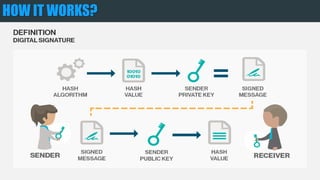
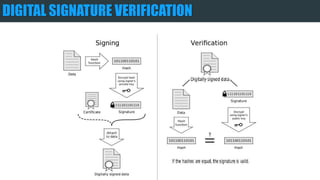
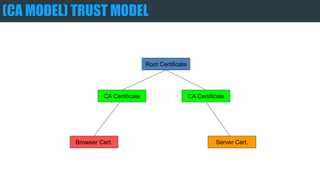
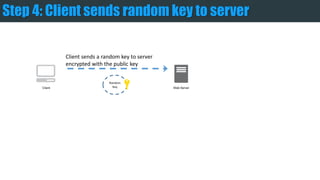
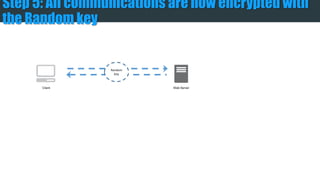
The document provides an overview of encryption, digital signatures, and SSL certificates. It discusses how public key encryption uses a private key and public key to encrypt messages. Digital signatures authenticate the identity of the sender and ensure messages remain intact. SSL certificates allow browsers and servers to establish an encrypted connection by containing a public key and verifying identity with a Certificate Authority. The client's browser verifies the server's certificate with the CA to trust the secure connection.