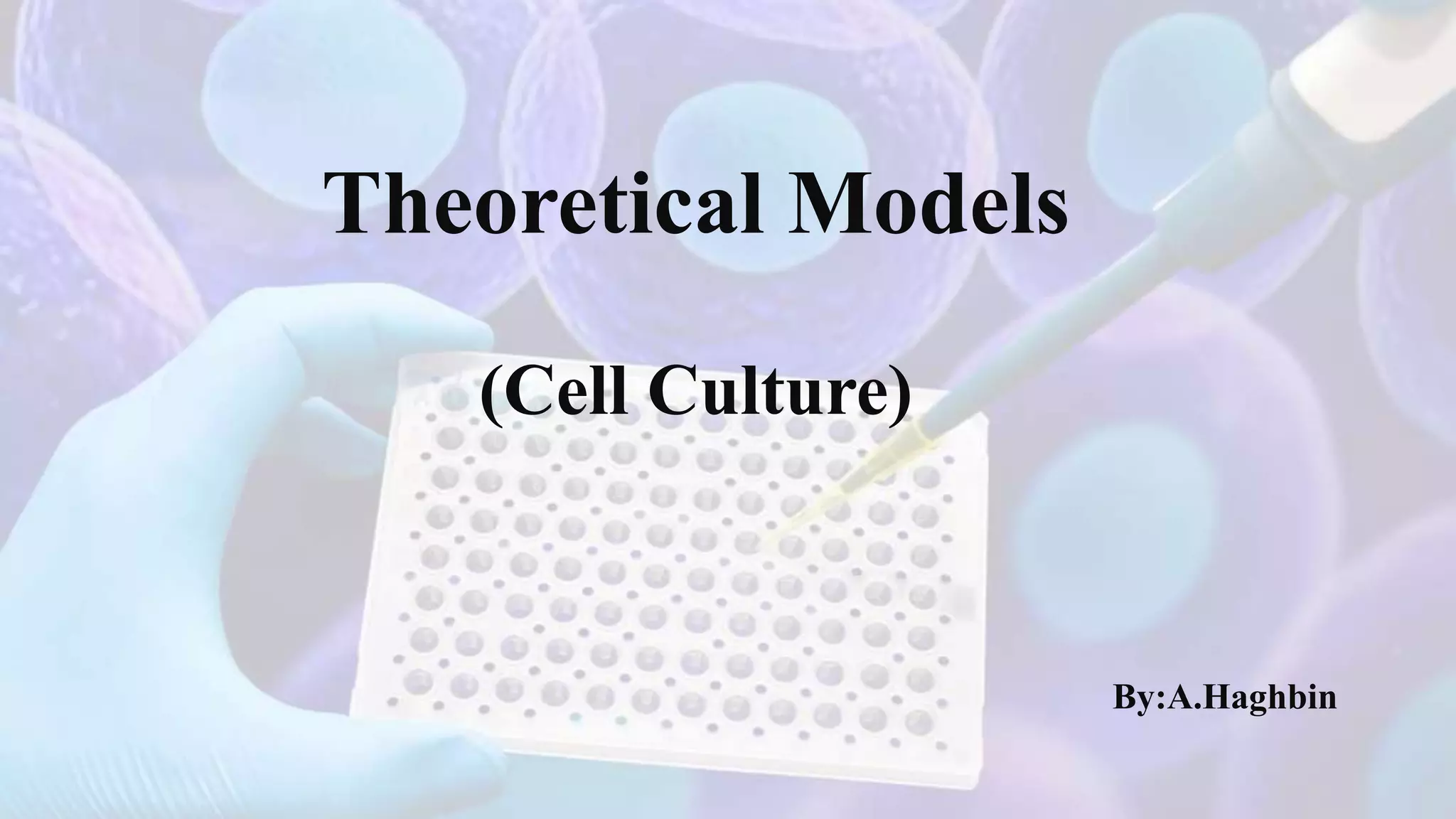
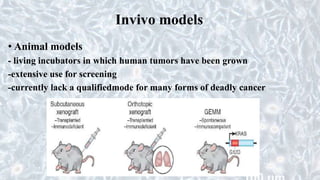
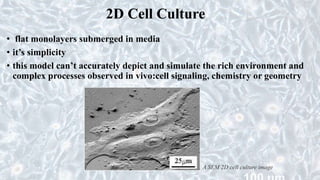
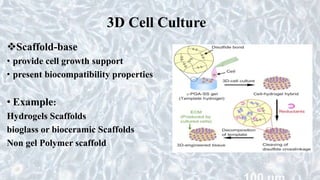
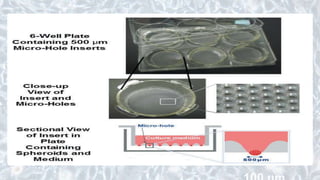
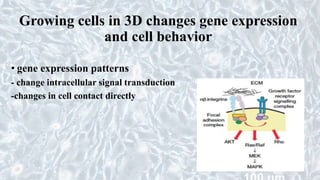
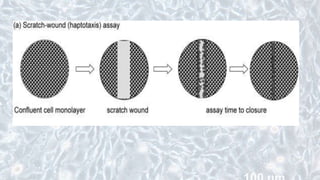
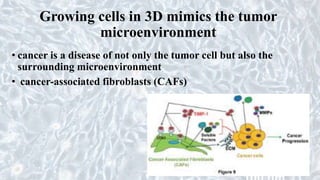
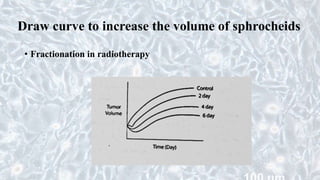
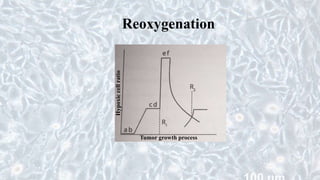
This document discusses different cell culture models, including 2D and 3D cell cultures. 2D cell cultures utilize a flat monolayer that does not accurately mimic the in vivo environment. 3D cell cultures, including scaffold-based and scaffold-free cultures, better simulate the complex 3D environment and cell-cell interactions seen in vivo. Growing cells in 3D alters their proliferation, morphology, drug response, gene expression, and behavior in ways that more closely resemble the in vivo tumor microenvironment compared to traditional 2D cell cultures. 3D cell cultures are useful tools for applications like cancer research, drug development, and modeling of complex tissue environments.