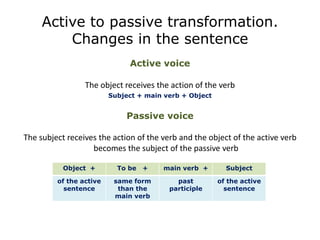
The document discusses the passive voice, including its main uses, formation, and how to transform sentences from active to passive voice. The main uses of the passive voice are when the receiver of the action is more important than the doer, the doer is unknown or unimportant, or the doer is too obvious to mention. To form the passive voice, the verb "to be" is used along with the past participle of the main verb. When transforming a sentence from active to passive voice, the object of the active sentence becomes the subject of the passive sentence.