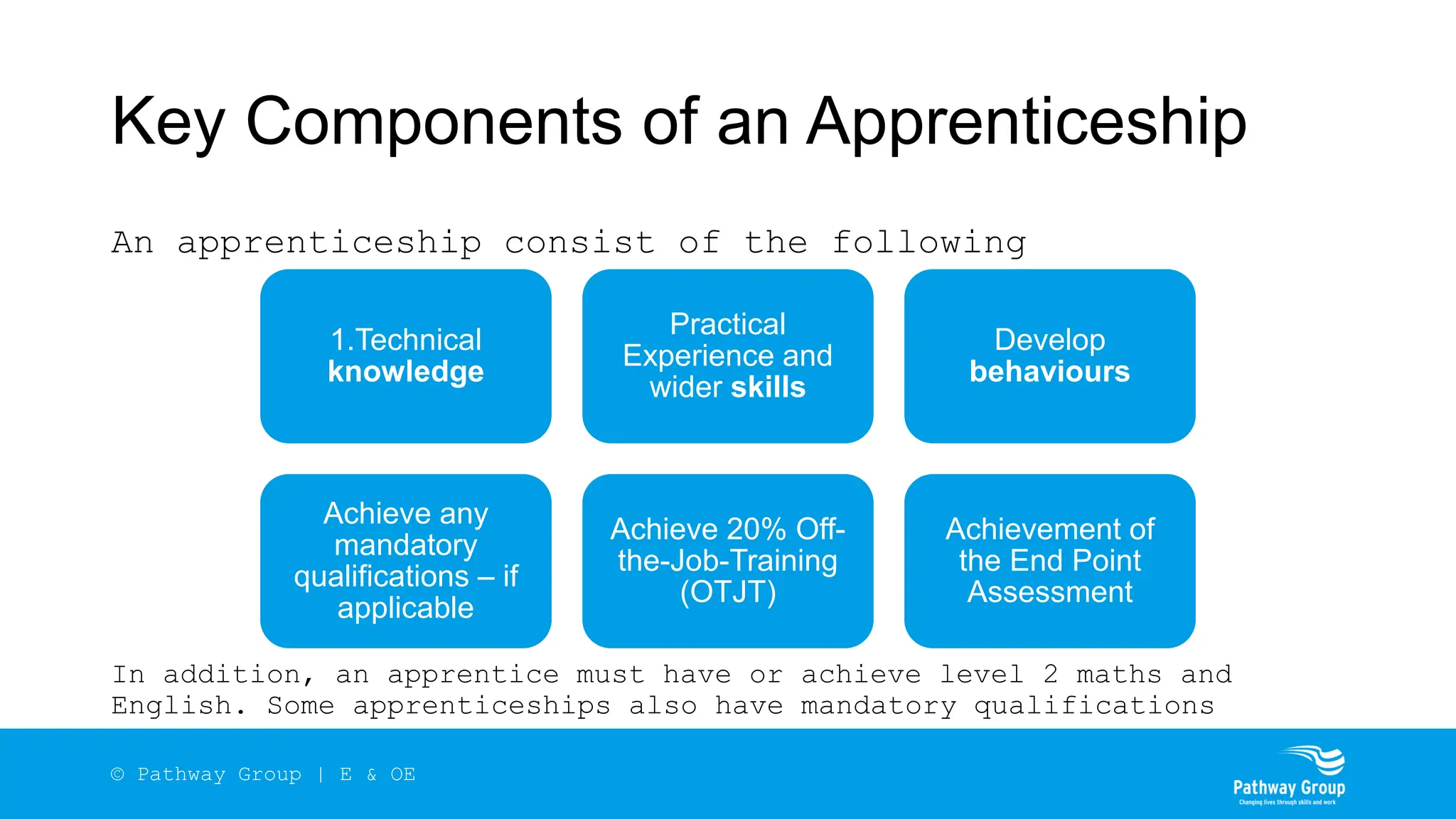
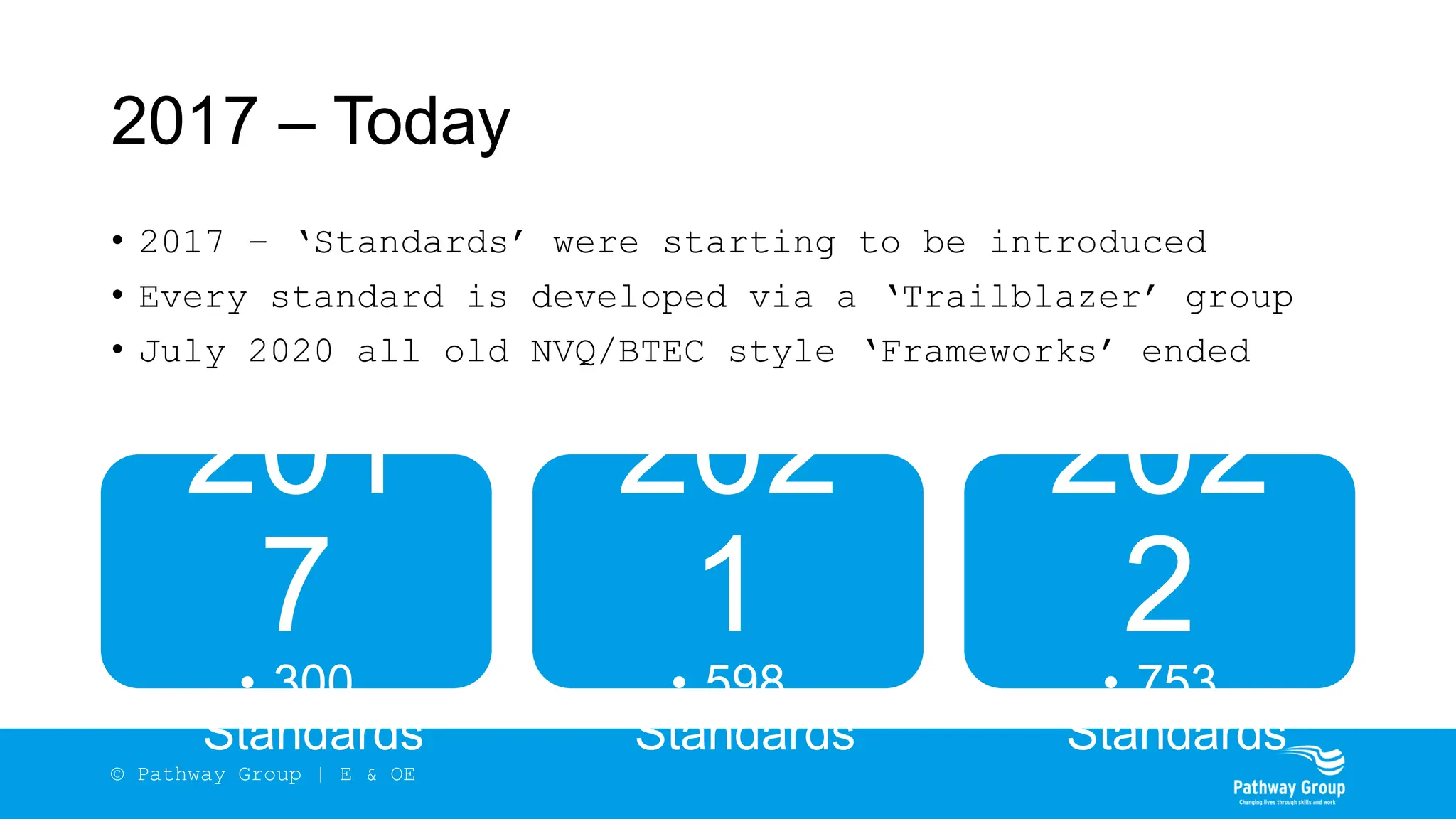
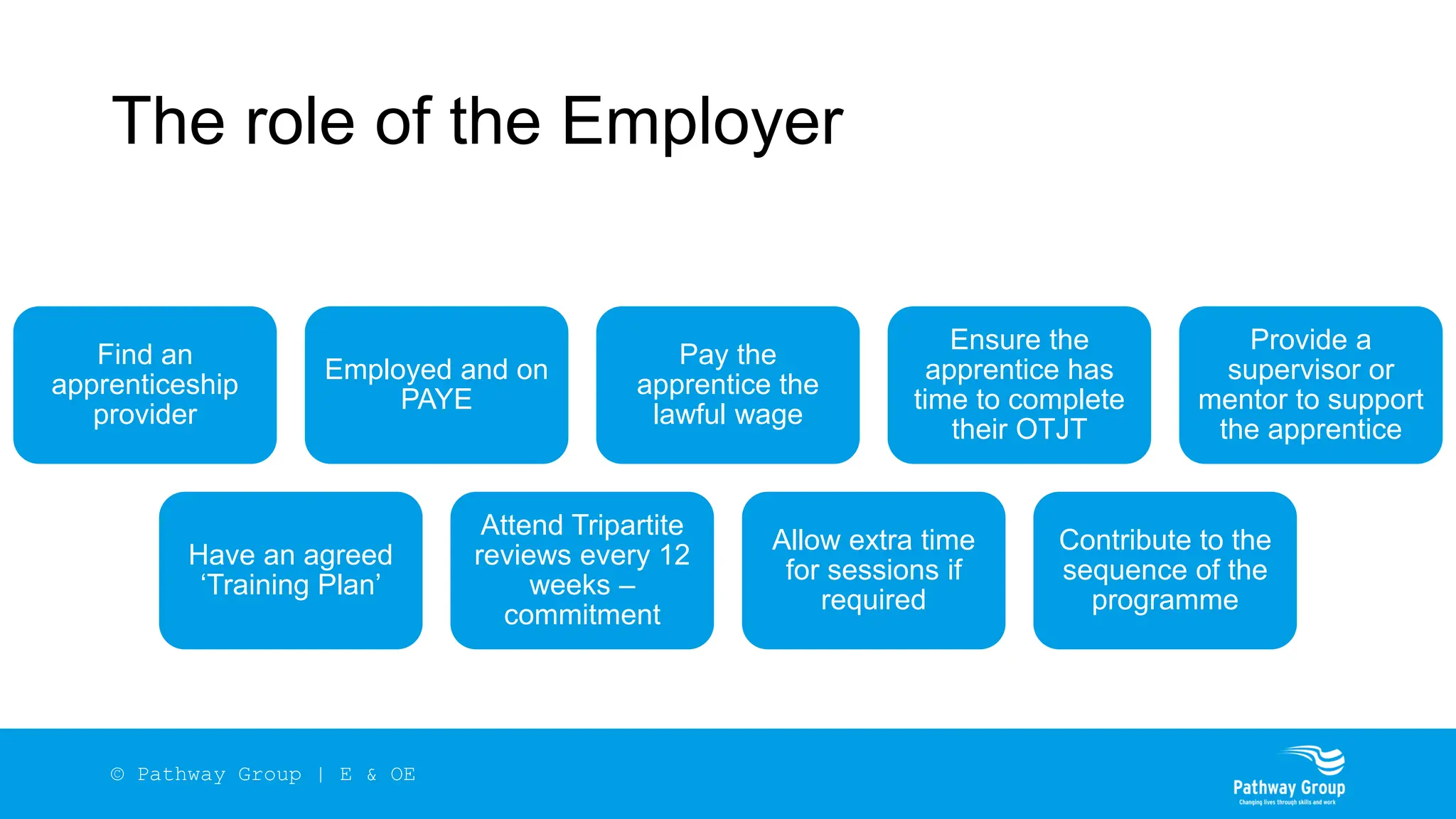
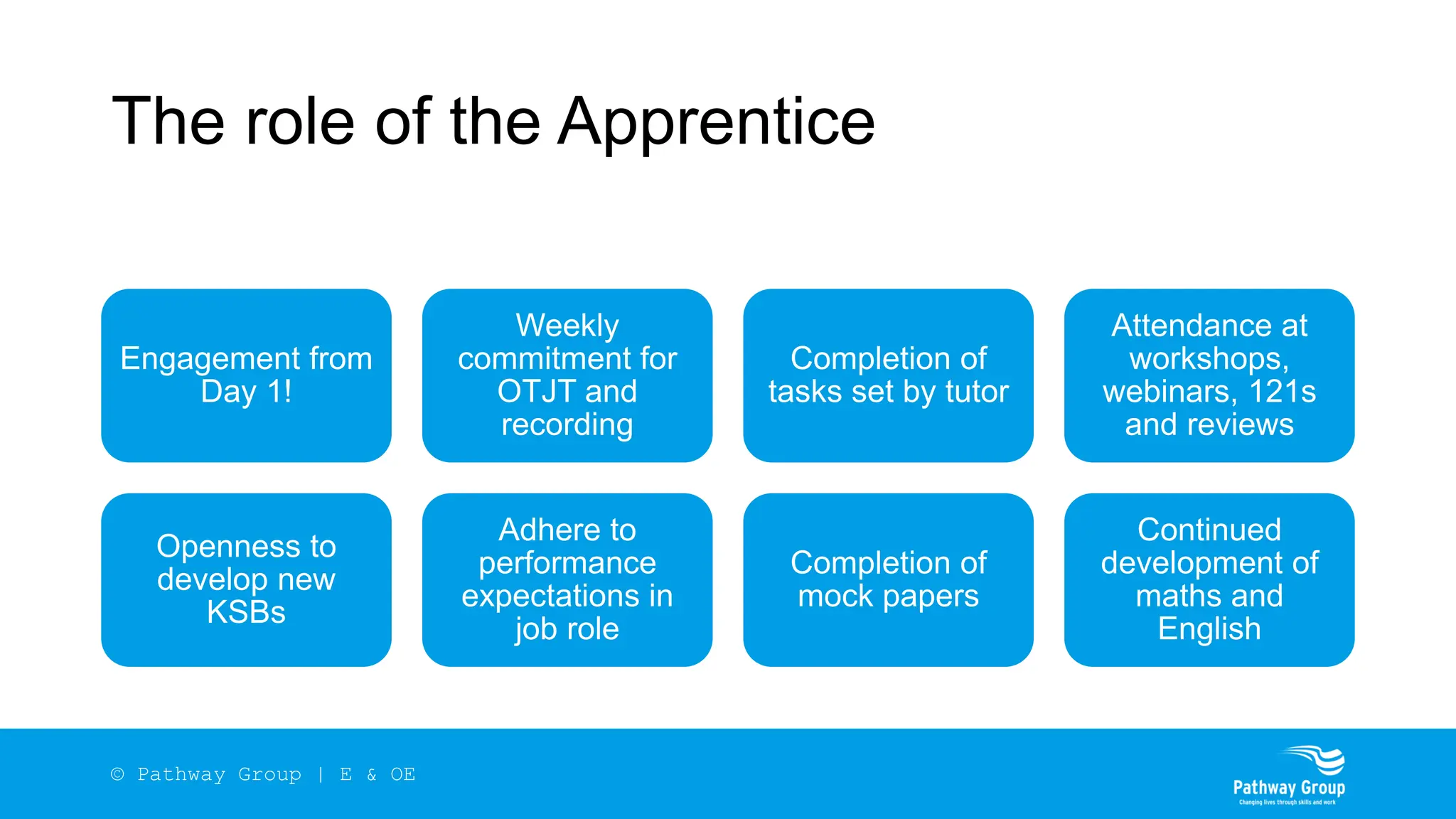
