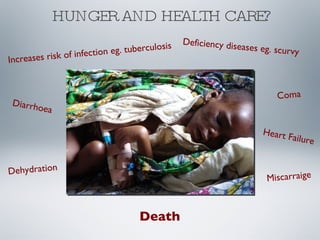
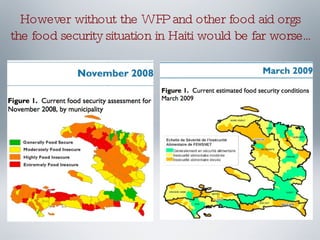
The World Food Programme (WFP) is the largest humanitarian organization that provides food aid to over 86 million people in emergencies worldwide, including in Haiti, where a significant portion of the population lives below the poverty line. The WFP responds to crises caused by factors like political turmoil and natural disasters, initiating emergency operations and logistical support to deliver aid effectively. Despite complications from gang violence, infrastructure challenges, and prior food crises, the WFP managed to feed 700,000 people in Haiti by the end of 2008 and continues to focus on long-term food security initiatives.