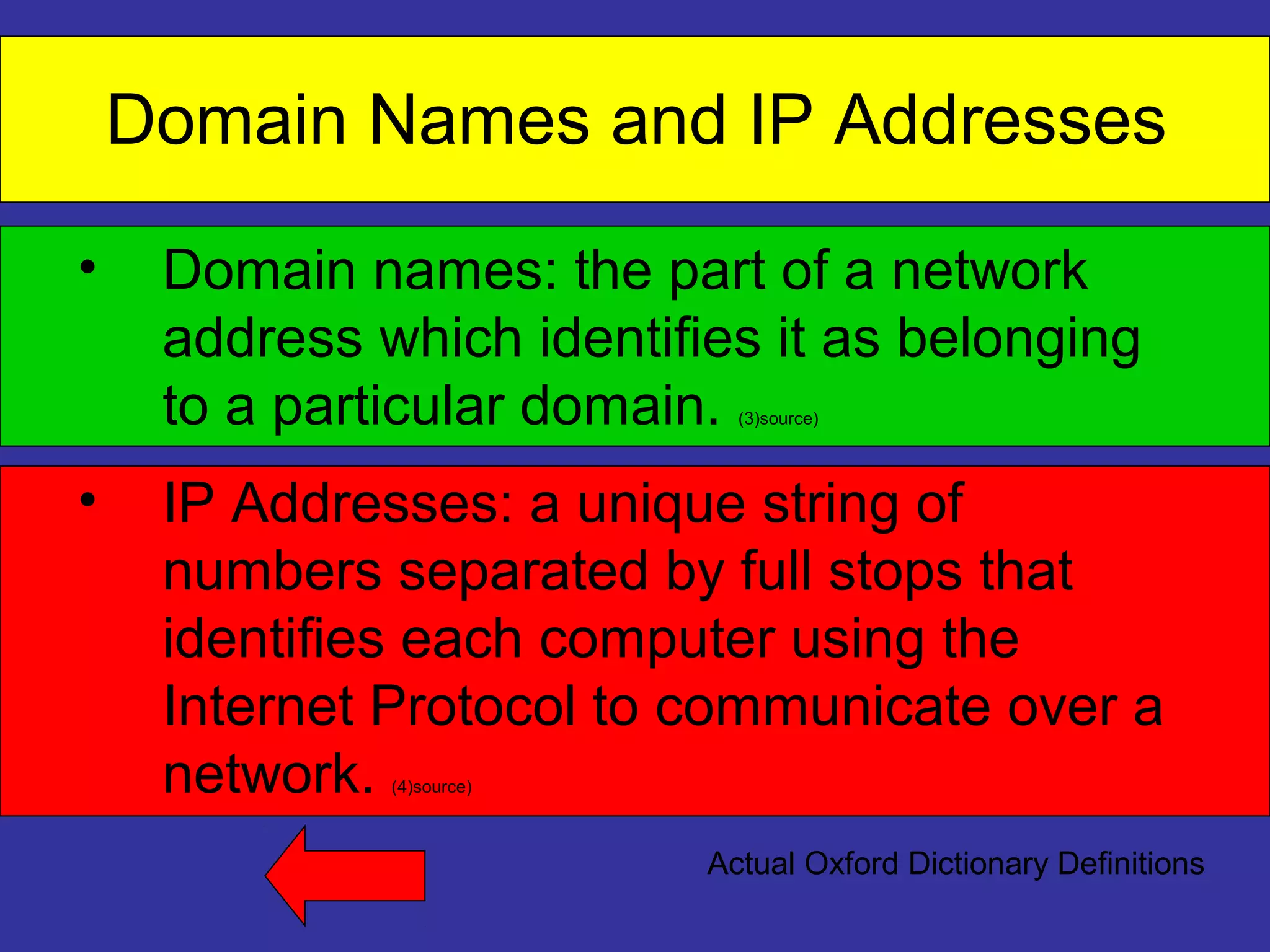
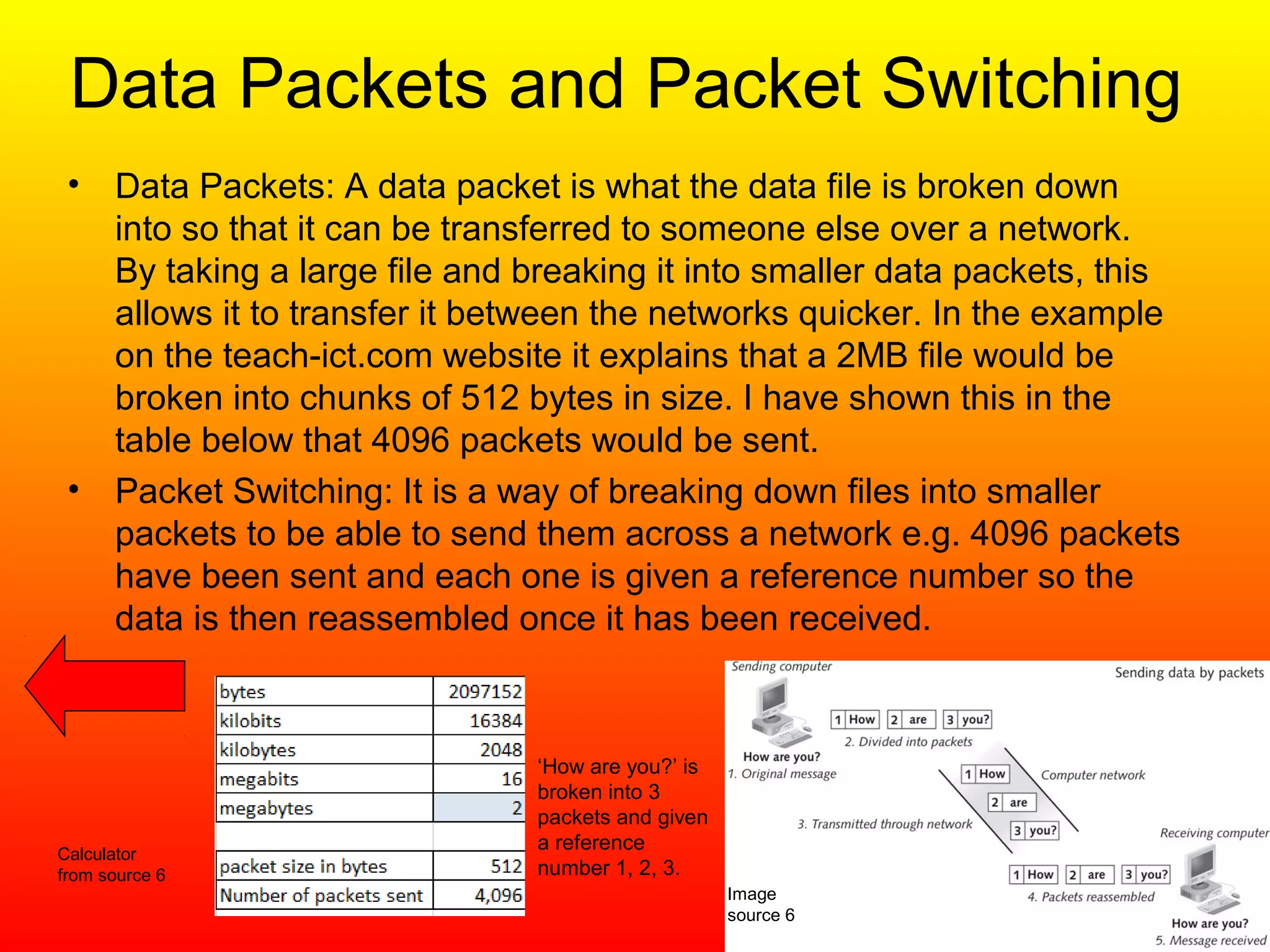
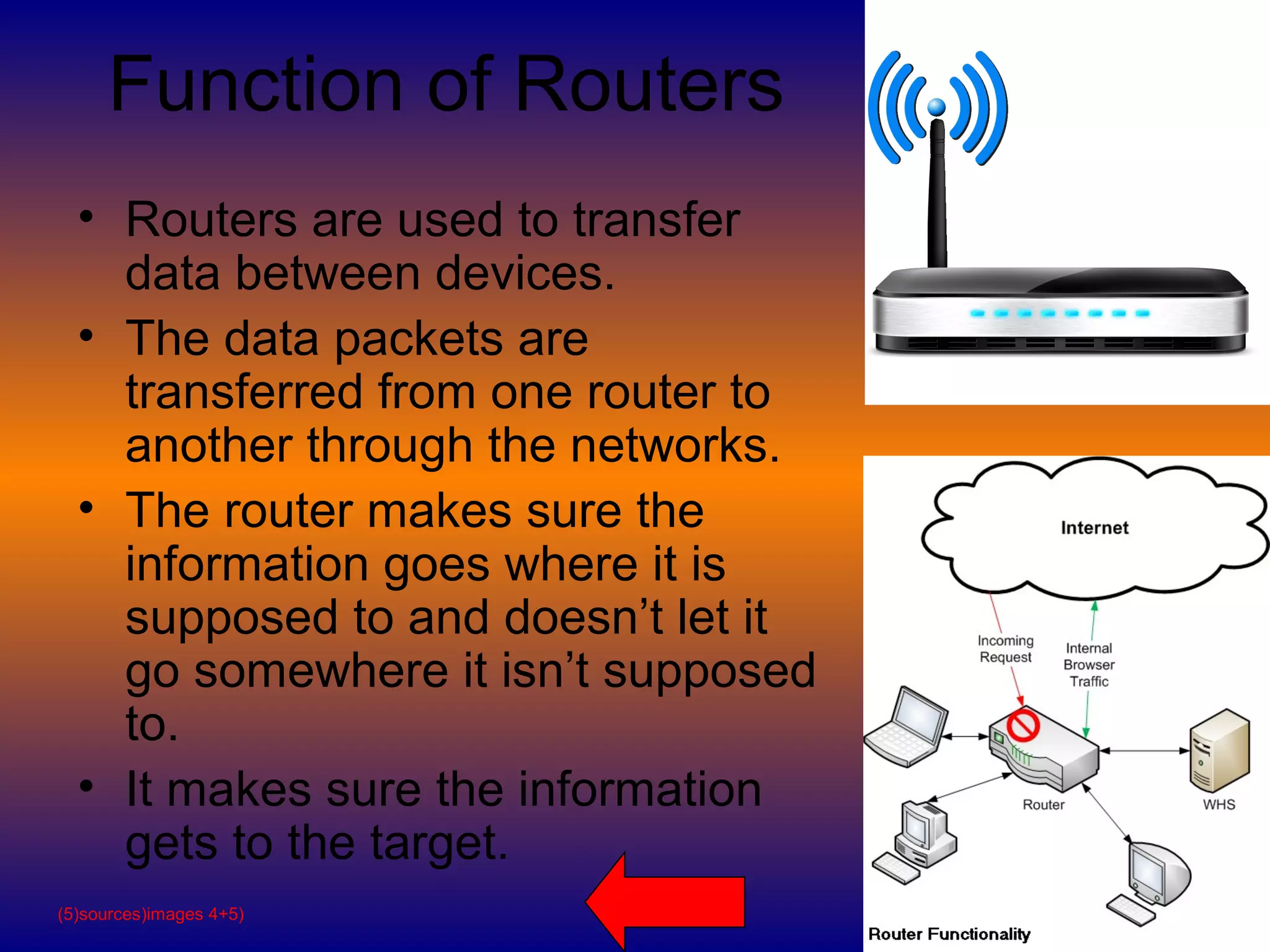
The document defines and explains key concepts related to how the Internet works. It describes the Internet as a global network of interconnected computer networks that uses standard protocols to provide information and communication services. It then defines domain names and IP addresses, explaining that domain names make addresses easier for people to remember while IP addresses are unique strings of numbers that identify devices. It also describes how data is broken into packets and sent over the network, with routers directing packets to their destinations.