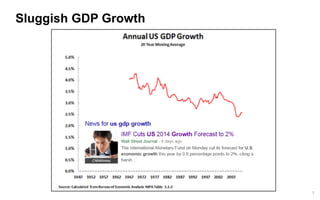
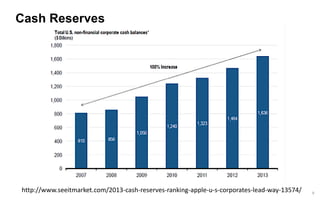
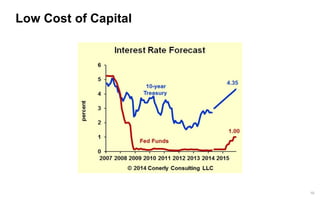
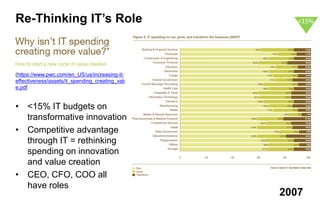
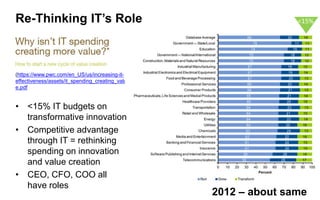
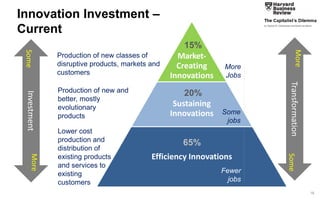
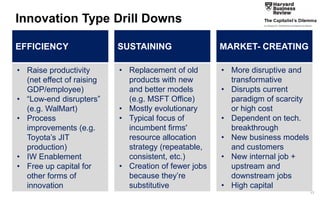
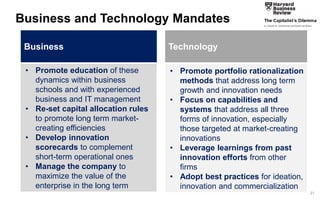
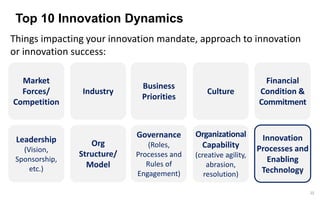
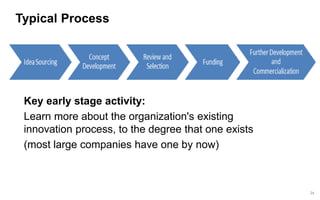
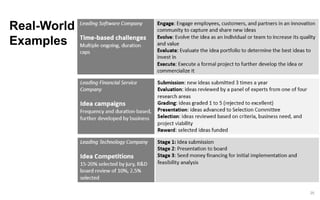
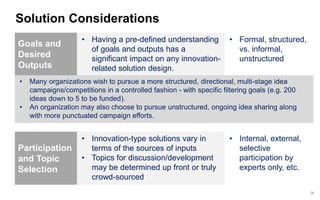
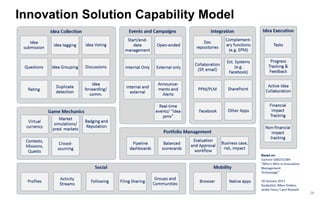
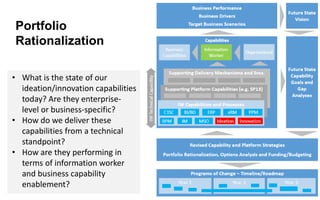
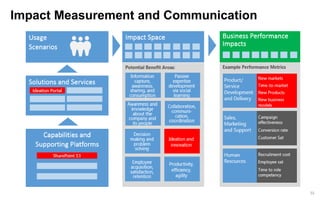
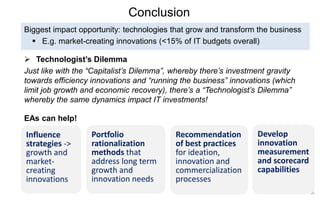
This document discusses strategies for promoting innovation in organizations. It argues that companies focus too much on efficiency innovations and not enough on market-creating innovations. It recommends that companies rationalize their portfolios to focus more on capabilities that enable all three types of innovation, especially market-creating innovations. Technologists can help by influencing strategies to prioritize growth and shifting IT thinking from efficiency to innovation and value creation. Measurement of innovation impact and processes also needs to be improved.