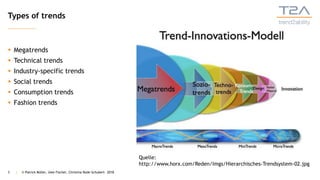
The document describes the trend2ability method, a 5-step process for identifying trends relevant to a company and developing a roadmap. Step 1 involves identifying trends from various sources. Step 2 prioritizes trends based on their impact. Step 3 maps trends to business levels. Step 4 derives skills needs as user stories. Step 5 creates a roadmap ordering capabilities by priority and dependencies. The method was developed by Patrick Müller, Christina Rode-Schubert, and Uwe Fischer to help companies transform based on trends.