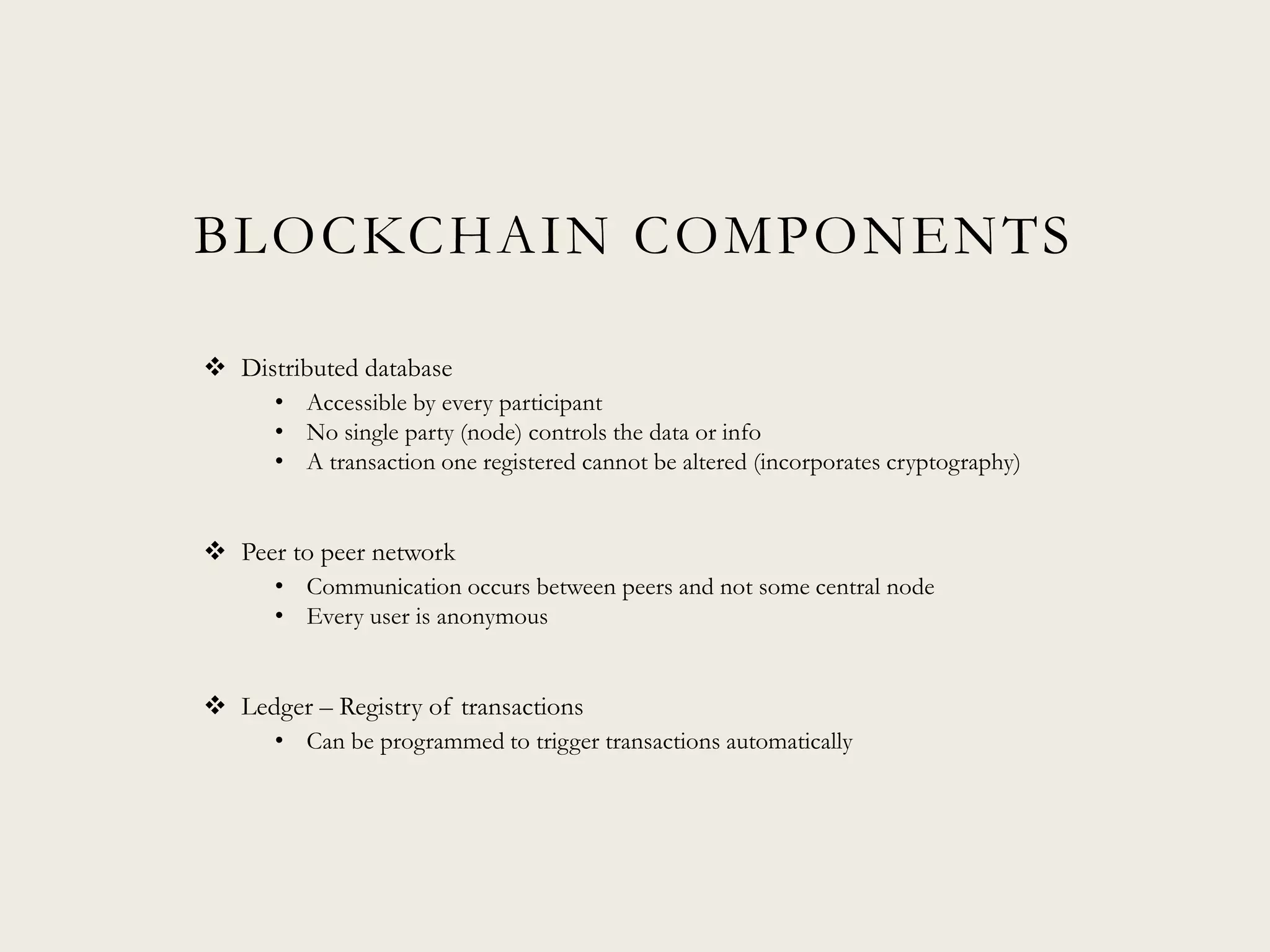
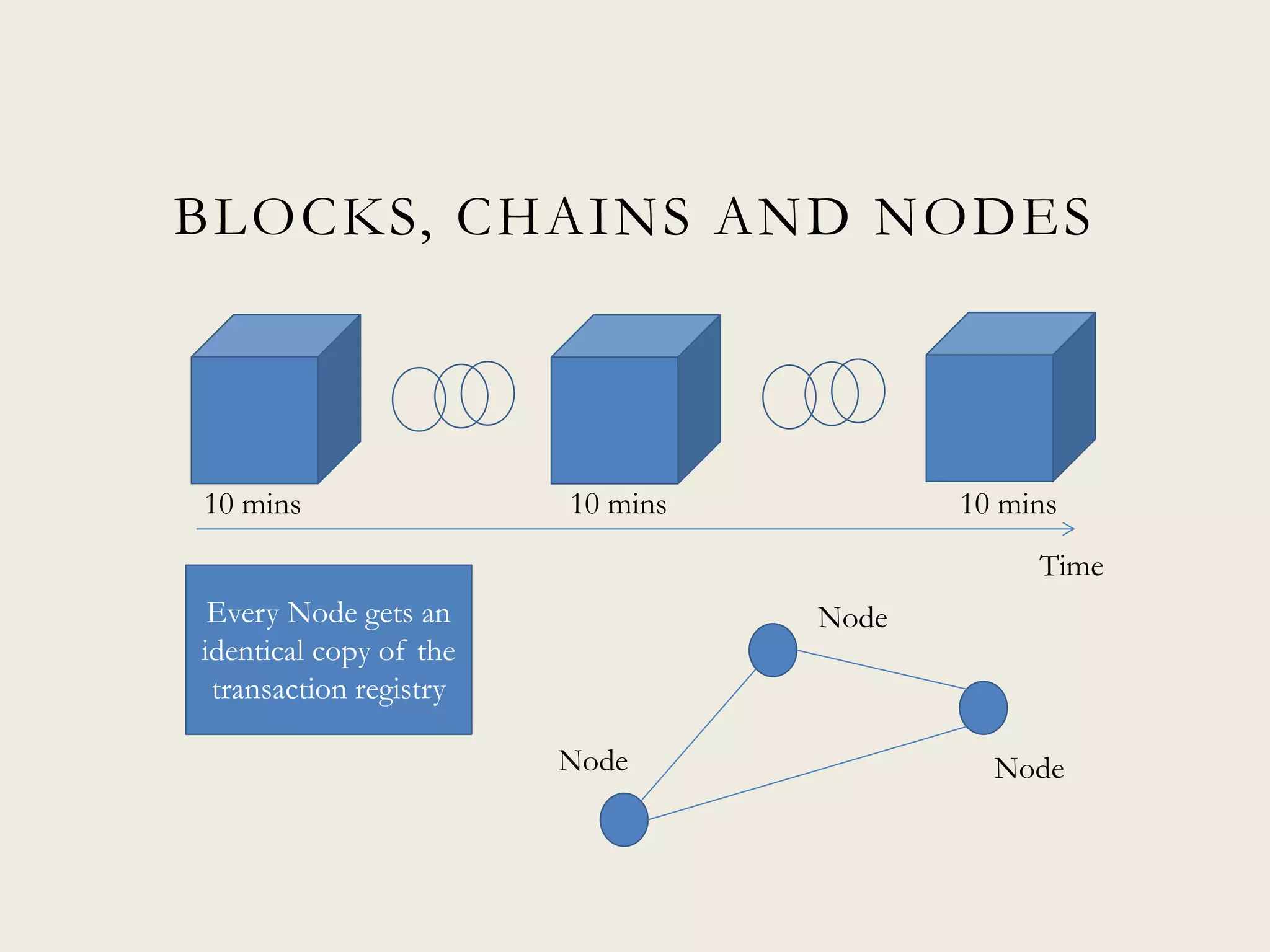
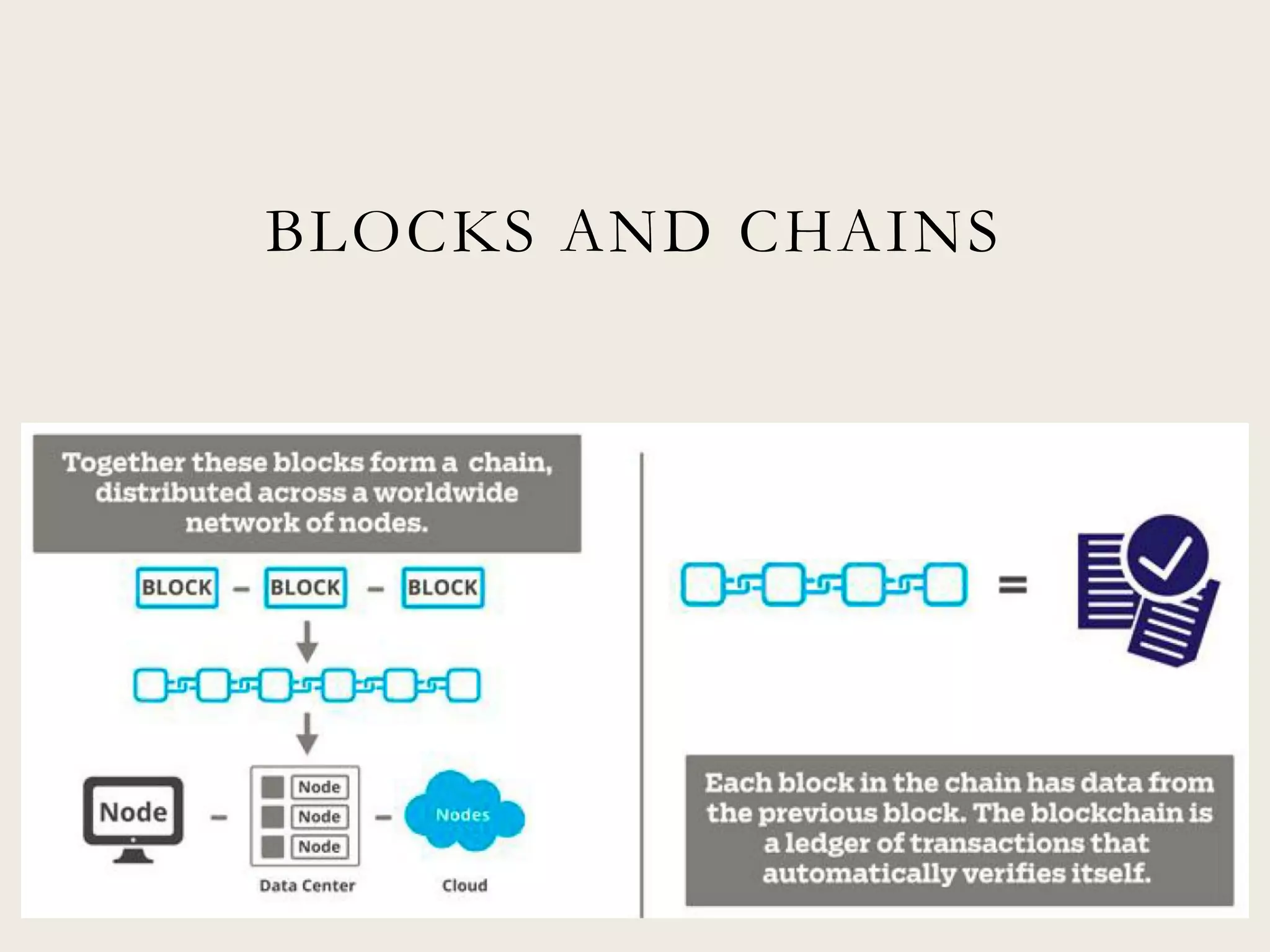
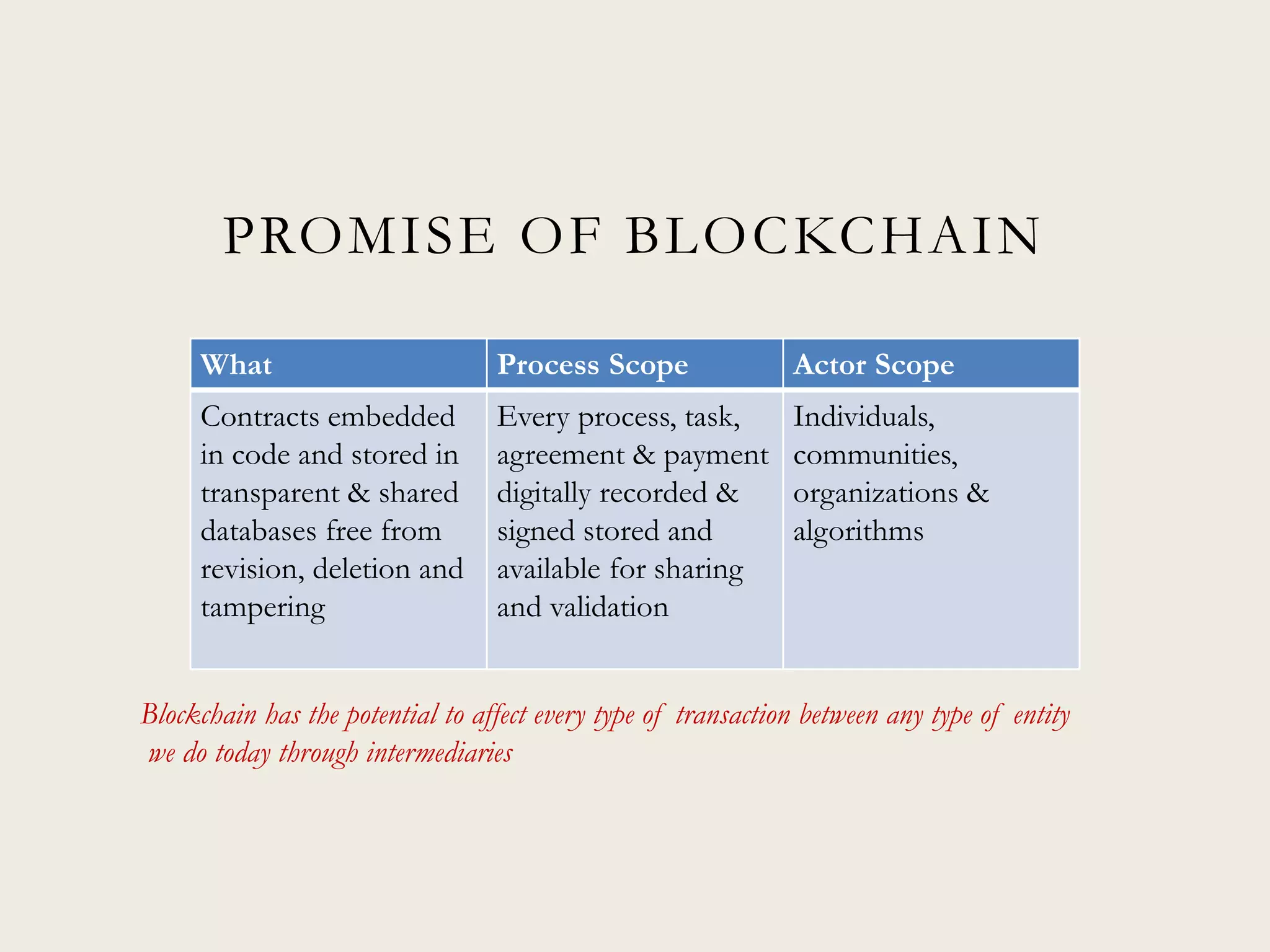
