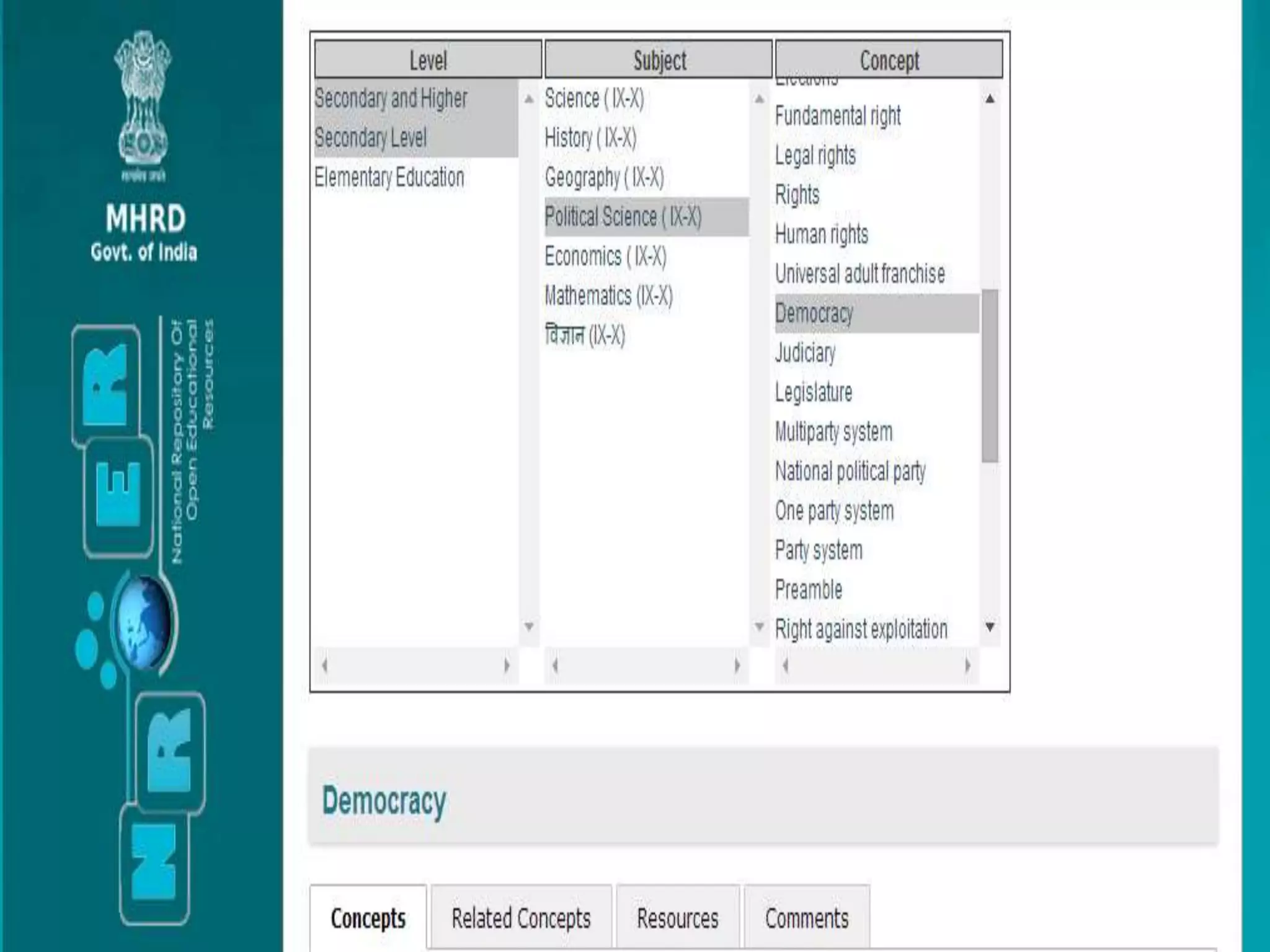
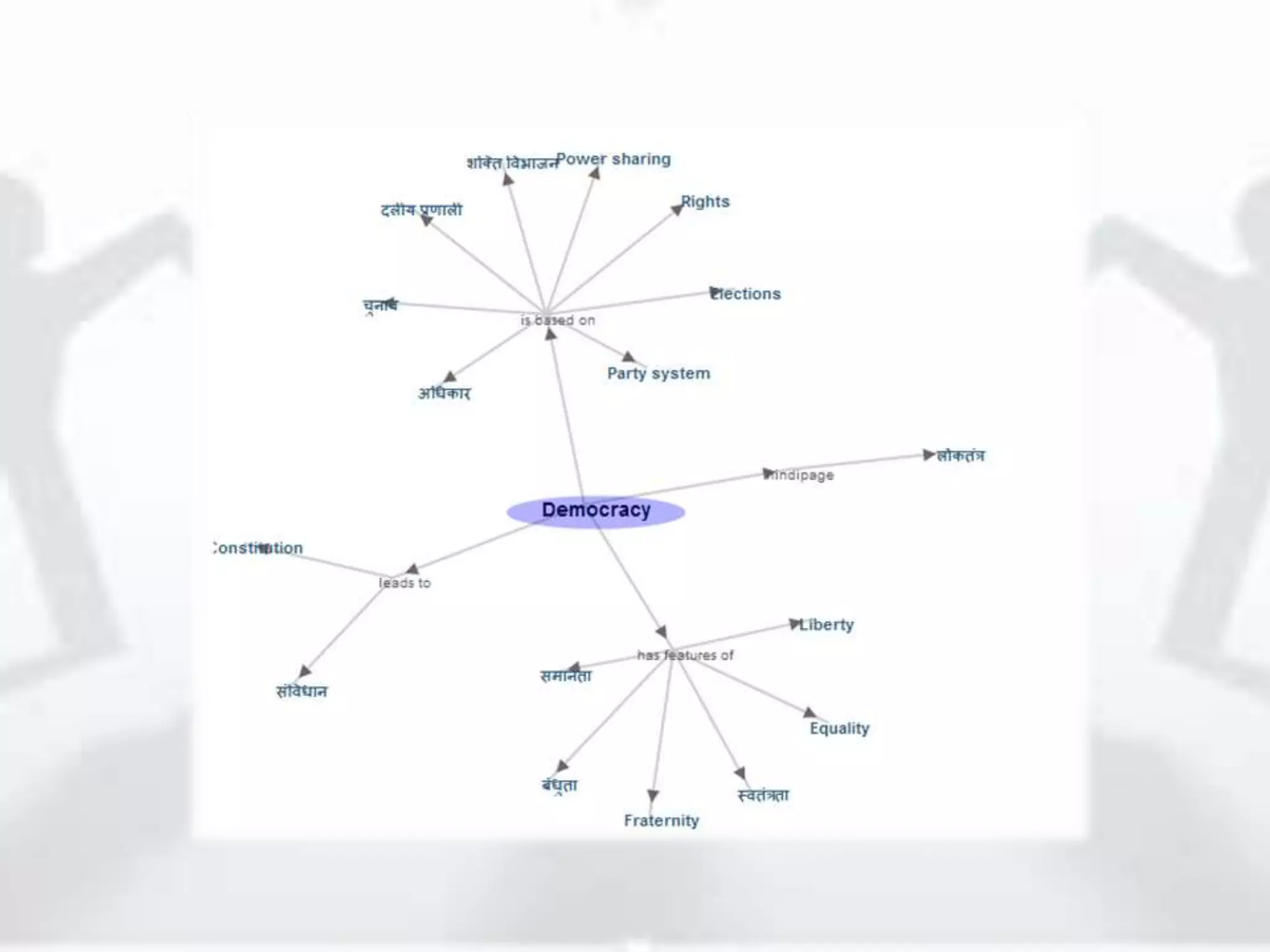
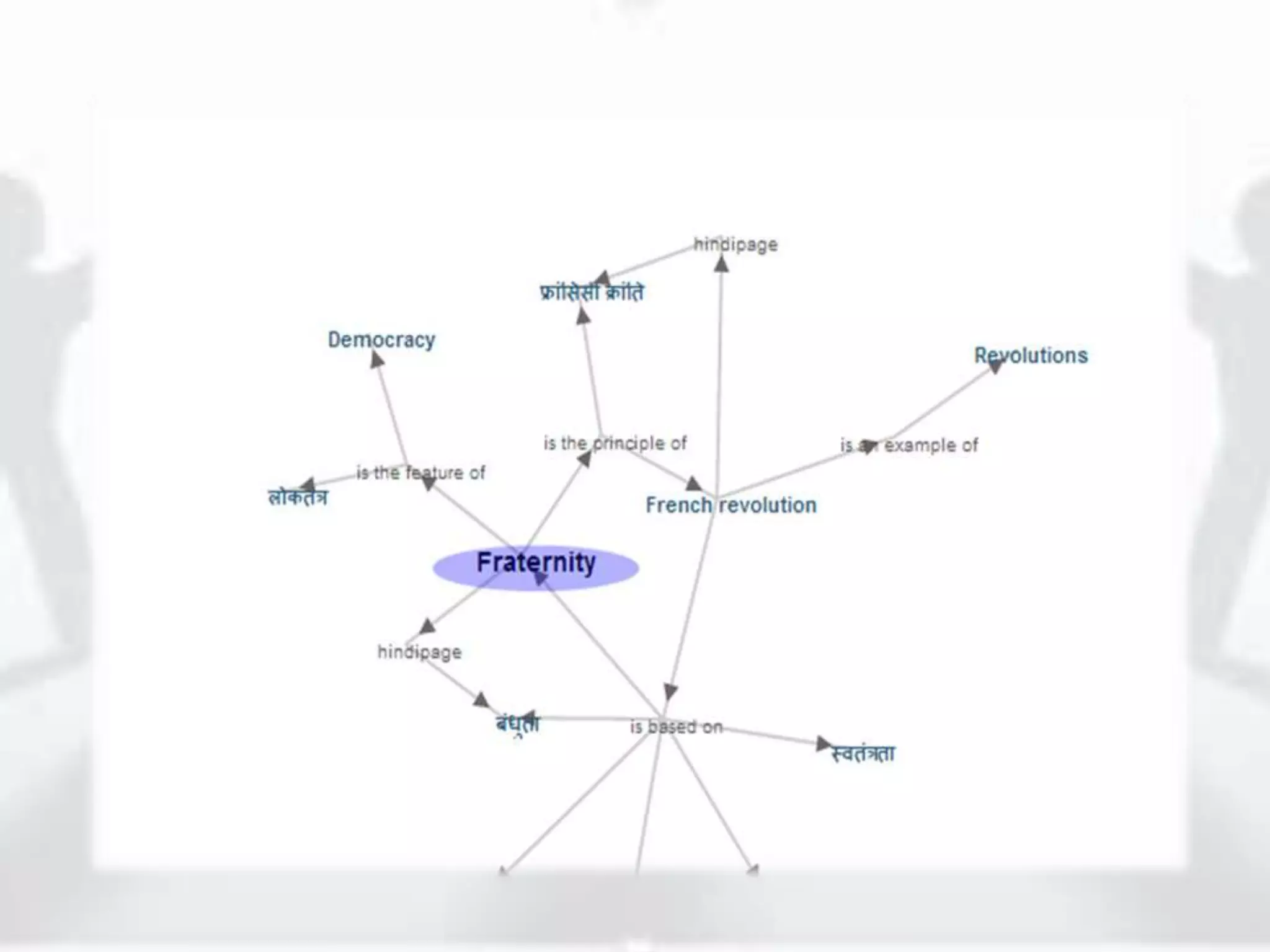