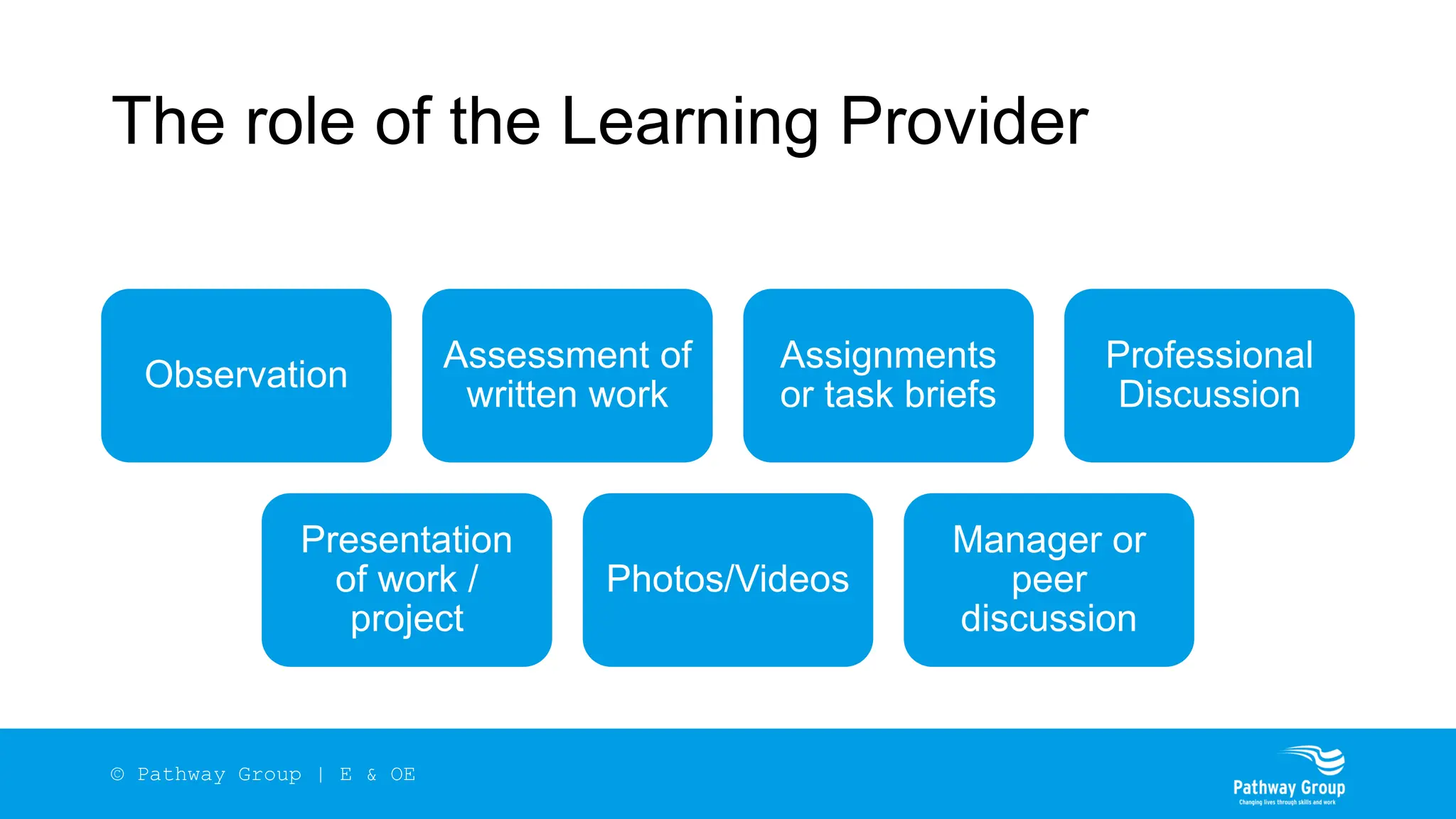
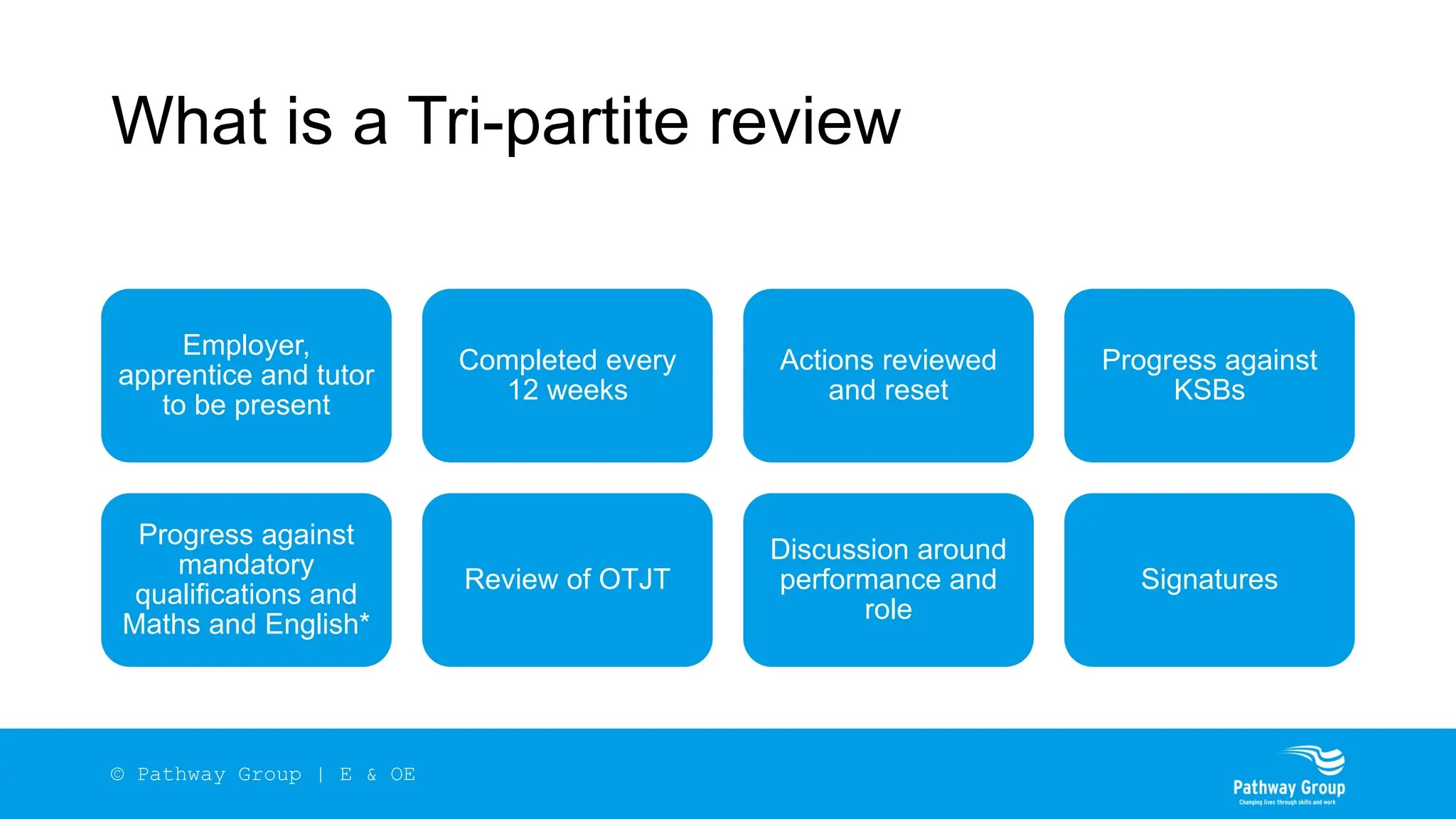
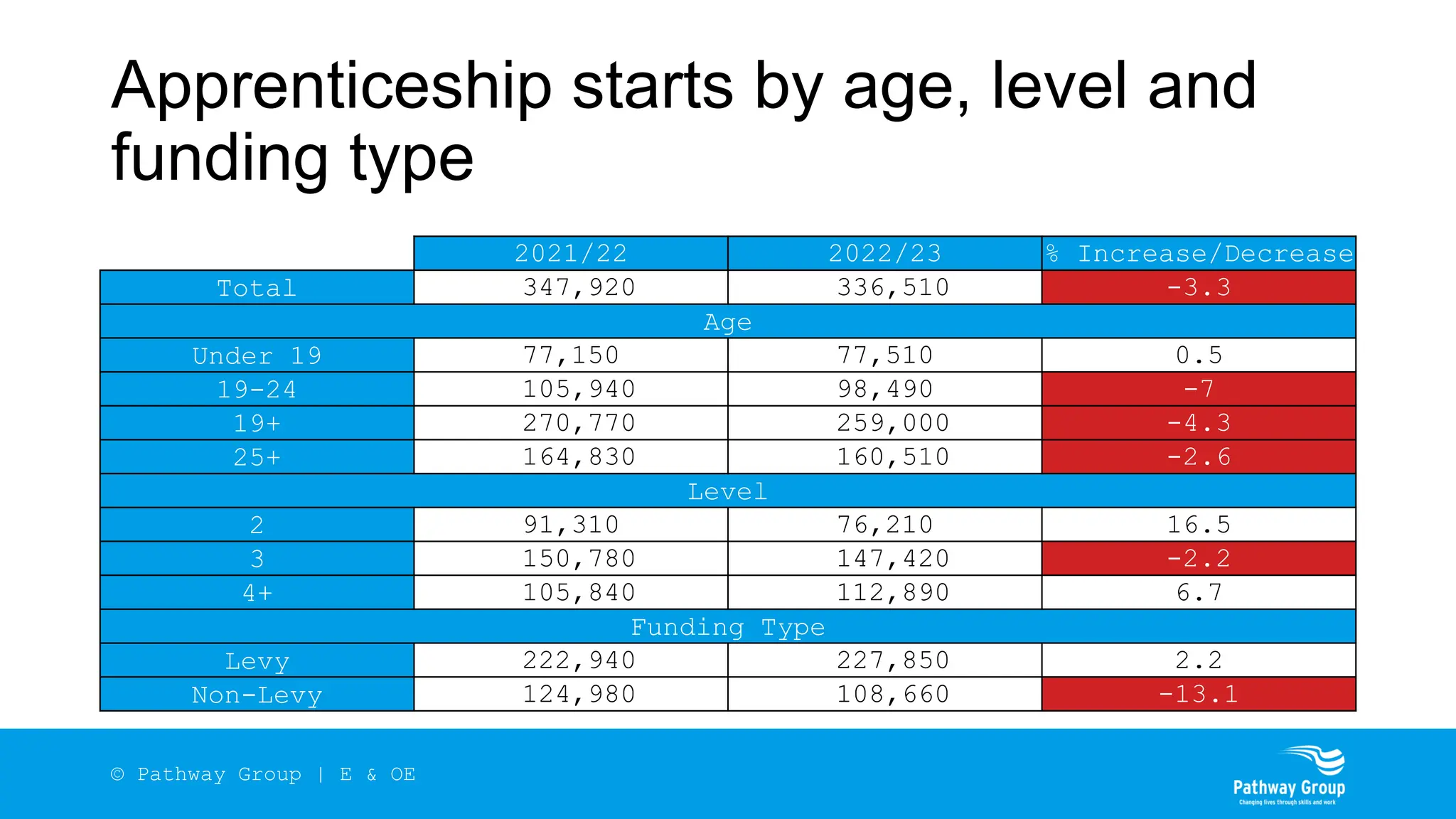
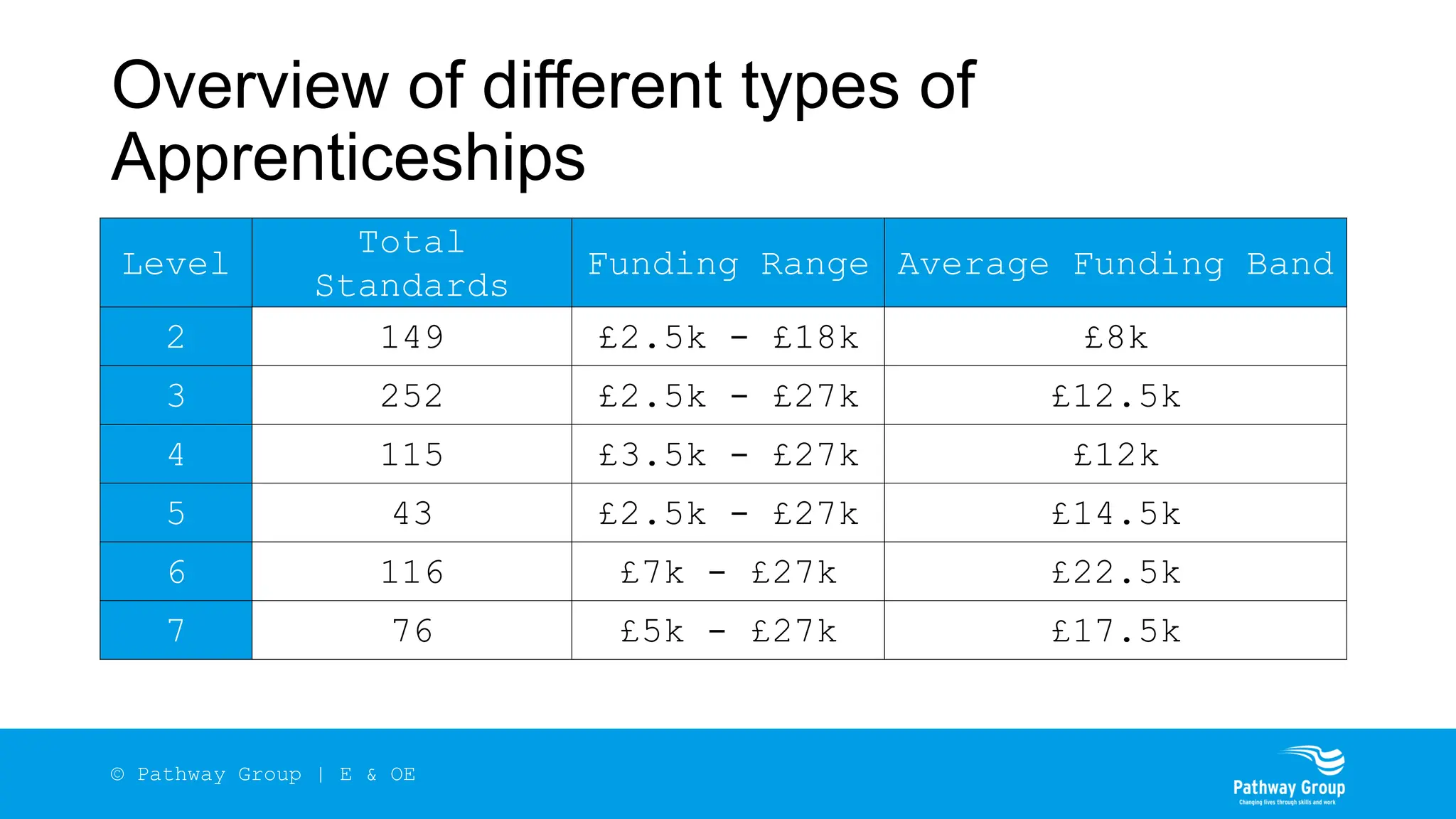
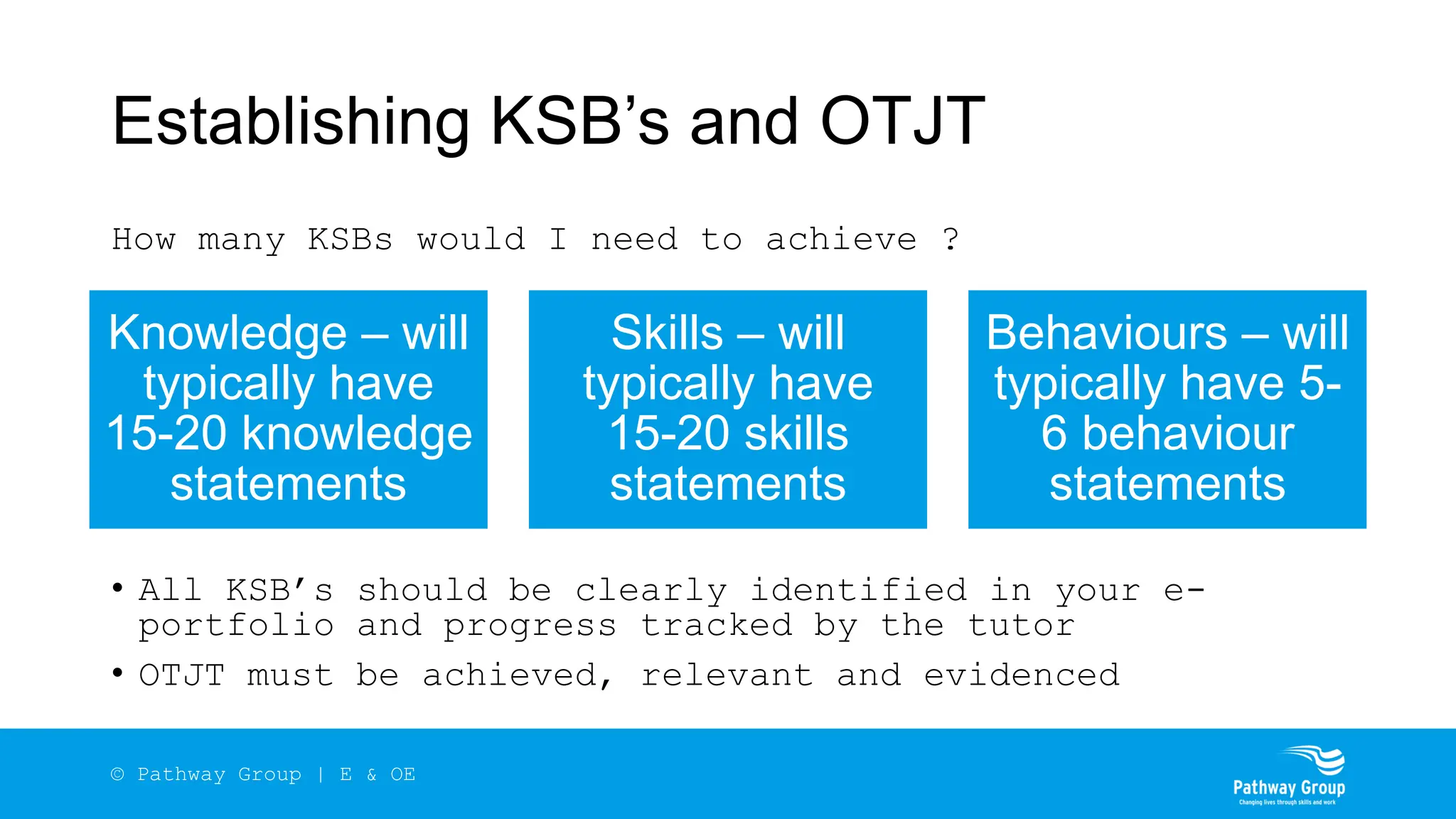
