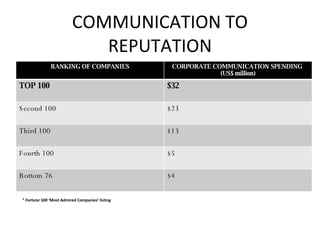
The document discusses the critical importance of corporate reputation in business strategy, highlighting that a significant portion of market value is derived from reputation and its impact on investor behavior, employee satisfaction, and overall business success. It emphasizes the CEO's role in building and managing corporate reputation through effective communication and relationship management while navigating organizational change. Key factors for maintaining a good reputation include product excellence, socially responsible conduct, and strong leadership.