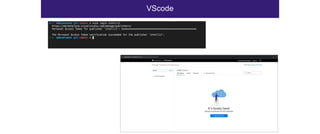
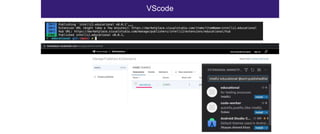
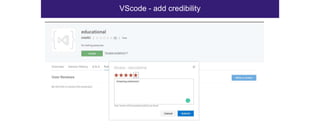
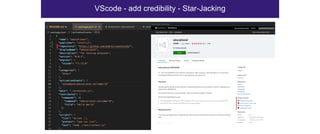
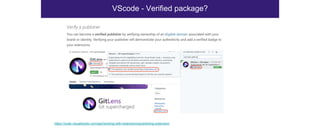
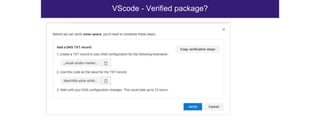
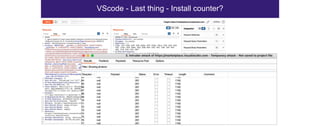
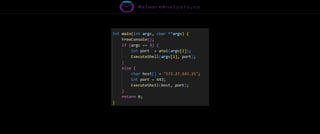
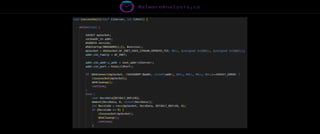
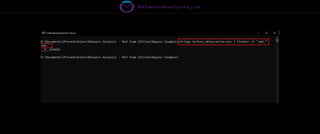
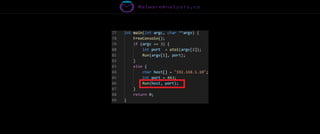
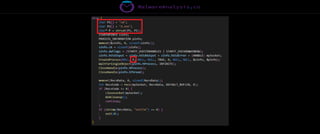
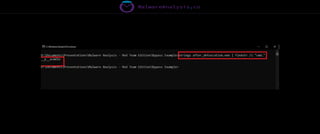
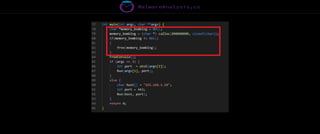
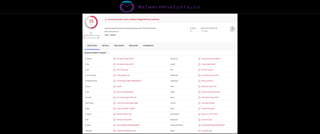
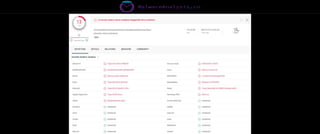
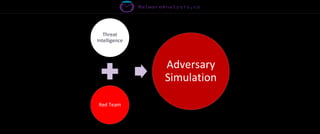
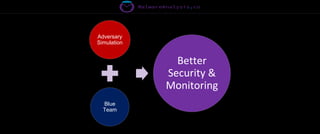
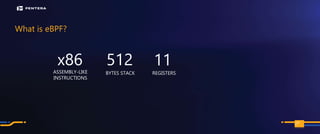
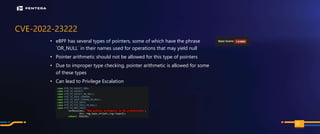
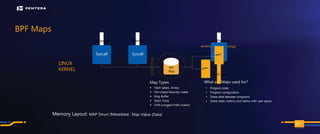
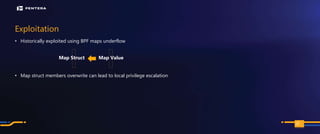
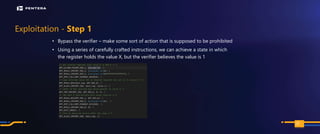
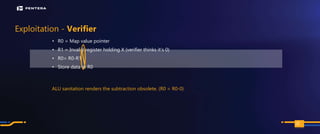
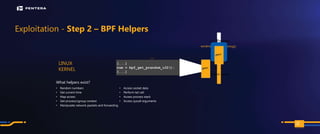
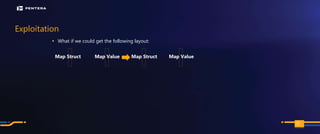
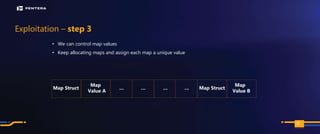
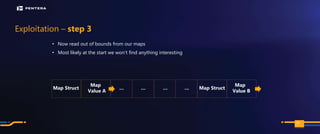
The document discusses the security risks associated with Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) and supply chain attacks targeting IDE extensions and plugins. It presents research findings that reveal vulnerabilities such as the ability to publish malicious packages anonymously and various manipulation techniques in popular IDEs like Visual Studio Code and IntelliJ. It emphasizes the need for developer awareness and tools to assess the security of IDE extensions to mitigate these threats.