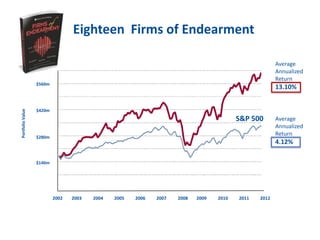
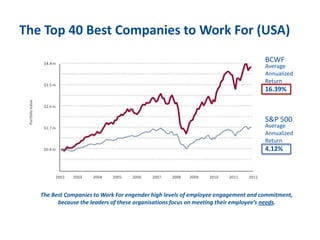
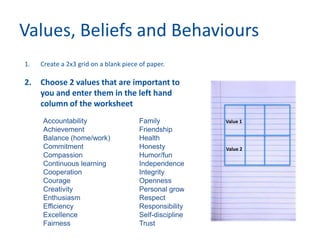
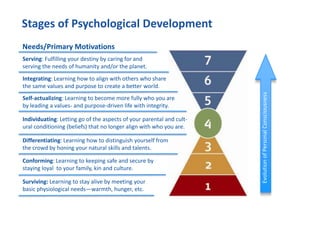
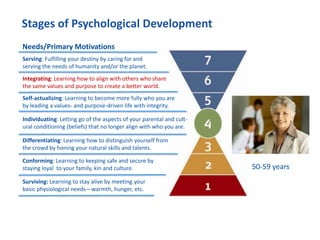
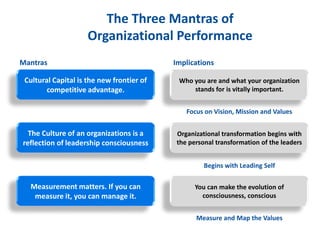
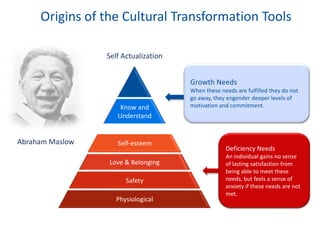
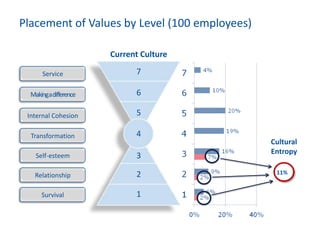
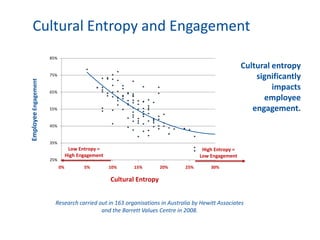
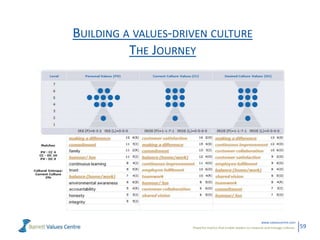
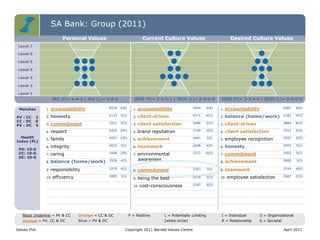
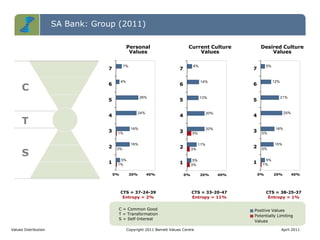
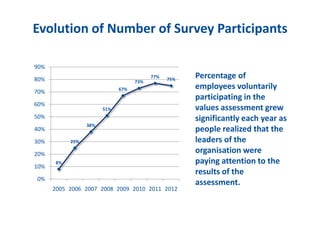
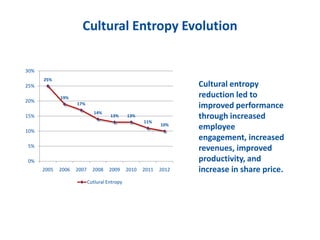
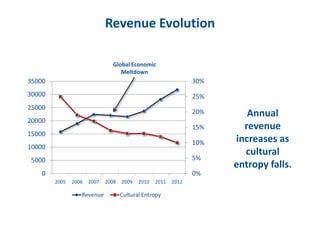
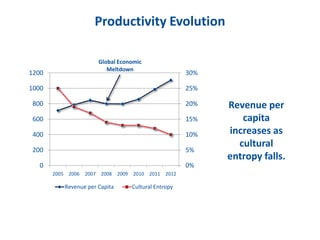
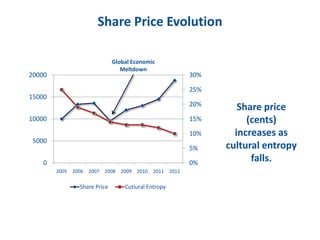
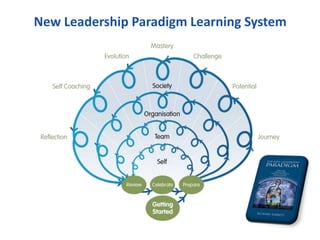
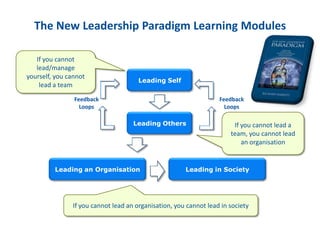
The document discusses the importance of creating a values-driven culture within organizations, highlighting that such cultures are linked to higher success and employee commitment. It emphasizes the need for leadership to understand and nurture values, alongside using effective metrics to measure cultural health. The framework presented is based on various stages of psychological development, suggesting that aligning values with personal and organizational goals fosters a more engaged and purposeful workforce.