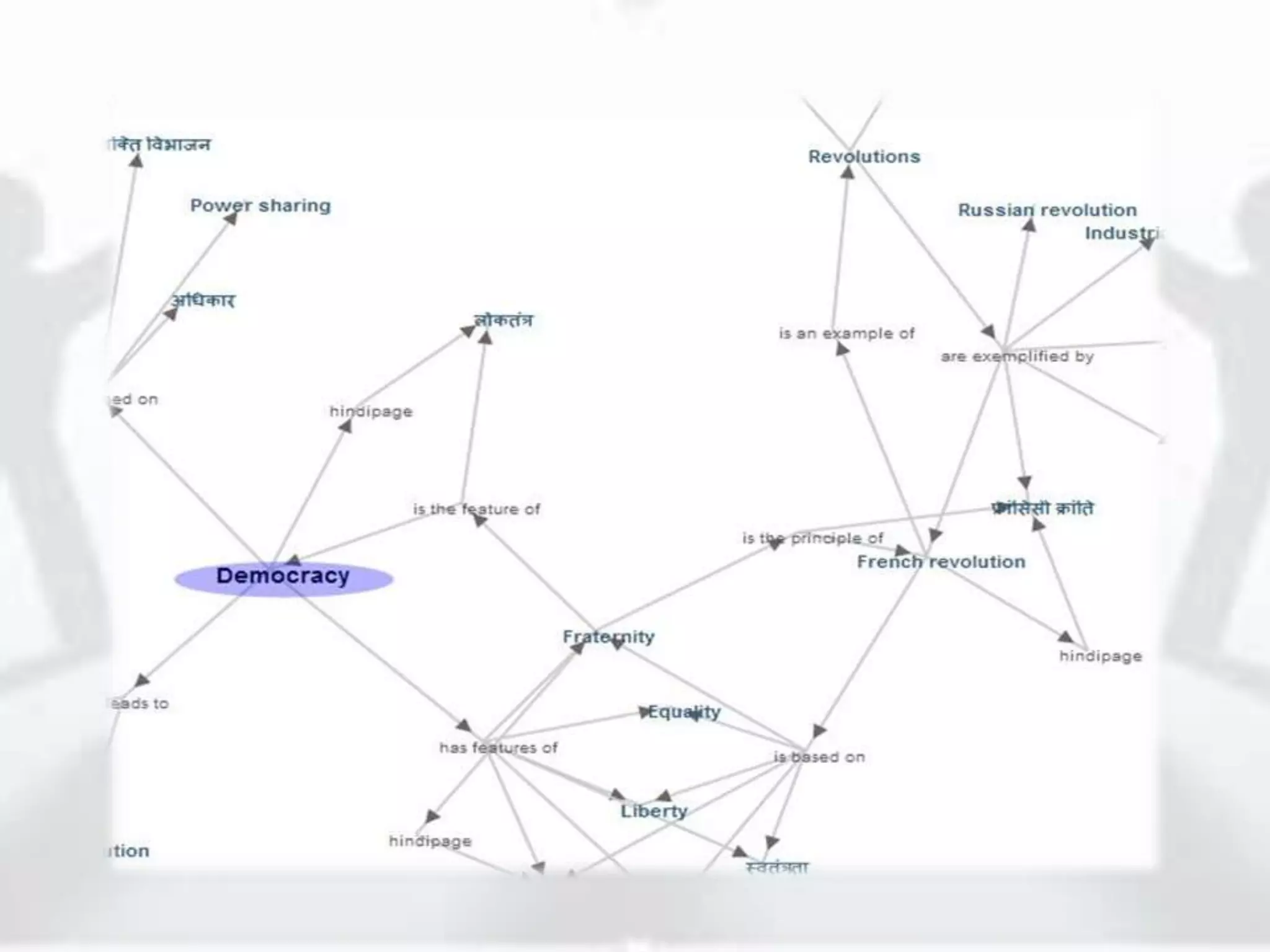
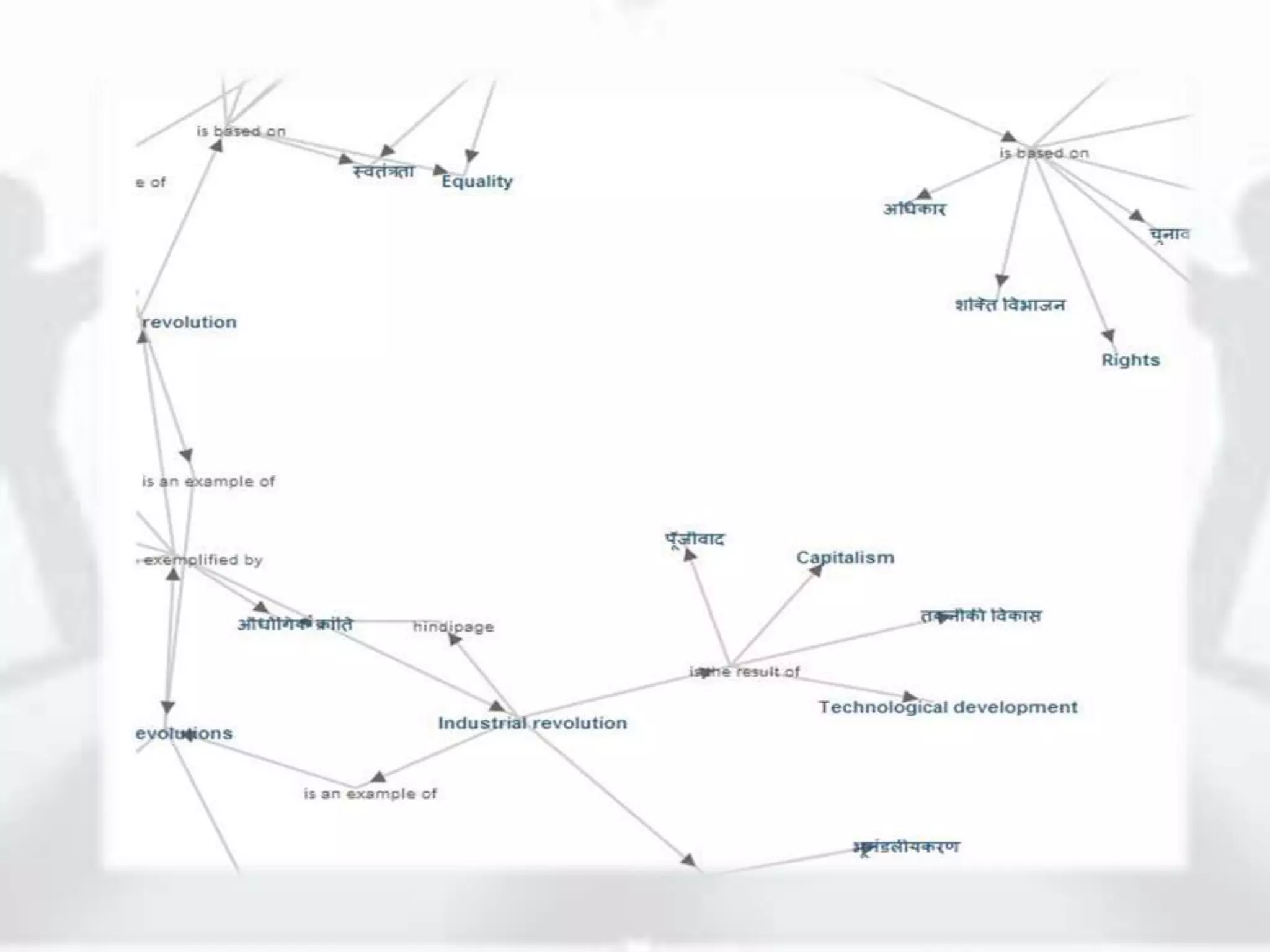
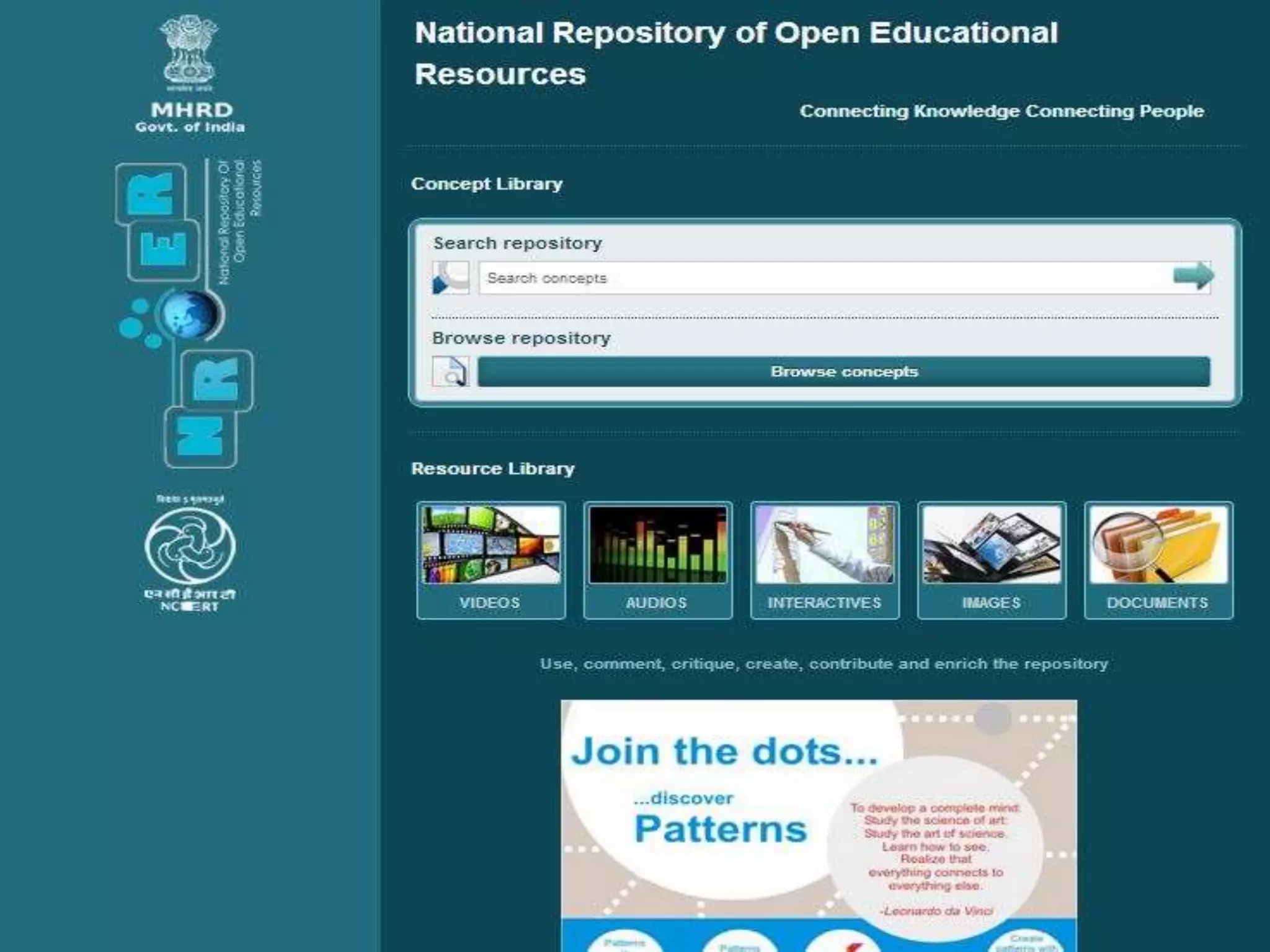
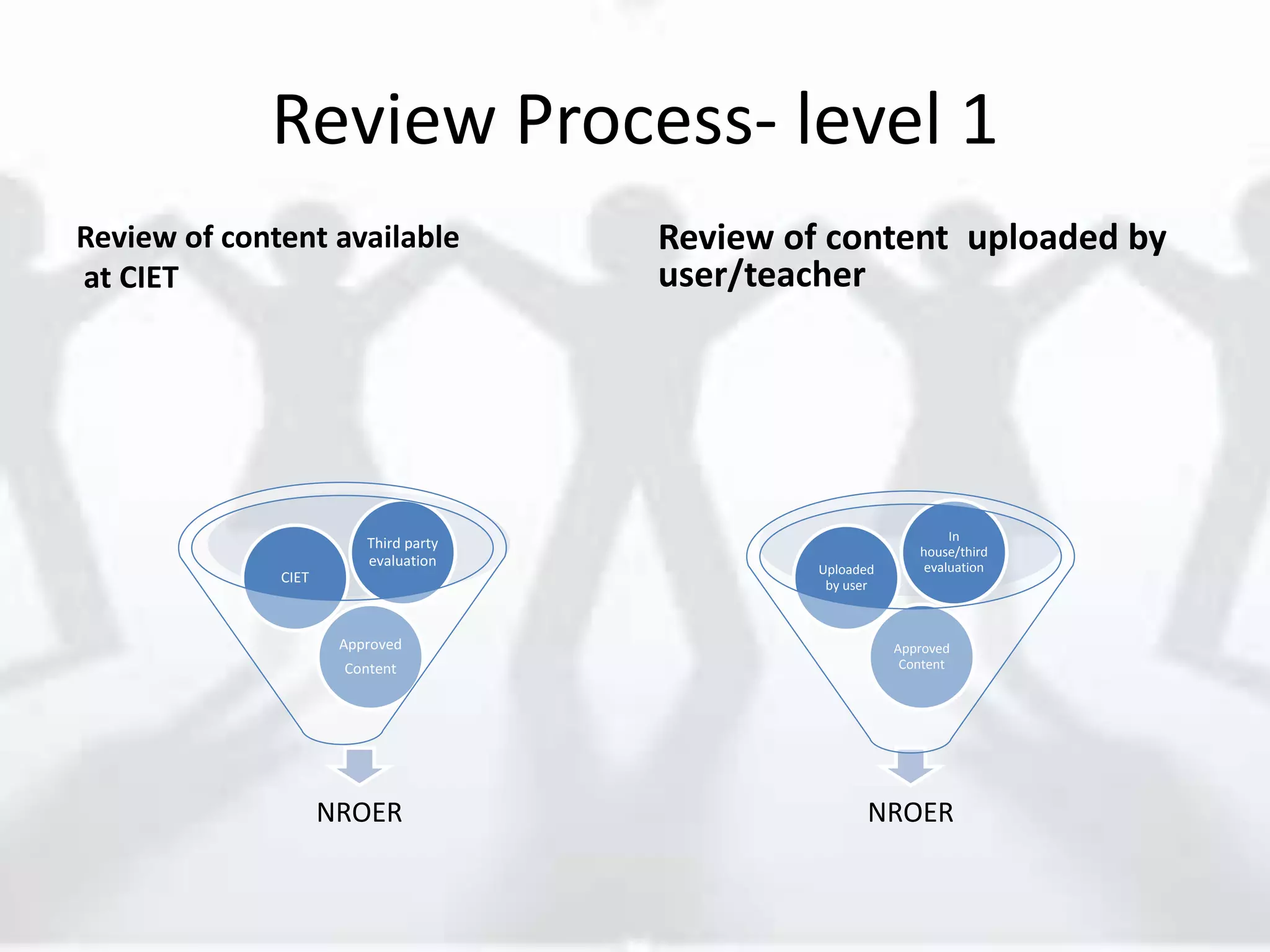
The document discusses the role of new media in knowledge generation through community participation. It outlines how new media can be used as a pedagogical tool to make education more efficient by promoting collaboration, creation of contextualized resources, and addressing challenges in the Indian education system like reach and access. It describes the Government's initiatives in promoting ICT in education as well as the open educational resources (OER) movement in India. The National Repository of Open Educational Resources (NROER) is highlighted as a platform that connects knowledge and people by making a variety of open resources available and involving the community in content creation.