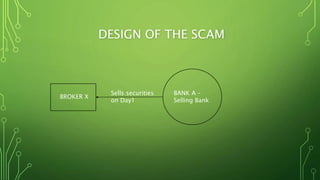
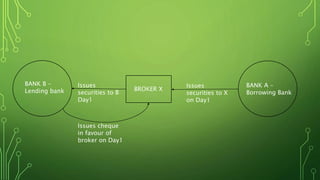
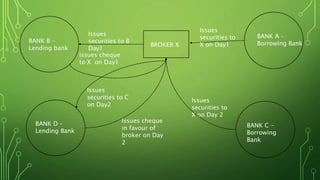
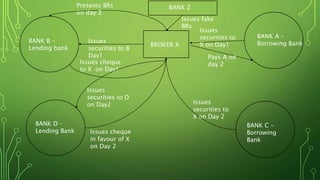
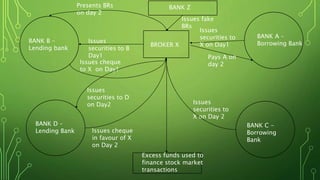
The Harshad Mehta securities scam that took place between 1991-1992 involved the diversion of Rs. 4000 crore from banks using "ready forward" deals and fake bank receipts. Harshad Mehta, a prominent stockbroker, engineered these deals to fund large-scale stock transactions. The scam had major impacts like a sharp drop in the stock market, loss of investor wealth, and delays in India's economic liberalization plans. The government established new regulatory bodies and laws in response and charged Harshad Mehta with multiple criminal offenses.