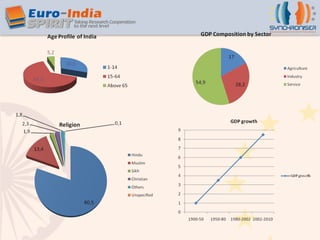
- India has a population of over 1.1 billion people with a young median age and is one of the fastest growing economies in the world, expected to grow over 10% annually.
- India has a large telecom sector that is also growing rapidly, with over 600 million telephone subscribers and internet users numbering over 80 million.
- The document discusses India's policies around ICT, including telecom deregulation, encouragement of open source, and focus areas like privacy, local language apps, broadband access, and computerizing government services.