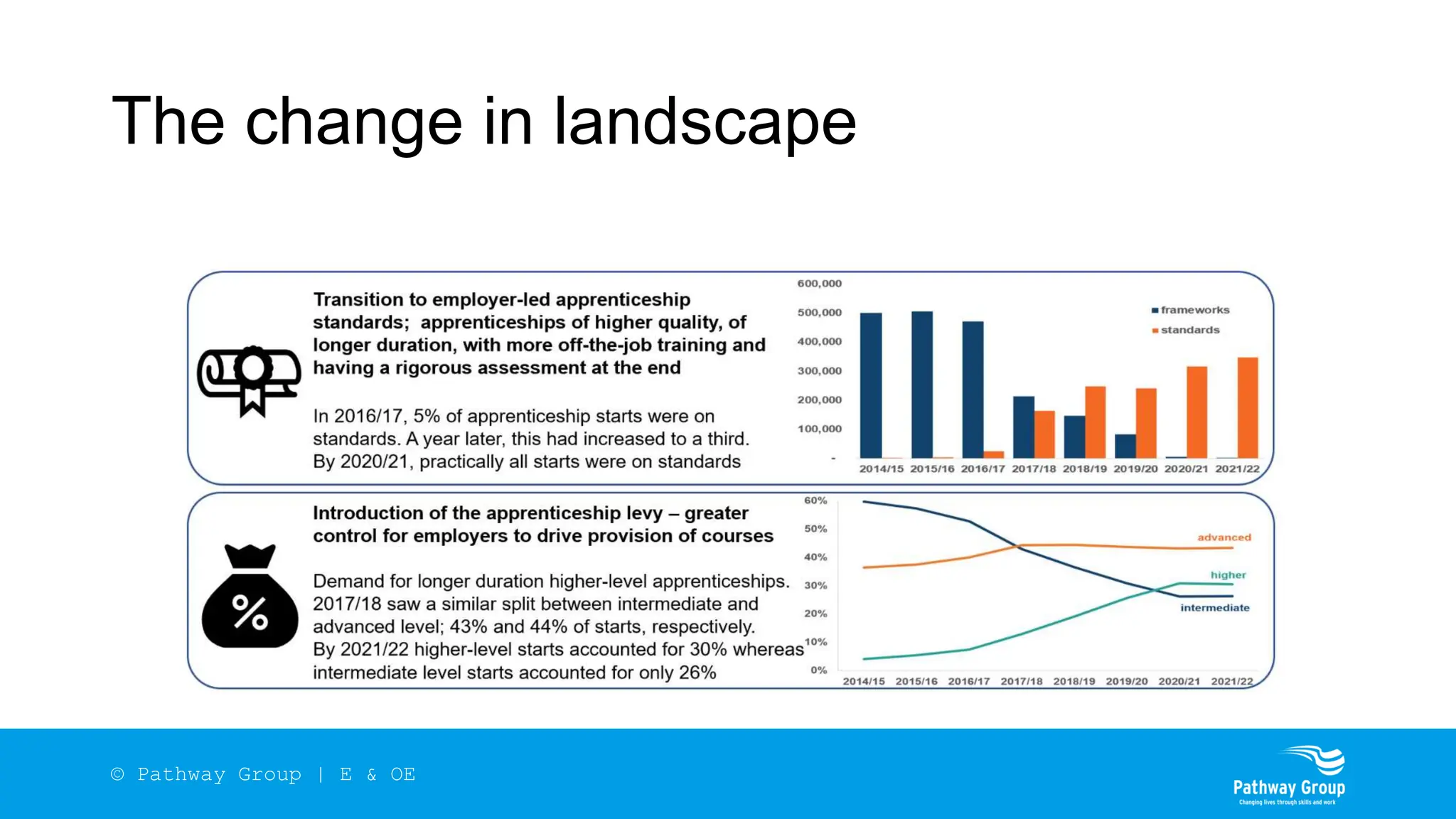
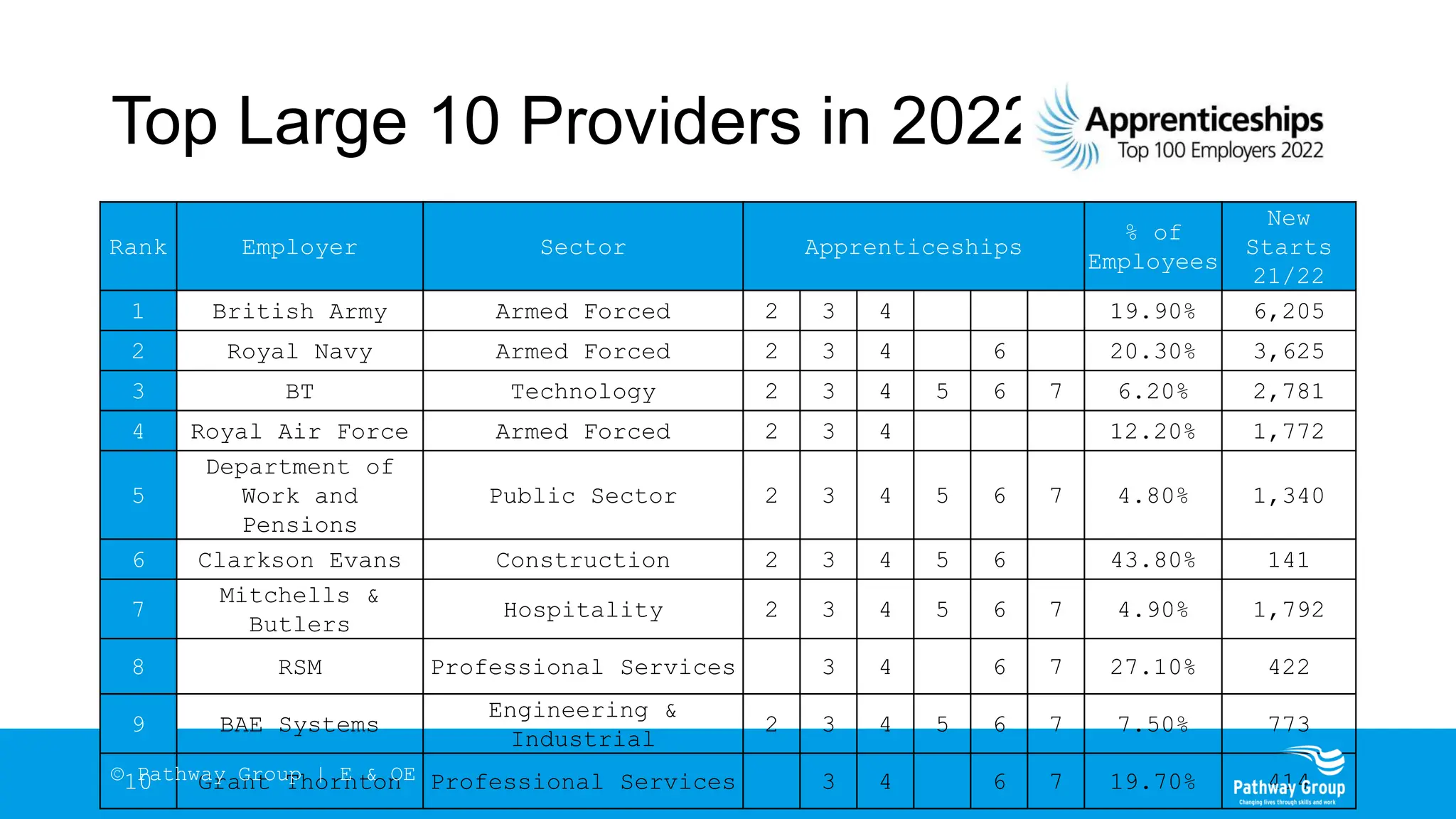
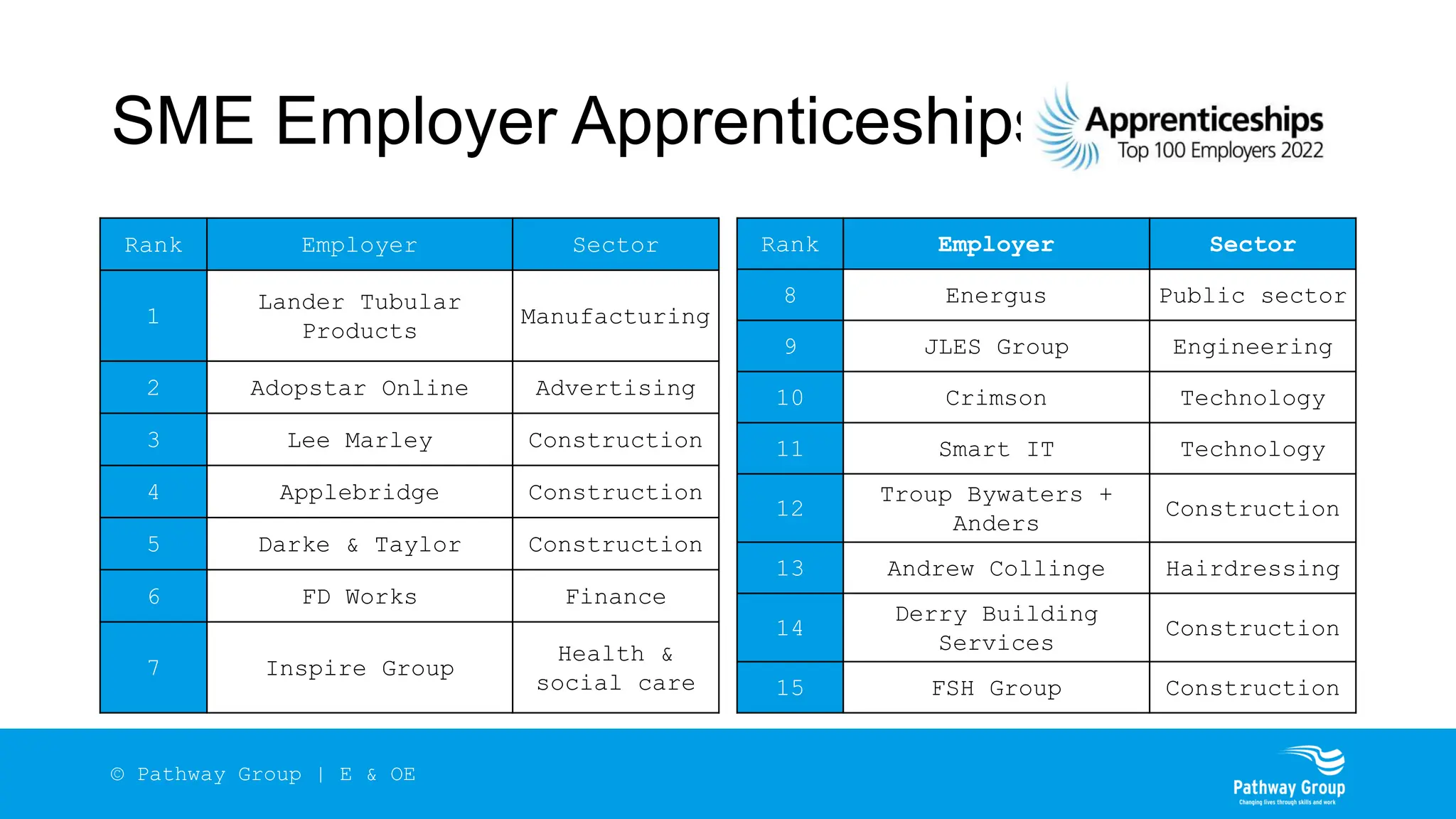
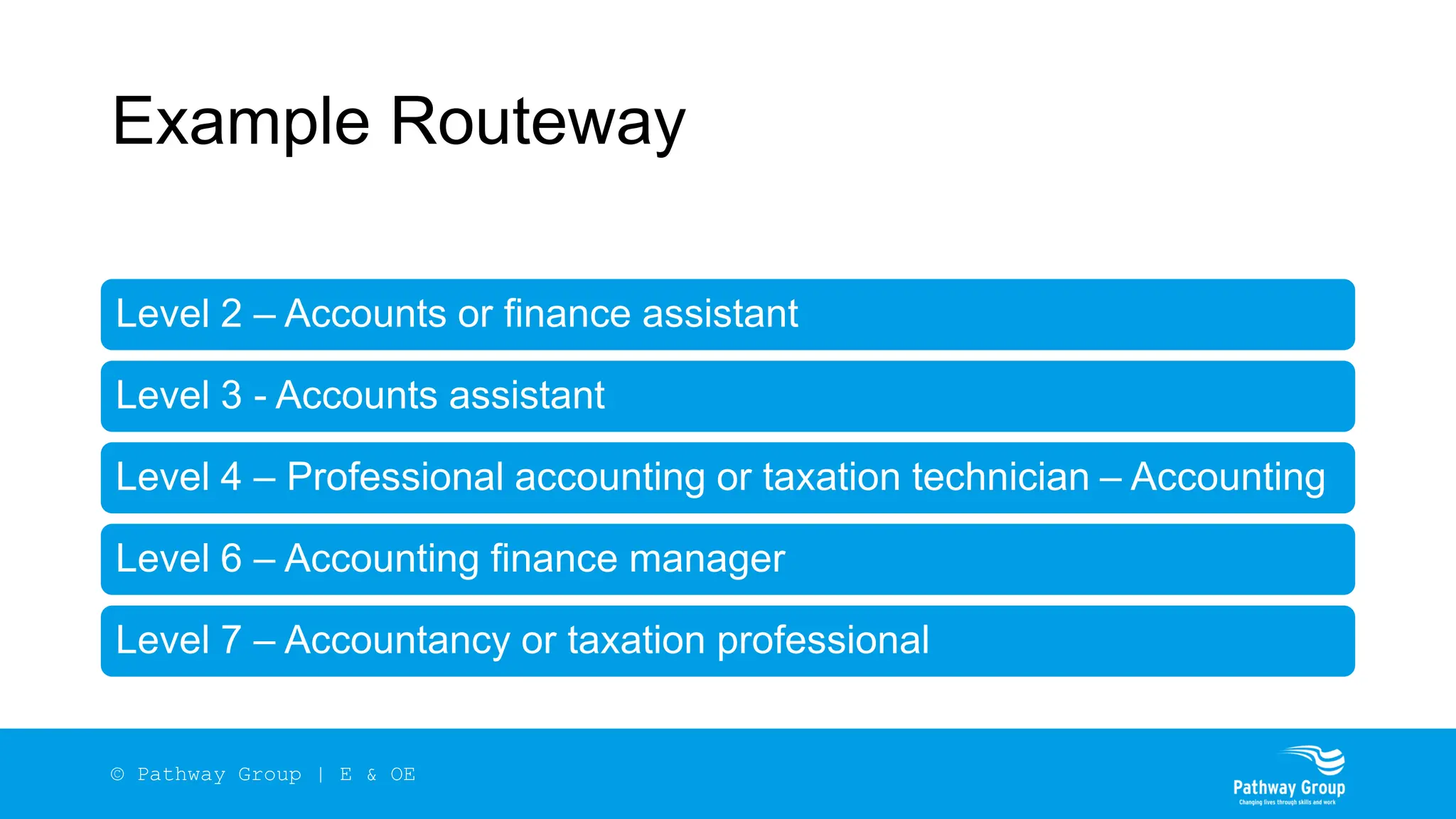
