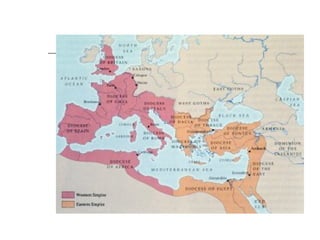
The document summarizes the history of Roman emperors from Augustus to the fall of the Western Roman Empire. It describes the transition from a republic to an empire under Augustus and highlights notable emperors like Trajan, Hadrian, Marcus Aurelius, and Constantine. It also discusses the decline of the empire due to military anarchy, invasions by barbarians, and the eventual split into Western and Eastern empires before the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD.