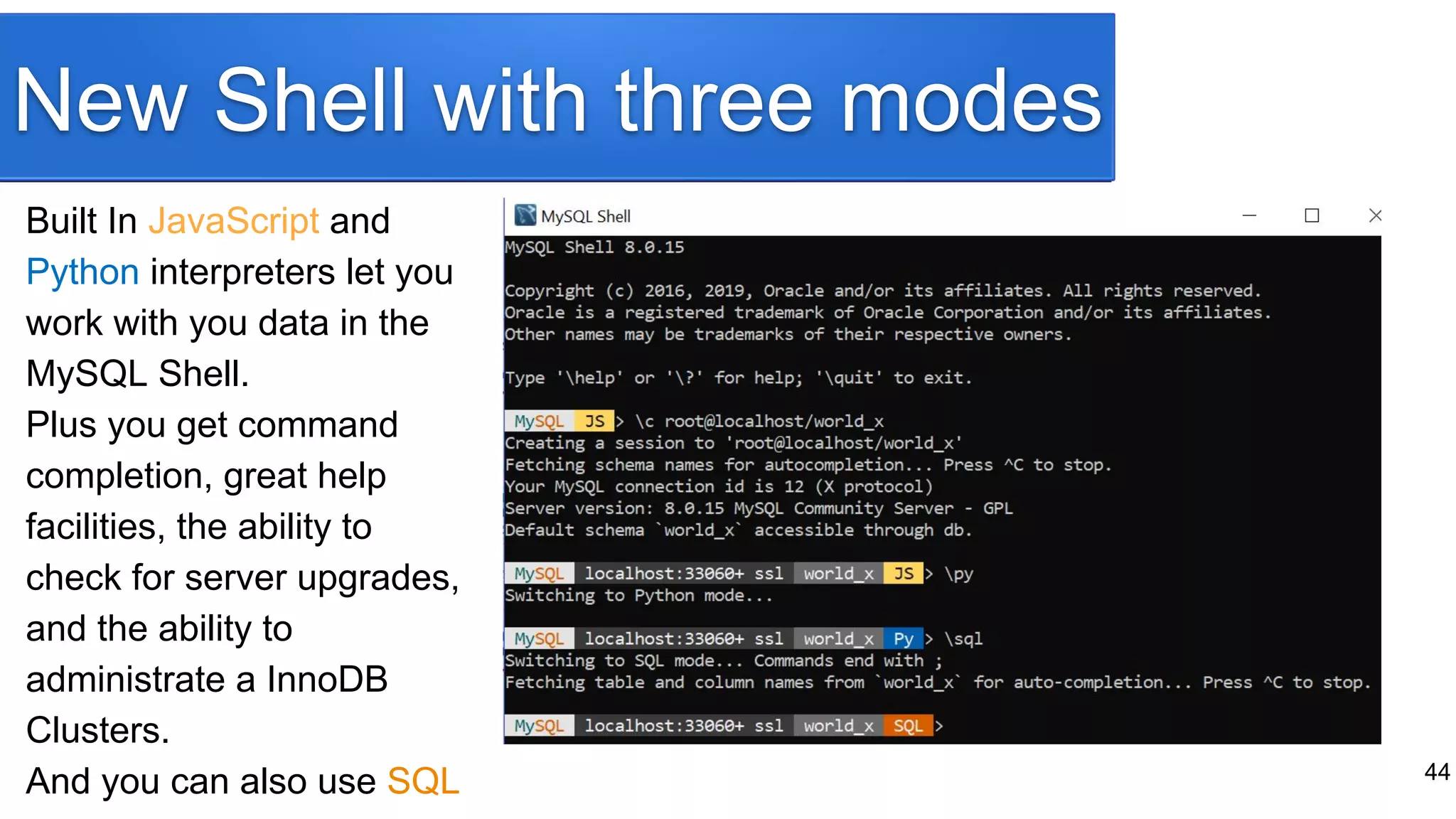
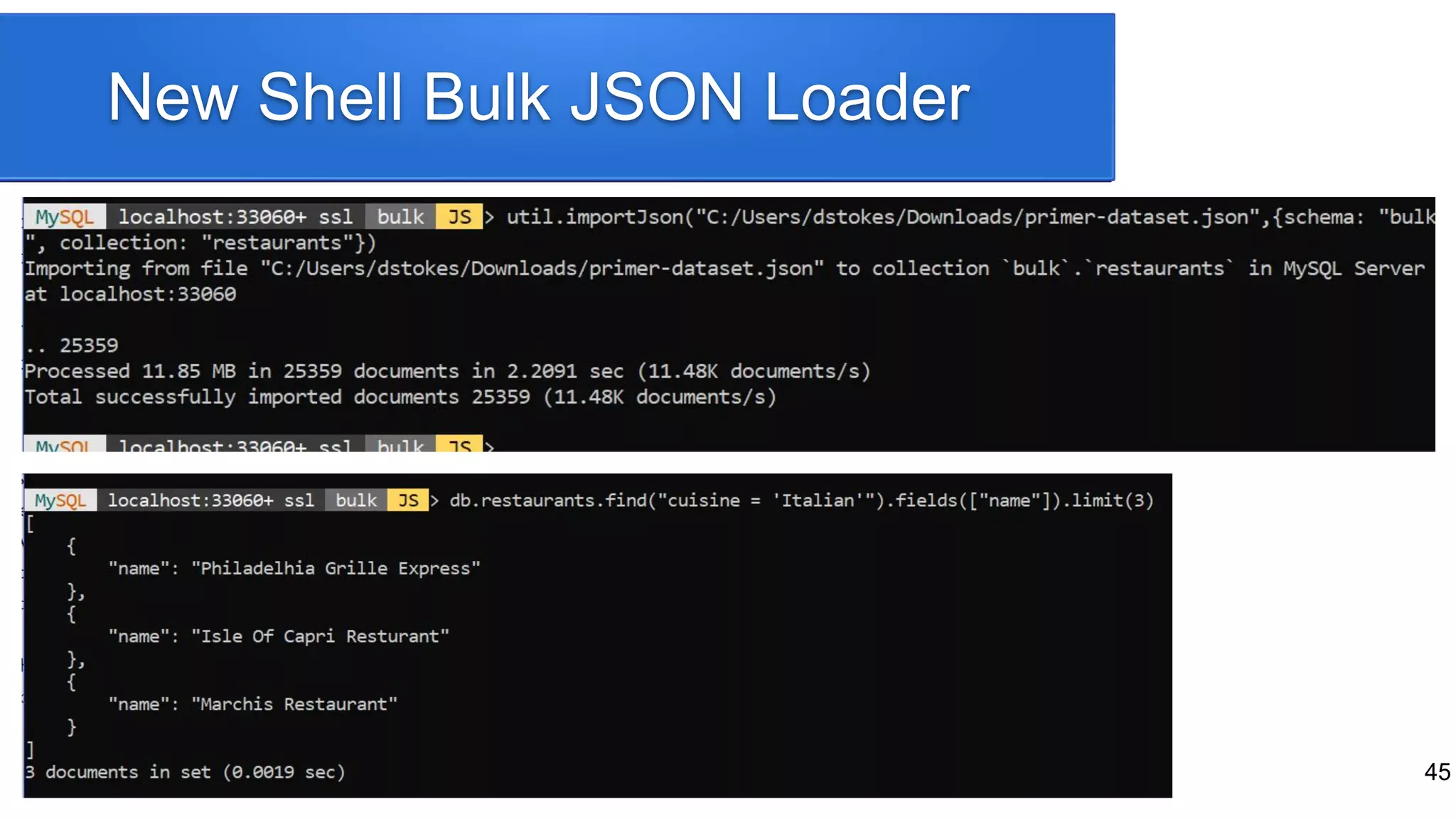
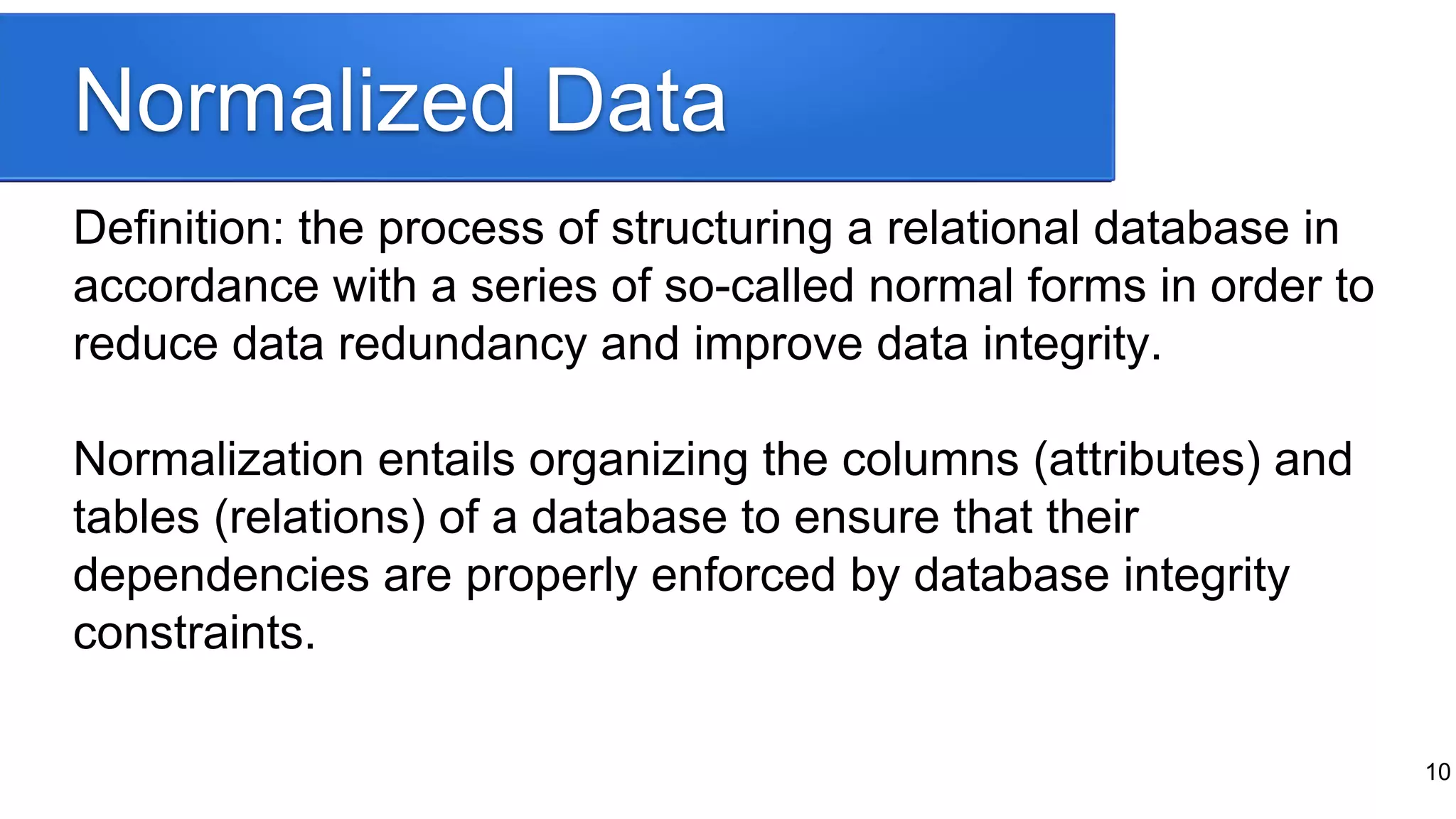
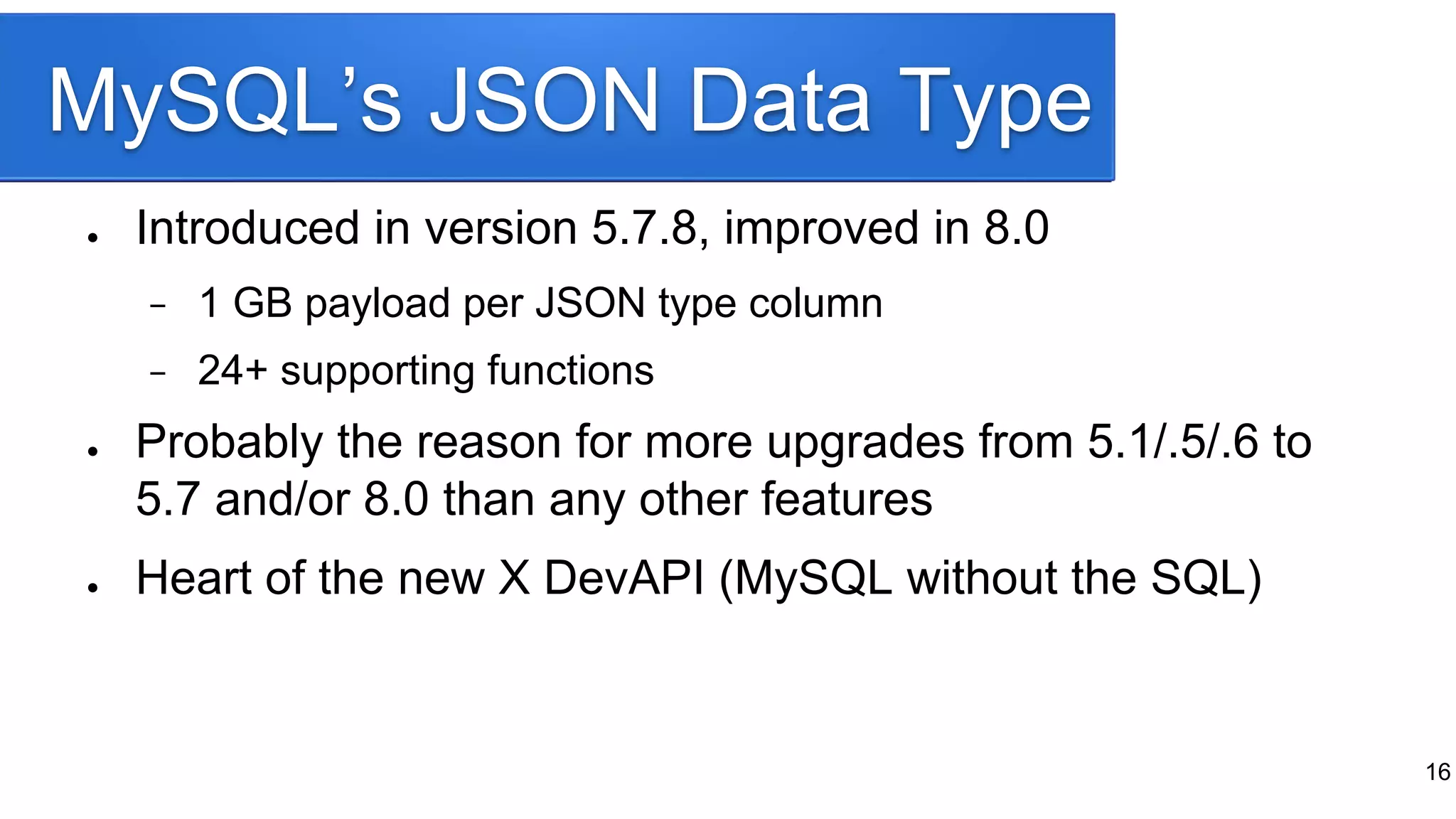
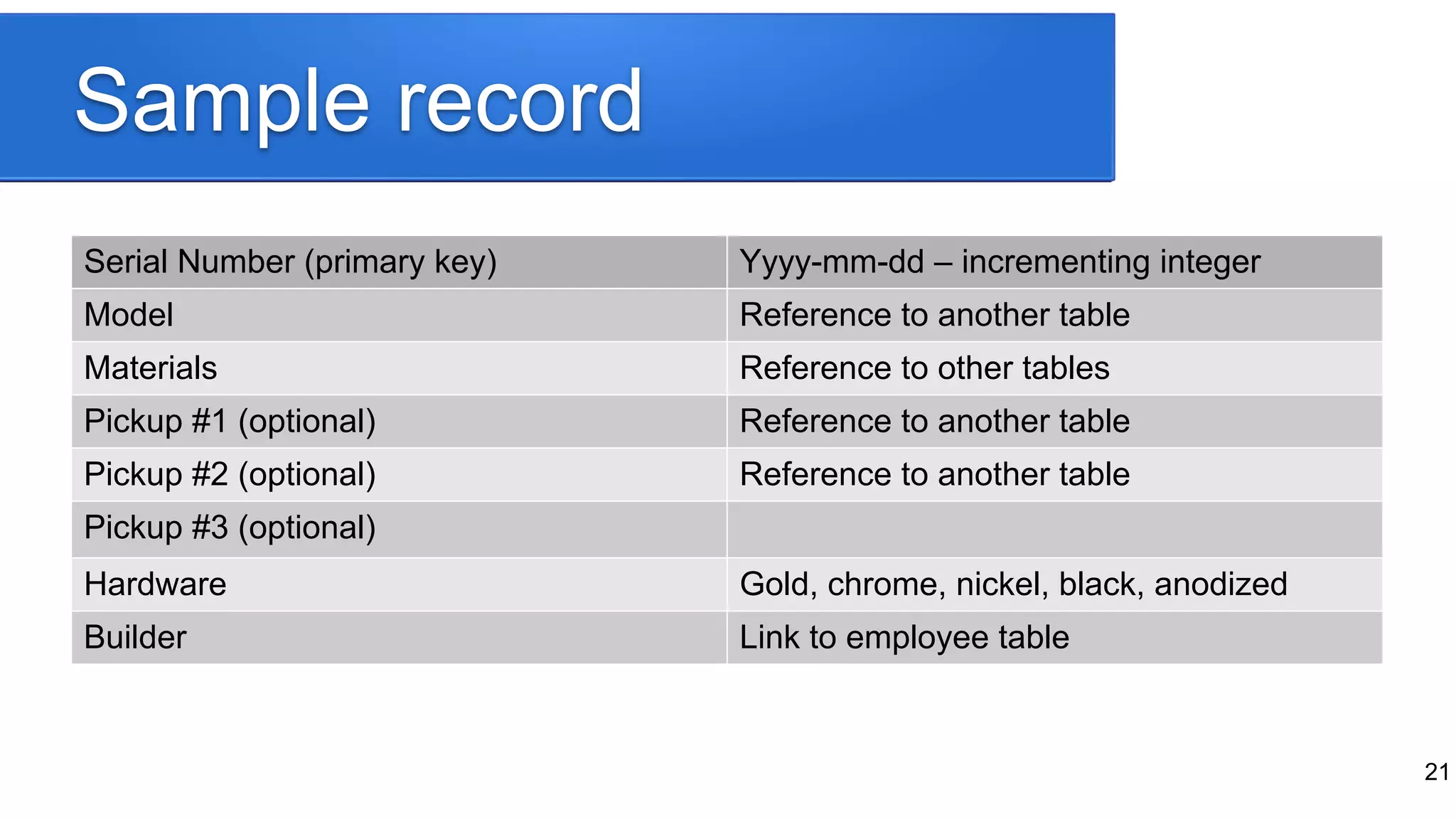
The document provides a historical overview of database development, focusing on the evolution from early data storage methods to the introduction of relational databases and SQL. It discusses the advantages and limitations of various database models, including ISAM, relational databases, and NoSQL, emphasizing the role of normalization and JSON support in MySQL's development. The presentation highlights MySQL's JSON data type and its implications for modern database usage, as well as the concept of hybrid databases that combine features from both SQL and NoSQL paradigms.


















![JSON Data
{ “neck” :
{ “material” :“maple”,
“fretboard” : “ebony”,
“tuners” : “Grover locking chrome”,
“frets” : [ “stainless”, “high” ],
“finish” : “urethane”},
“body” :
{ “material” : “one piece swamp ash”,
“pattern” : “tele - H H”,
“finish” : “Dupont red #4”
“binding” : “none”}
}
Because the JSON data
is mutable, we can later
add details as needed
without have to
restructure underlying
database structure.
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpuk2019-190222104800/75/Hybrid-Databases-PHP-UK-Conference-22-February-2019-30-2048.jpg)


![36
db.dave_guitar.createIndex("guitar_type",
{fields:[{"field": "$.type",
"type":"TEXT(20)",
required:true}]
});
Index: Document Store or SQL
ALTER TABLE dave_guitar ADD type_index
VARCHAR(30) AS
(JSON_UNQUOTE(doc->"$.type"));
OR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpuk2019-190222104800/75/Hybrid-Databases-PHP-UK-Conference-22-February-2019-36-2048.jpg)
![37
db.dave_guitar.find("type = 'Les Paul'").fields("type")
[
{
"type": "Les Paul"
}
]
Find desired record](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpuk2019-190222104800/75/Hybrid-Databases-PHP-UK-Conference-22-February-2019-37-2048.jpg)
![38
db.dave_guitar.find().fields("[type]").sort("[type]")
[
{
"[type]": [
"semi-hollow"
]
},
{
"[type]": [
"Telecaster"
]
},
{
"[type]": [
"Les Paul"
]
}
]
Refine find()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpuk2019-190222104800/75/Hybrid-Databases-PHP-UK-Conference-22-February-2019-38-2048.jpg)
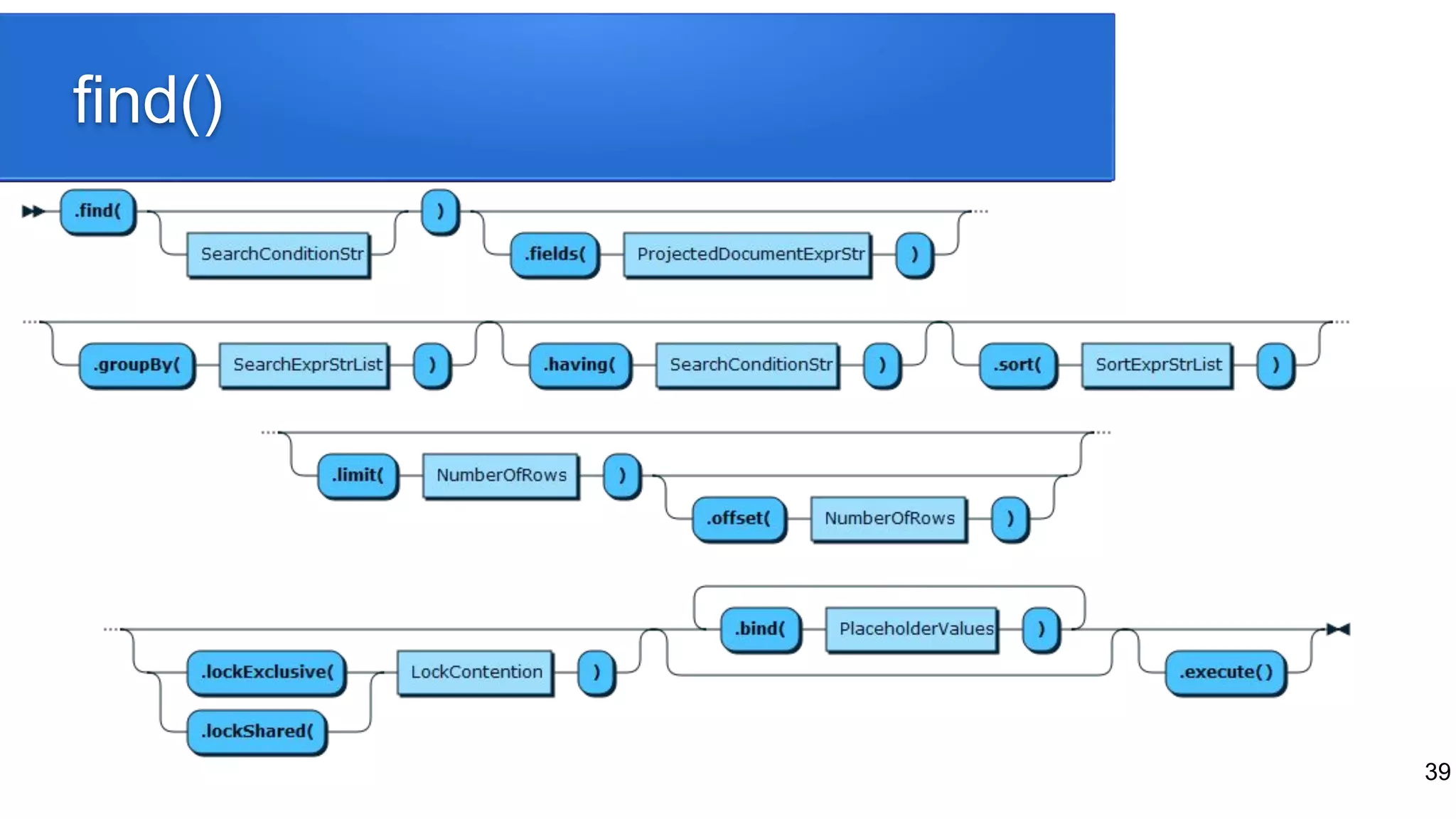
![40
No More Embedded SQL in PHP
$SQLQuery = “SELECT * FROM people WHERE job LIKE
“ . $job . “ AND age > $age”;
Versus
$collection = $schema->getCollection("people");
$result = $collection
->find('job like :job and age > :age')
->bind(['job' => 'Butler', 'age' => 16])
->execute();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpuk2019-190222104800/75/Hybrid-Databases-PHP-UK-Conference-22-February-2019-40-2048.jpg)
![41
Also Works With Tables
#!/bin/php
<?php
$session =
mysql_xdevapigetSession("mysqlx://root:hidave@localhost:33060");
if ($session === NULL) {
die("Connection could not be established");
}
$schema = $session->getSchema("world");
$table = $schema->getTable("city");
$row = $table->select('Name','District')
->where('District like :district')
->bind(['district' => 'Texas'])
->limit(25)
->execute()->fetchAll();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpuk2019-190222104800/75/Hybrid-Databases-PHP-UK-Conference-22-February-2019-41-2048.jpg)
![42
Complex Analytics
WITH cte1 AS
(SELECT doc->>"$.name" AS name,
doc->>"$.cuisine" AS cuisine,
(SELECT AVG(score) FROM
JSON_TABLE(doc, "$.grades[*]" COLUMNS
(score INT PATH "$.score")) AS r) AS
avg_score
FROM restaurants)
SELECT *, RANK() OVER
(PARTITION BY cuisine ORDER BY avg_score
DESC) AS `rank`
FROM cte1
ORDER BY `rank`, avg_score DESC LIMIT 10;
JSON_TABLE turns unstructured
JSON documents in to temporary
relational tables that can be
processed with SQL
Windowing Function for
analytics
Common Table Expression
make it easy to write sub-queries](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpuk2019-190222104800/75/Hybrid-Databases-PHP-UK-Conference-22-February-2019-42-2048.jpg)