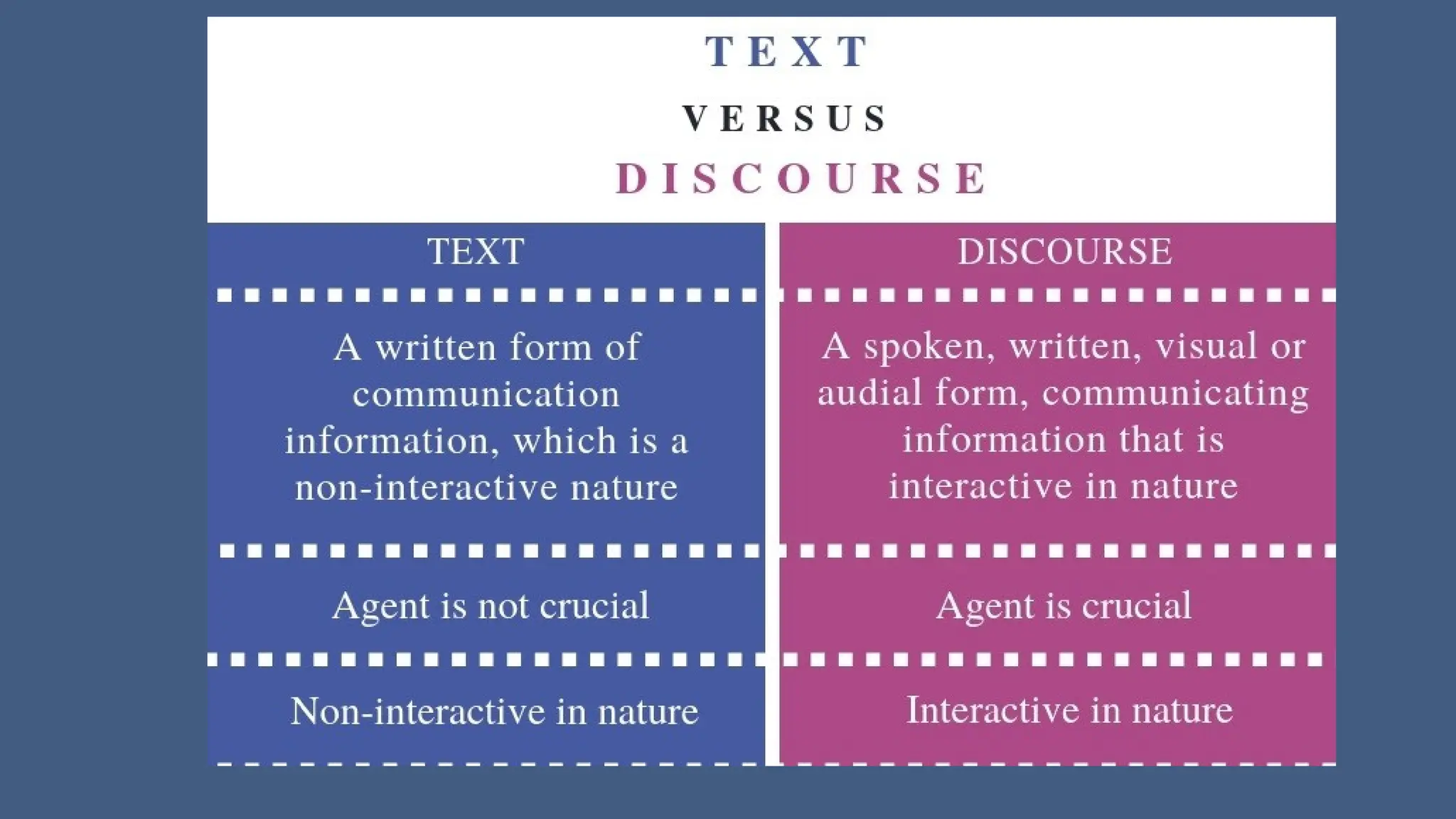
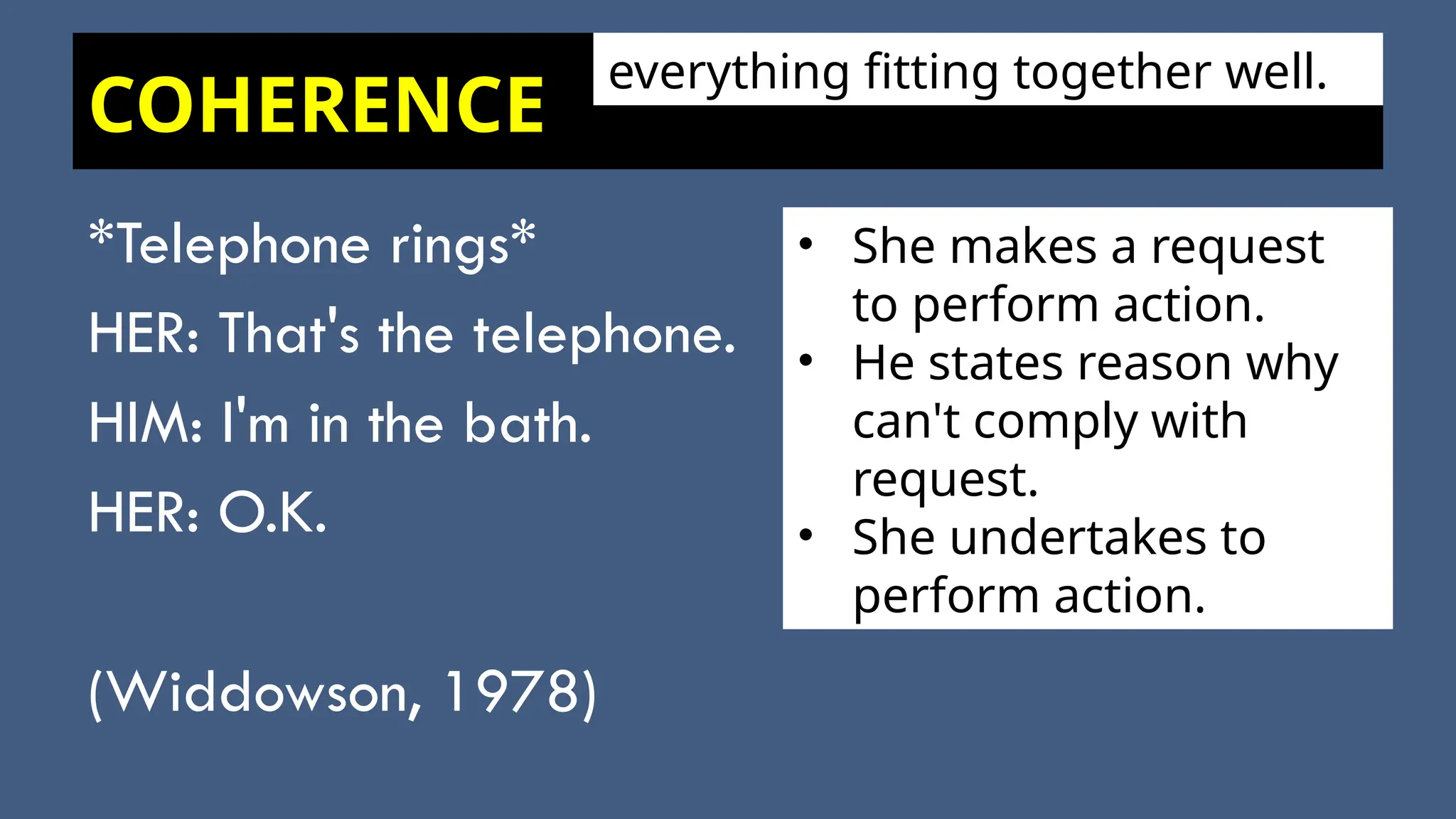
The document discusses the concept of discourse analysis, differentiating between text and discourse while exploring various types of discourse, such as argumentation, description, exposition, and narration. It emphasizes the importance of context, culture, and social environment in shaping a writer's perspective and highlights the necessity of coherence and cohesion for constructing well-written texts. Additionally, it provides examples, mistakes to avoid, and activities to reinforce understanding of these concepts.