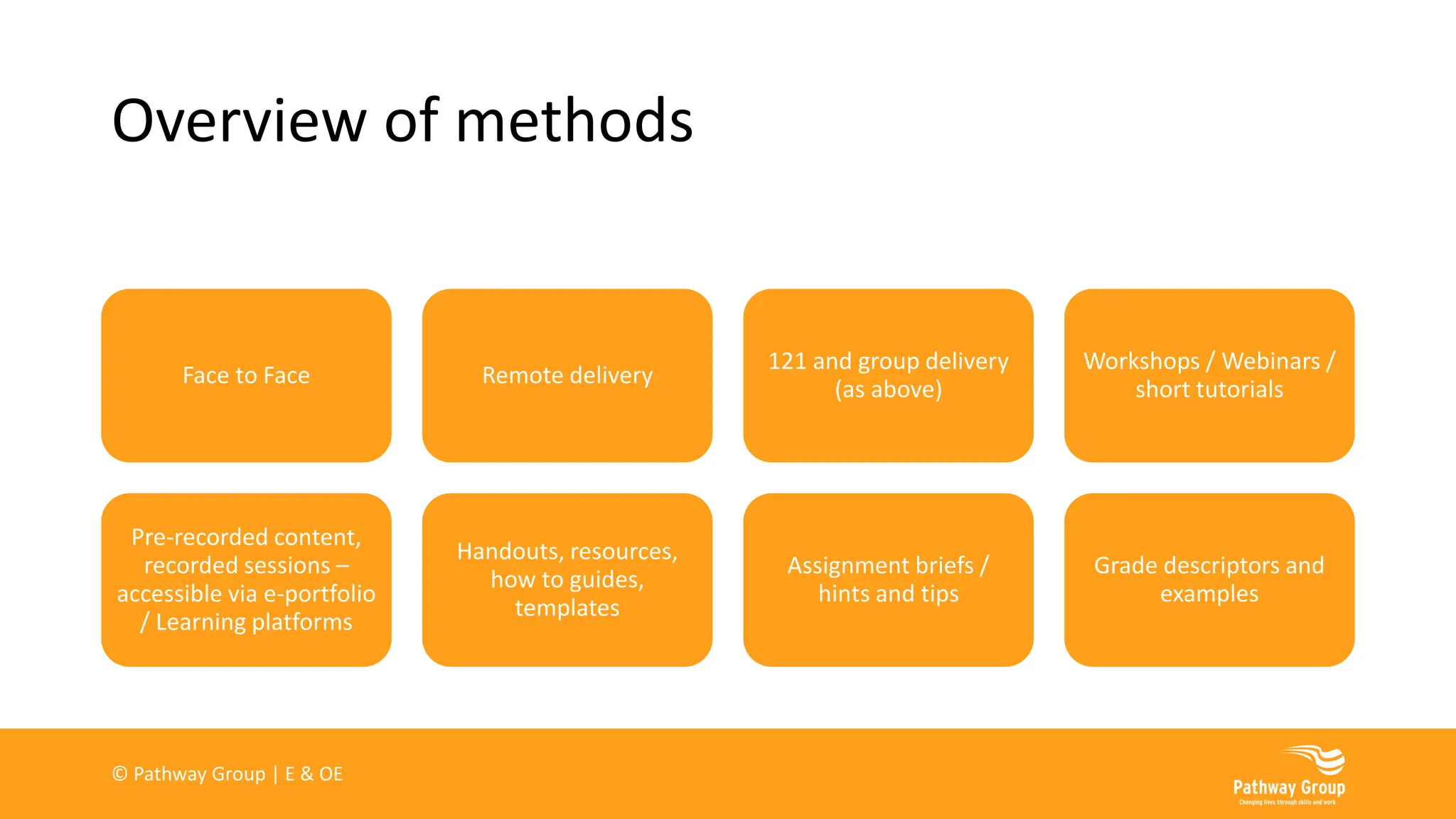
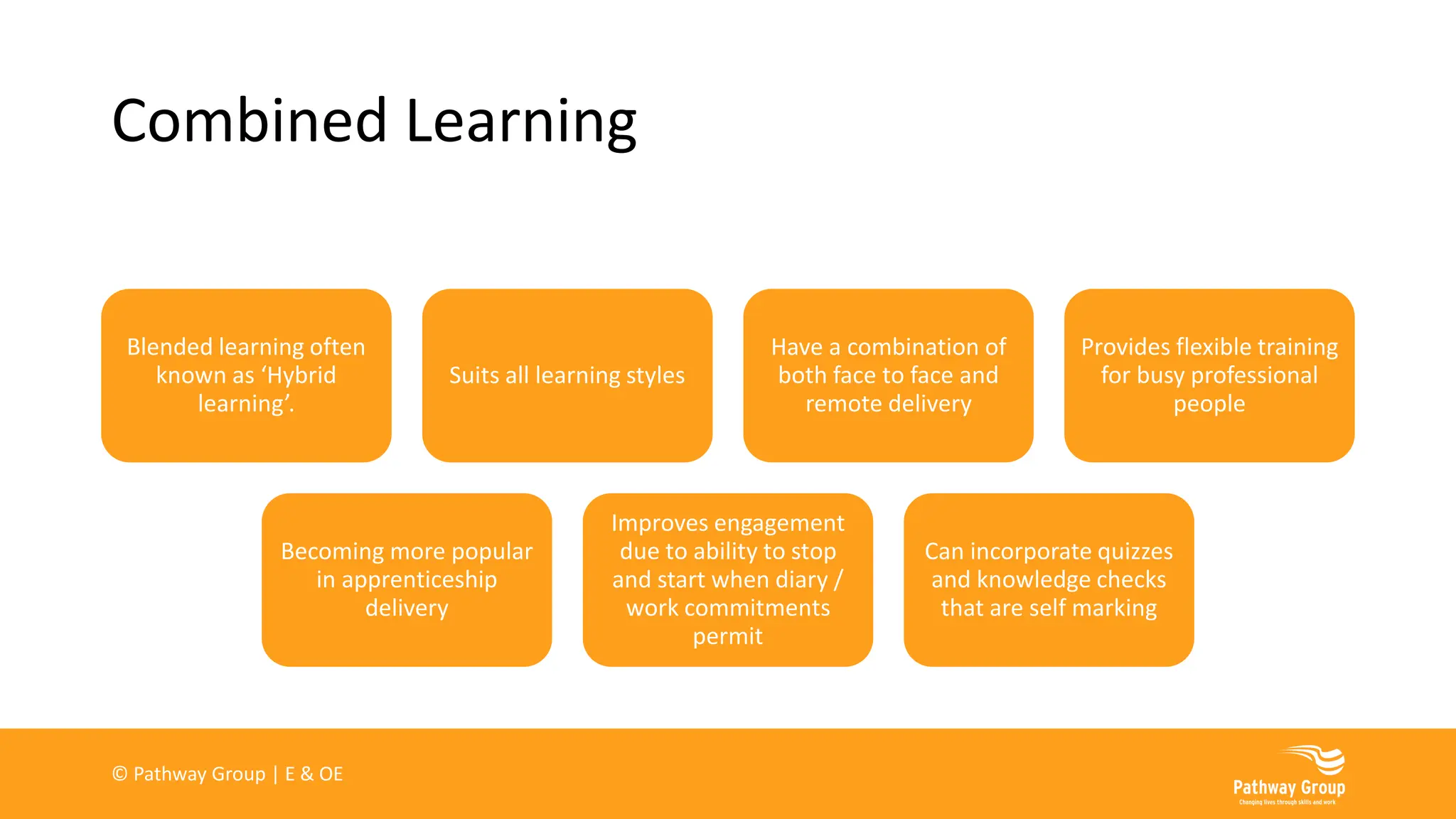
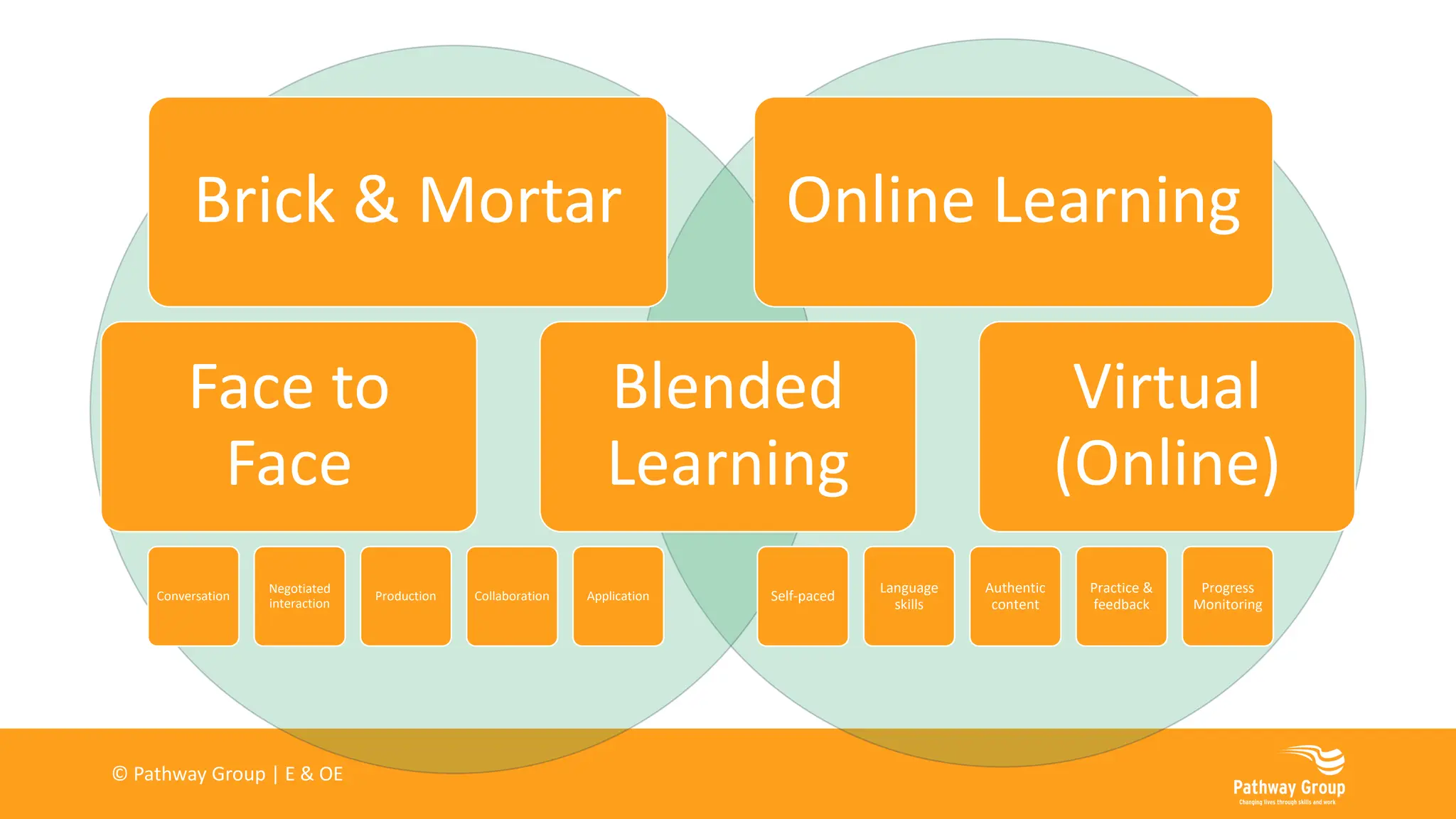
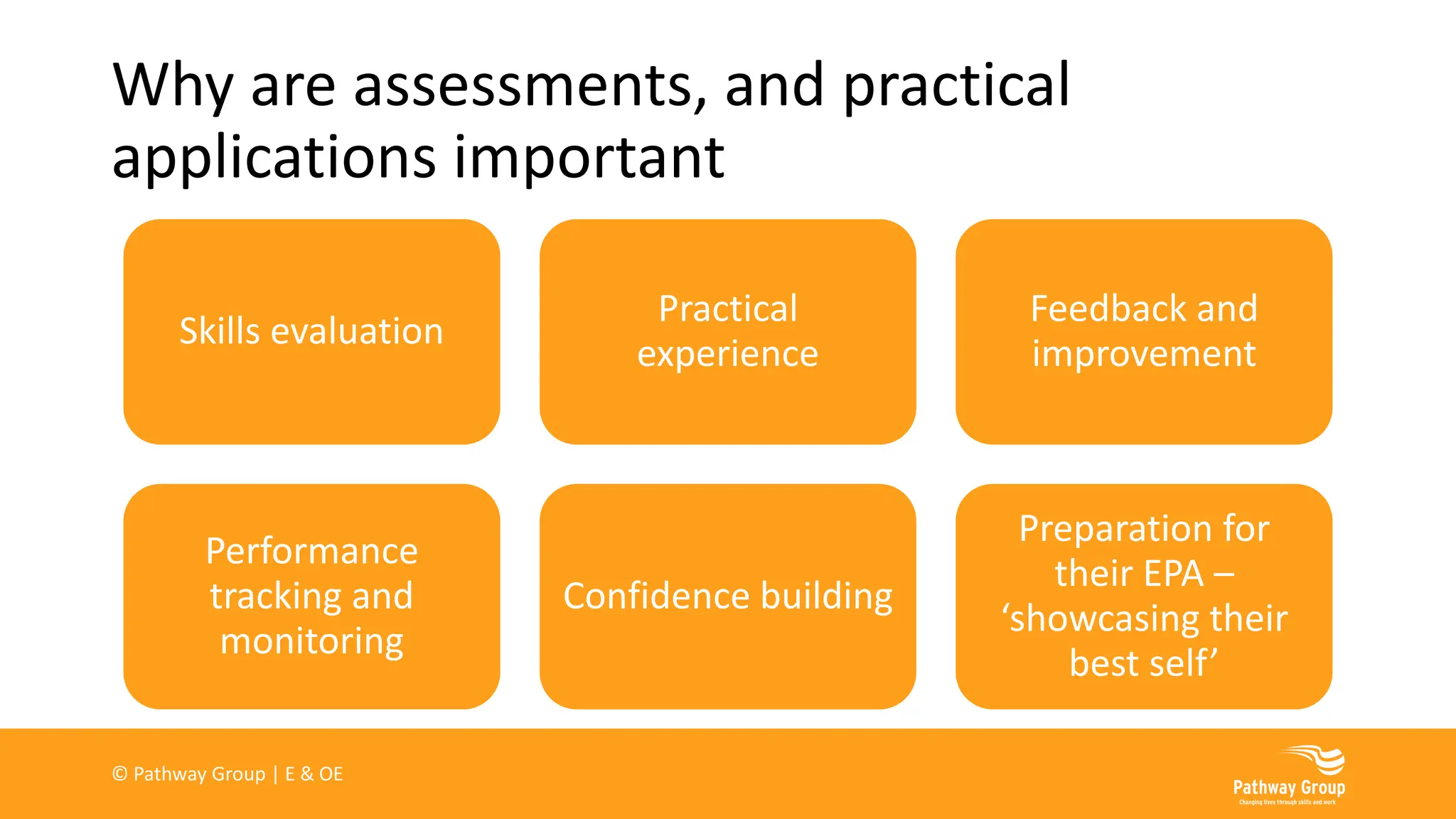
The document outlines various delivery styles and approaches for apprenticeship training, emphasizing blended learning models that cater to different learning styles through a mix of face-to-face and online methods. It highlights the significance of off-the-job training as a legal requirement for apprenticeships, detailing what can and cannot be included in such training. Additionally, the text discusses the roles of supervisors and mentors, the importance of work-based projects, and the necessity of assessments for tracking apprentice progress.