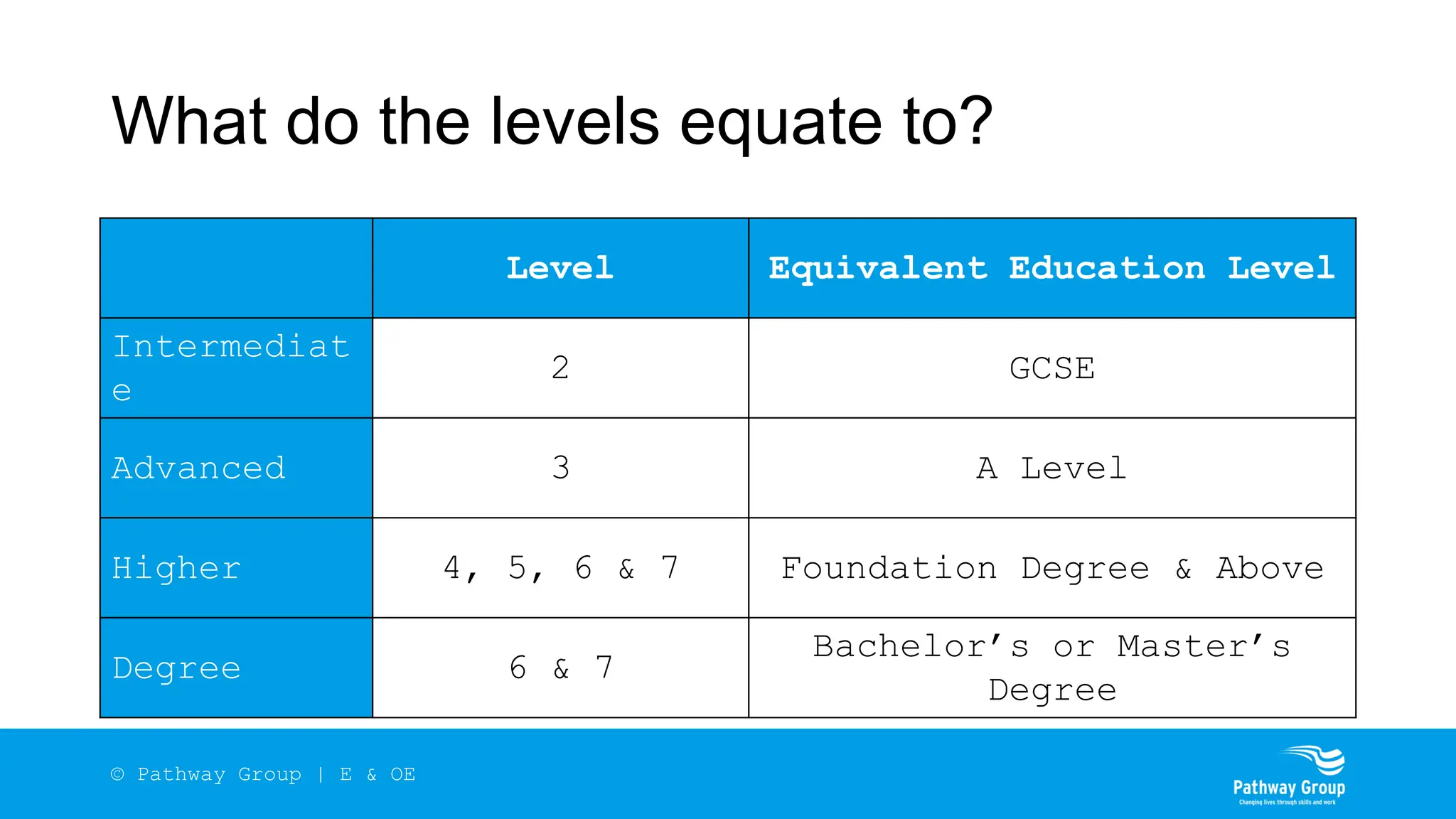
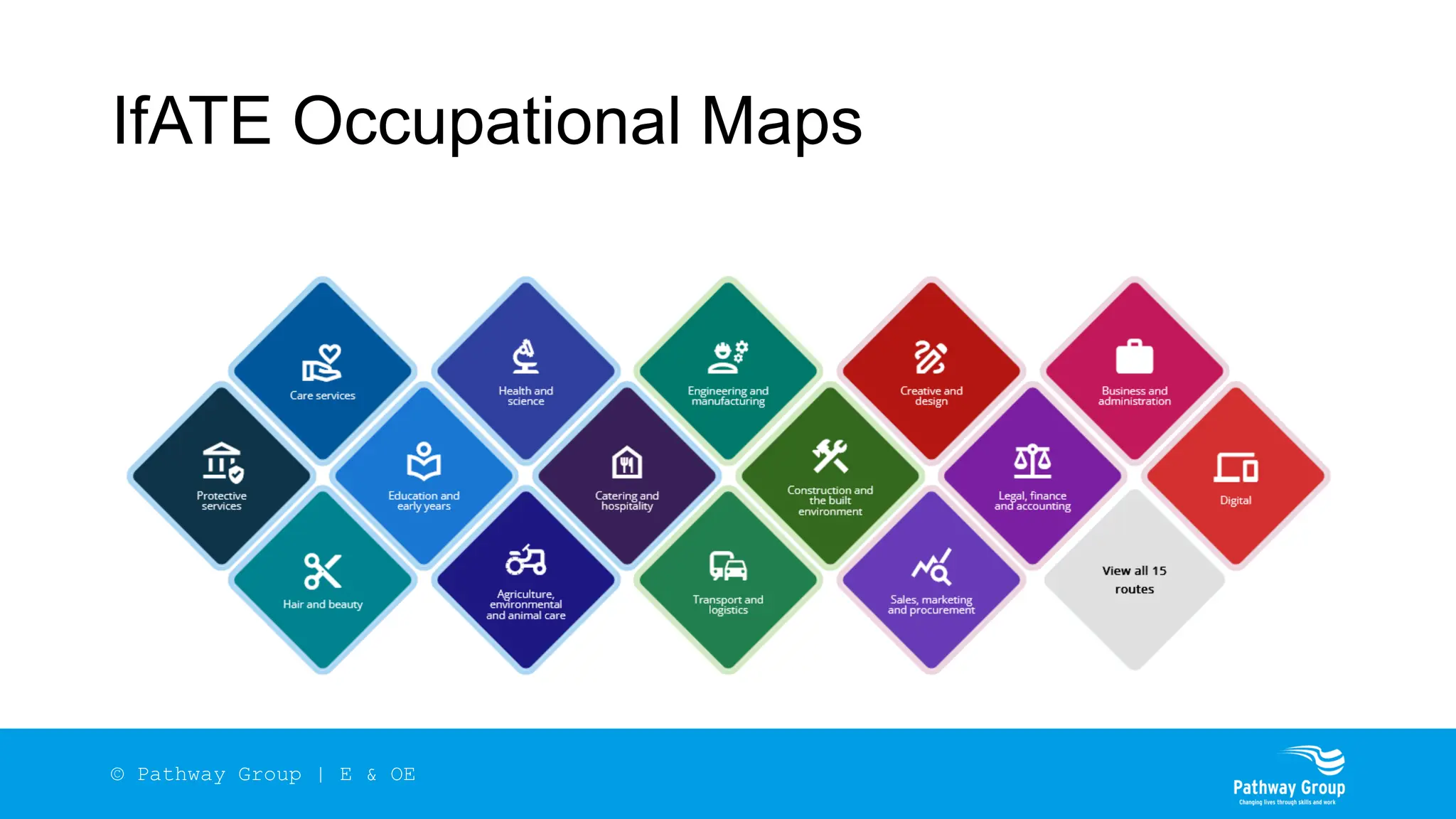
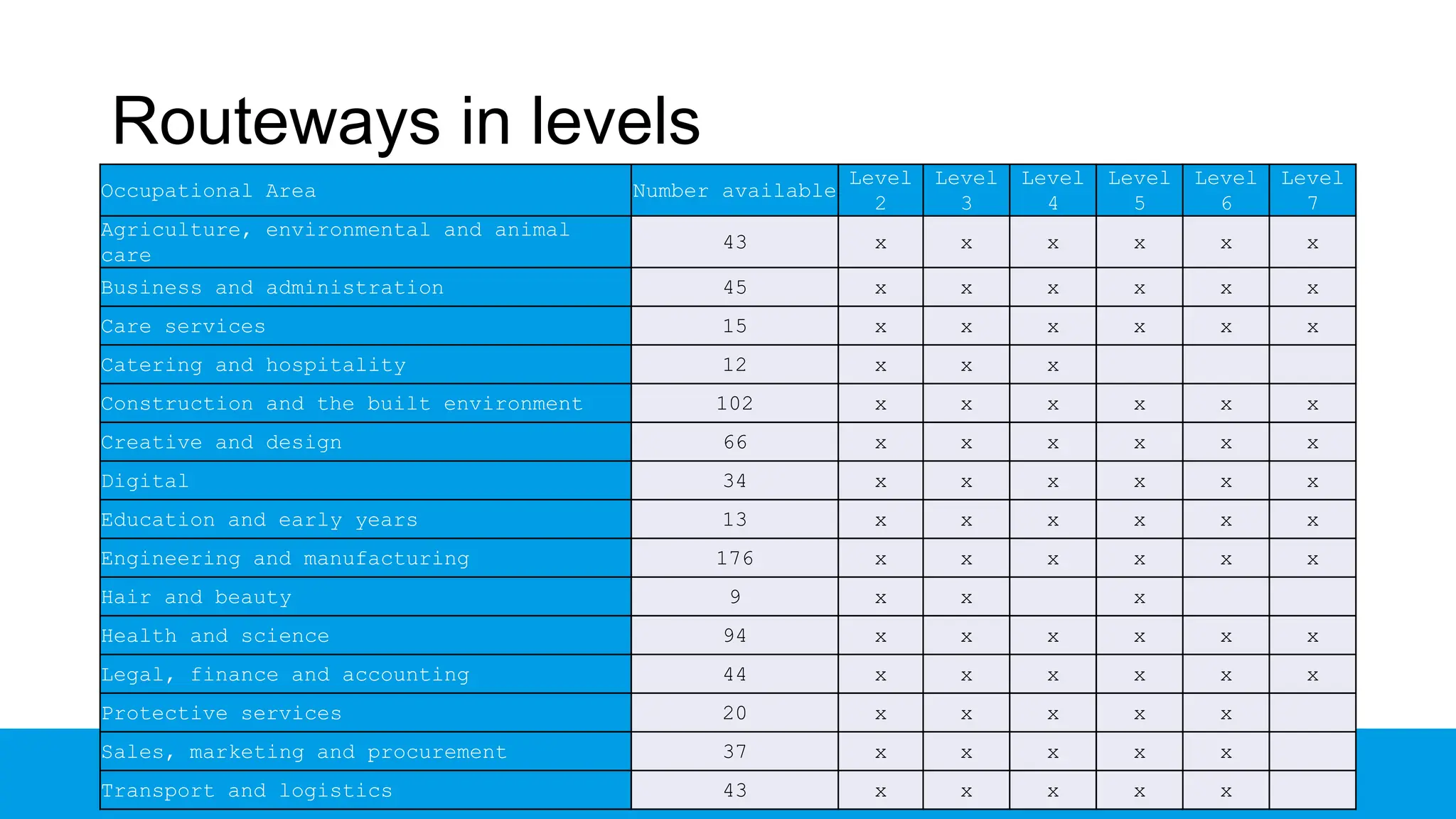
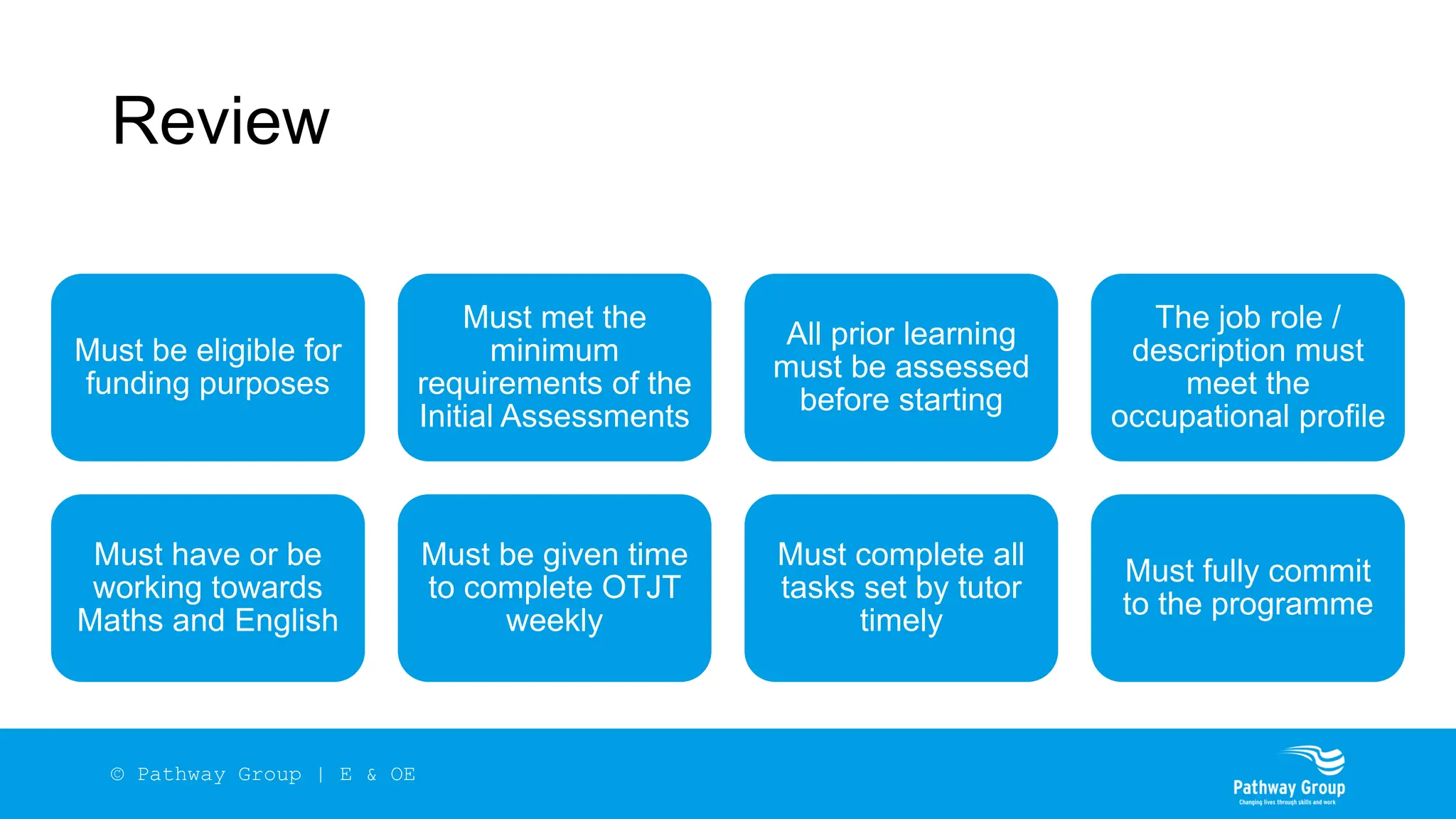
