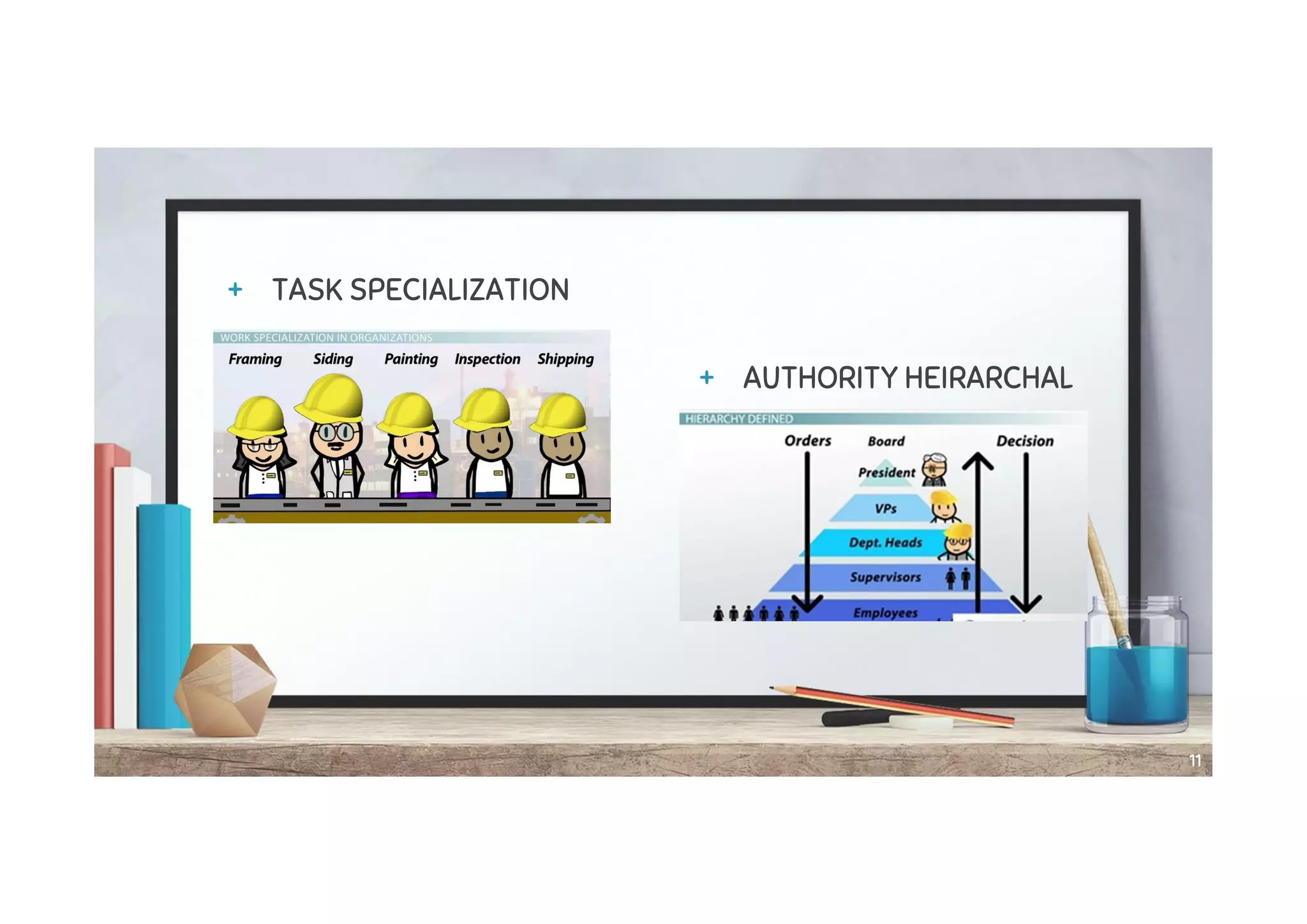
This document provides an overview of several classic management theories, including:
- Max Weber's bureaucratic theory which emphasizes hierarchy, rules, and impersonality.
- Elton Mayo's human relations theory which found that social and relational factors motivate employees more than environmental factors.