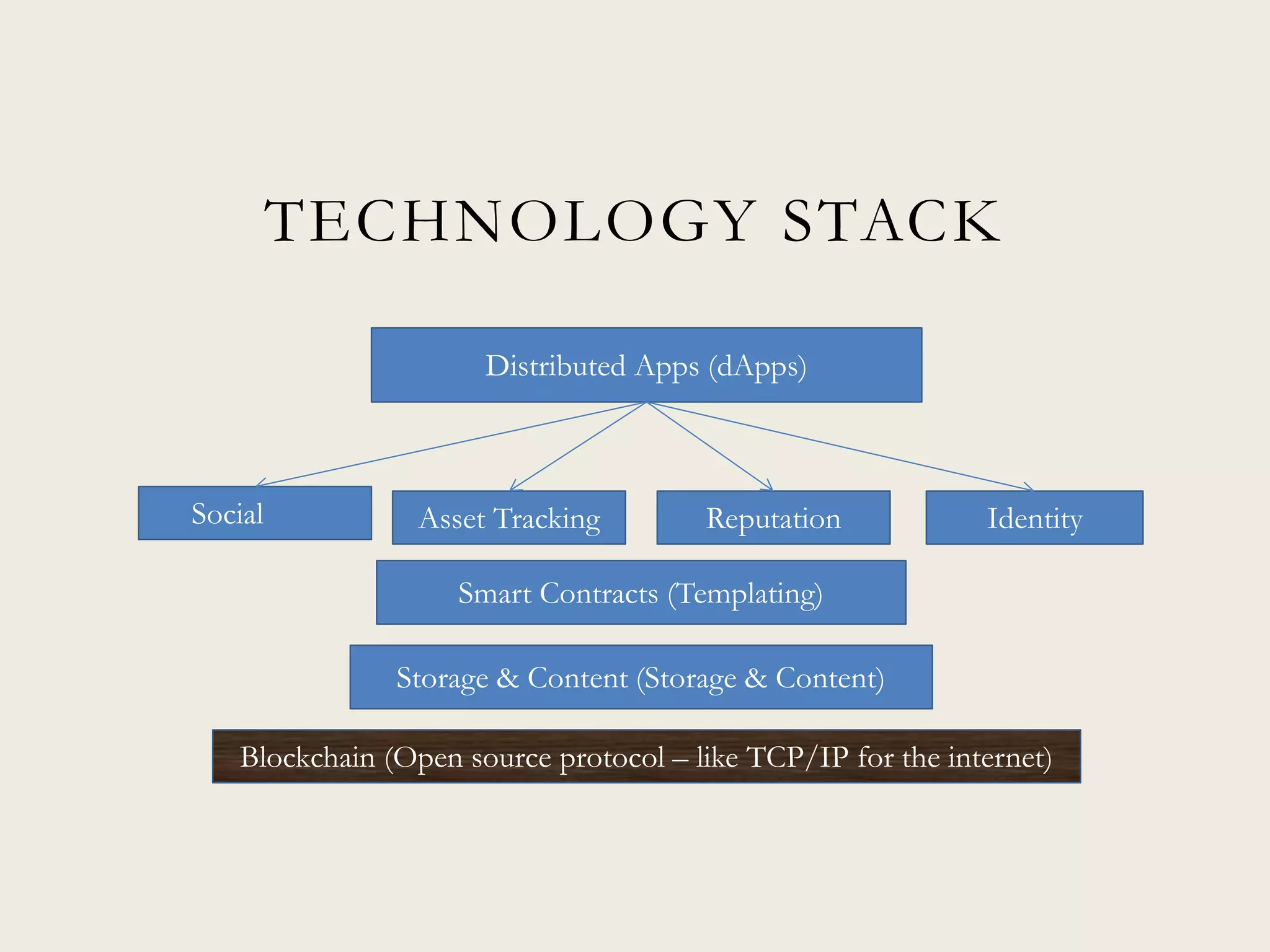
This document discusses the promise and potential of blockchain technology. It begins with an overview of blockchain components like distributed databases, peer-to-peer networks, and cryptographic hashing. It then discusses how blockchain could transform transactions by embedding smart contracts in digital code stored transparently on shared databases. Blockchain may affect any type of transaction between individuals, organizations, and algorithms. The document compares blockchain to TCP/IP and how it drove innovation on the internet over decades. It outlines potential applications and provides examples of companies already experimenting in areas like asset tracking, identity, and IoT.