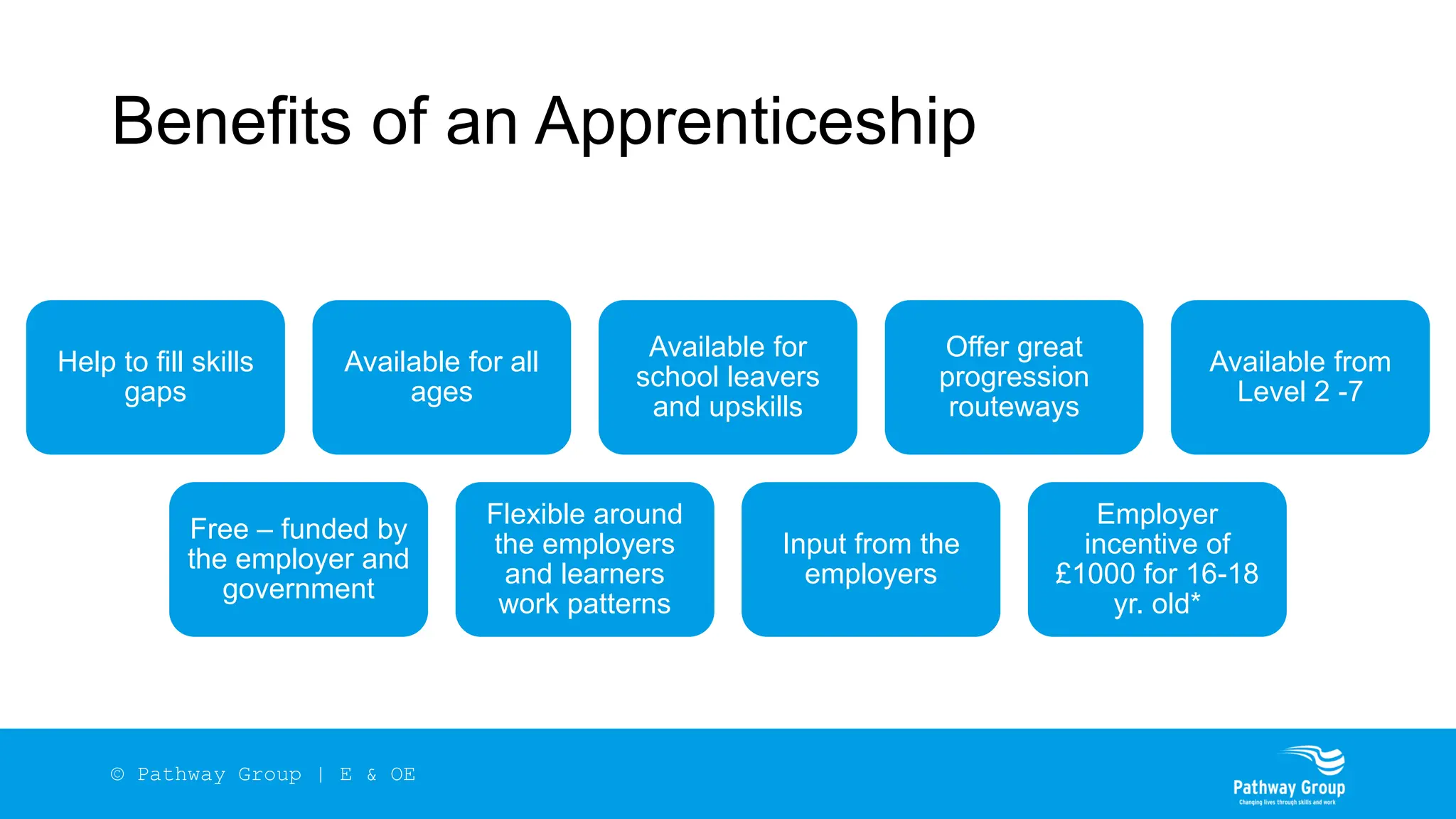
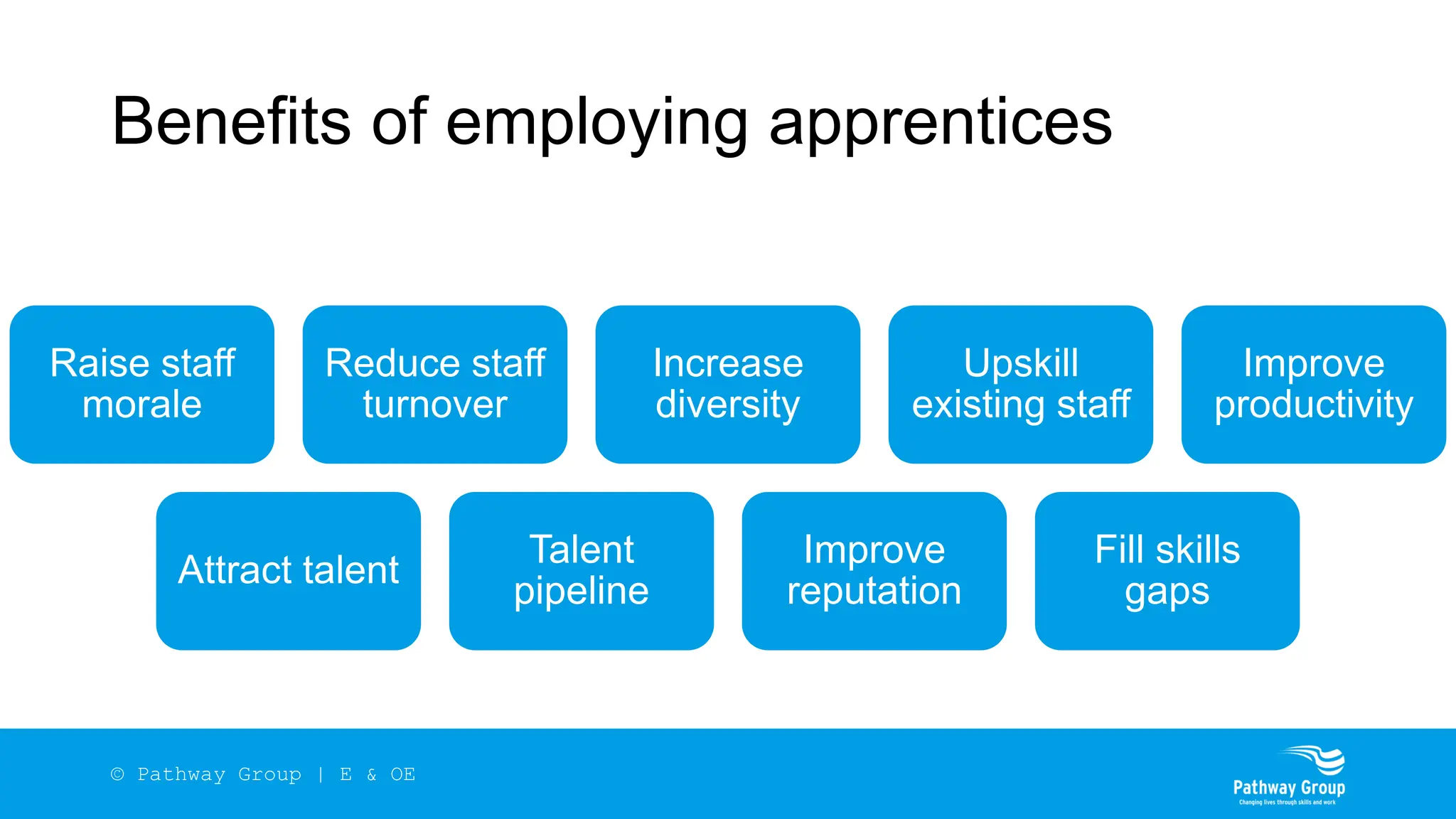
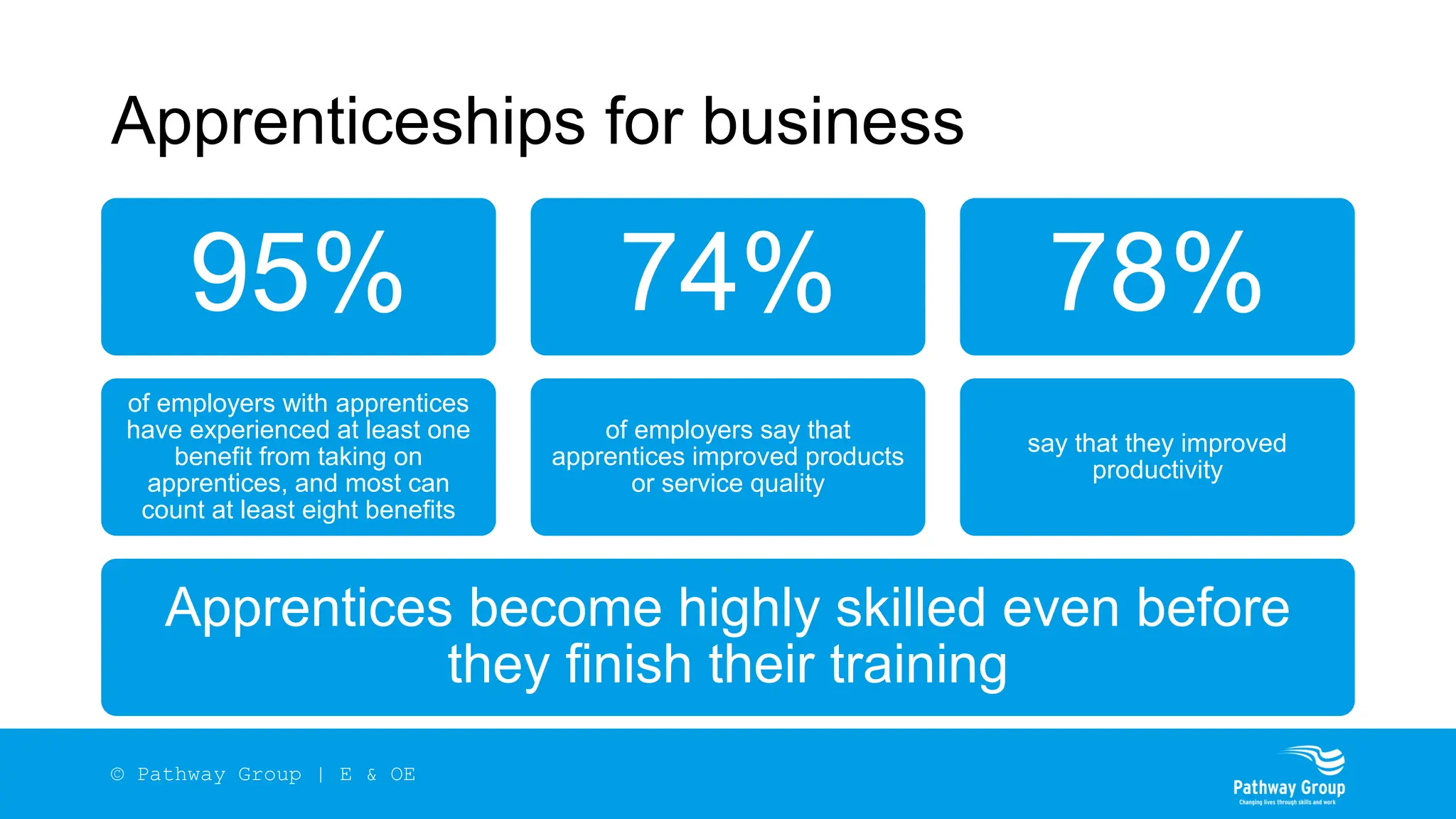
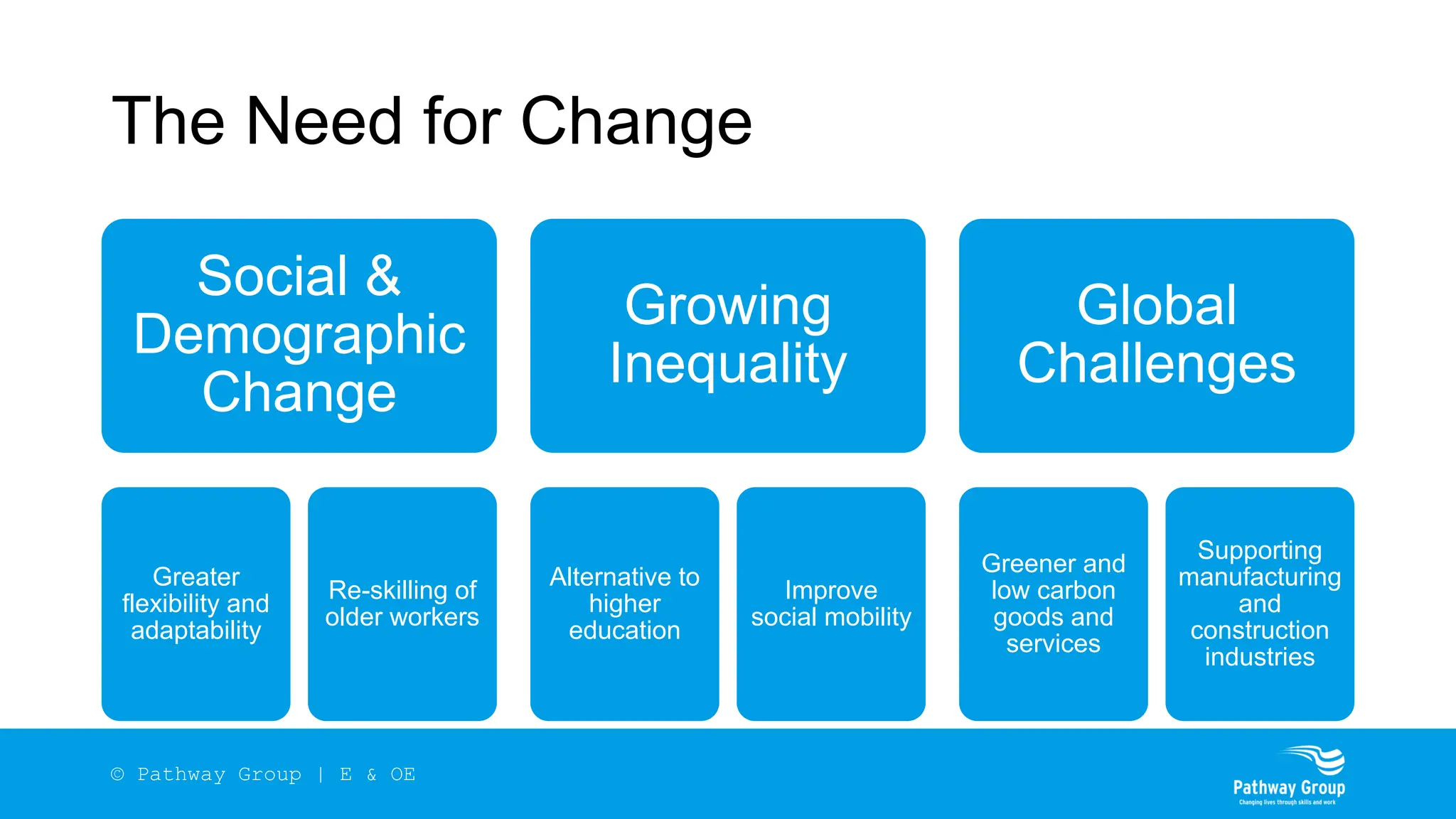
The document outlines the structure and benefits of apprenticeships, detailing key components such as technical knowledge, practical experience, and mandatory qualifications, while emphasizing the roles of employers, apprentices, and learning providers. It presents data on apprenticeship statistics, including types, levels, and funding sources, as well as the positive impacts on businesses and the workforce. The need for change and improvements in social mobility, workforce adaptability, and skills development are also highlighted.