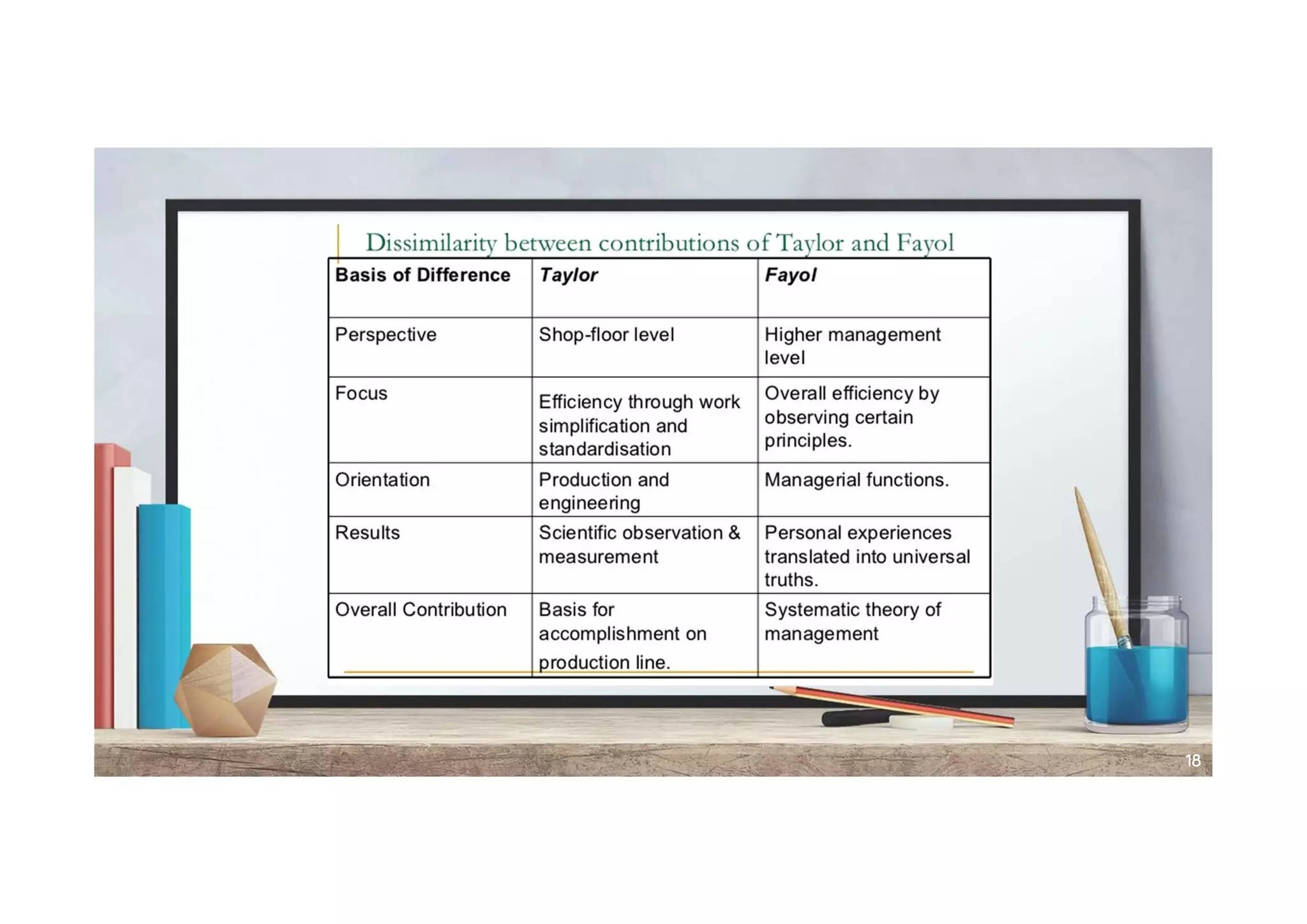
- Frederick Taylor's scientific management theory which broke down tasks and financially rewarded performance.
It also discusses Henri Fayol's administrative principles, Douglas McGregor's Theory X and Y, and classical and modern management theories. The document aims to explain how management theories have evolved from an authority focus to emphasizing employees and different views on employee motivation.