Building Your Secure AI Roadmap Meetup
Stay safe and join us virtually for our upcoming "Building Your Secure AI Roadmap" Meetup to hear directly from practitioners who are addressing these challenges today — from discovery and risk analysis to runtime monitoring and governance.
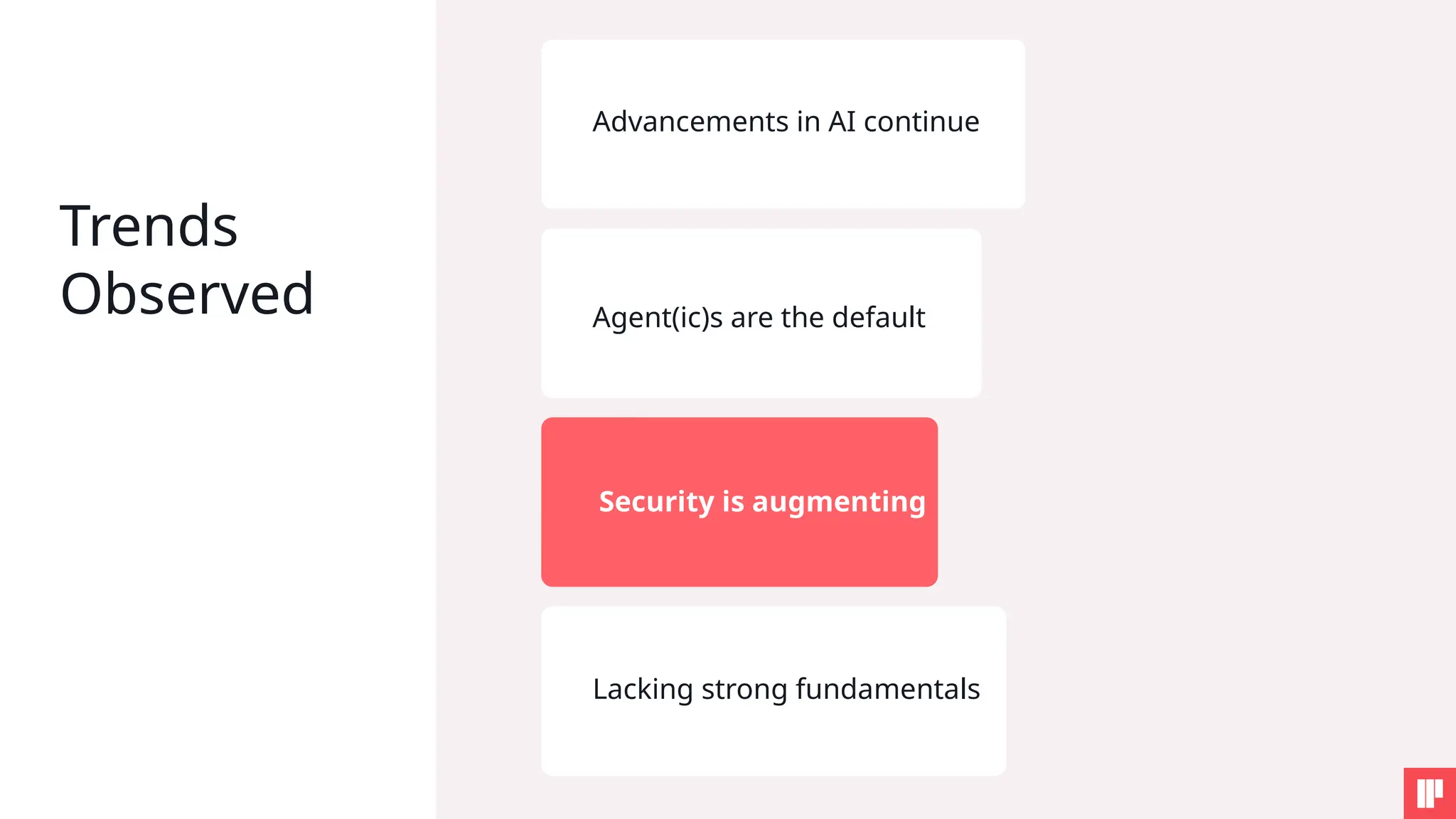
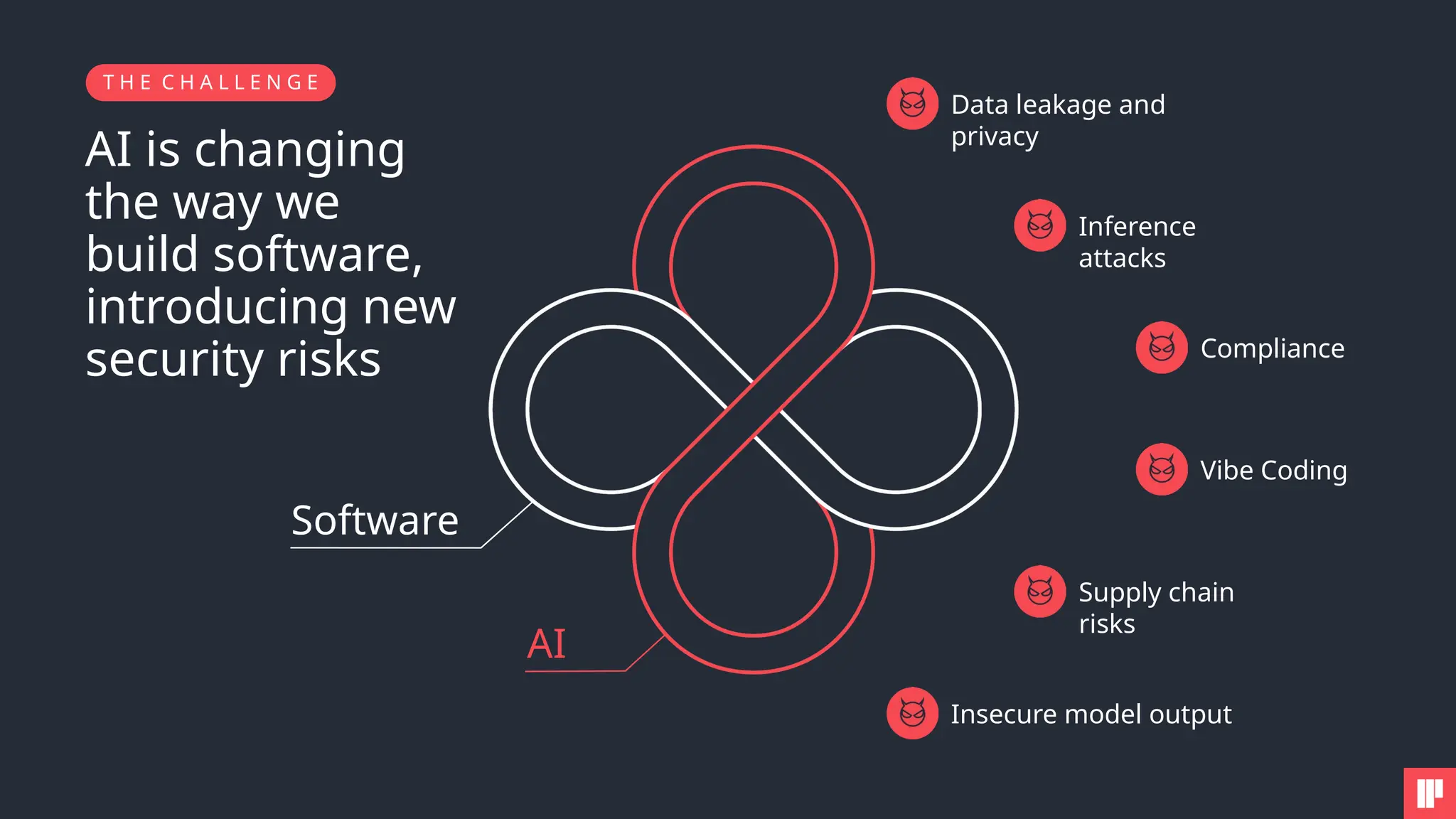
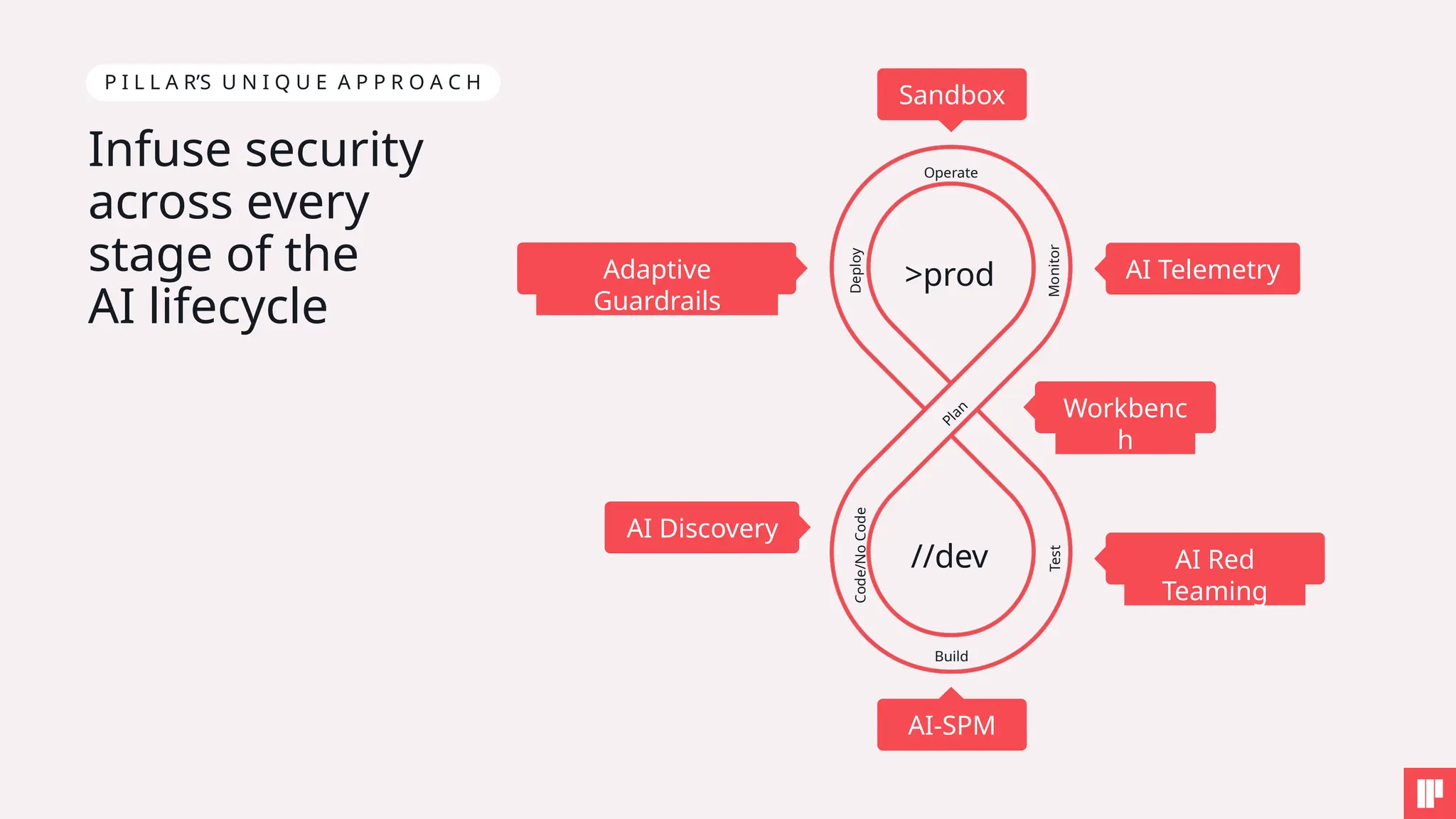
AI is reshaping security risks across every stage of development and deployment. This session will help you cut through the noise, understand the key risks, and walk away with practical steps to strengthen your AI security posture.
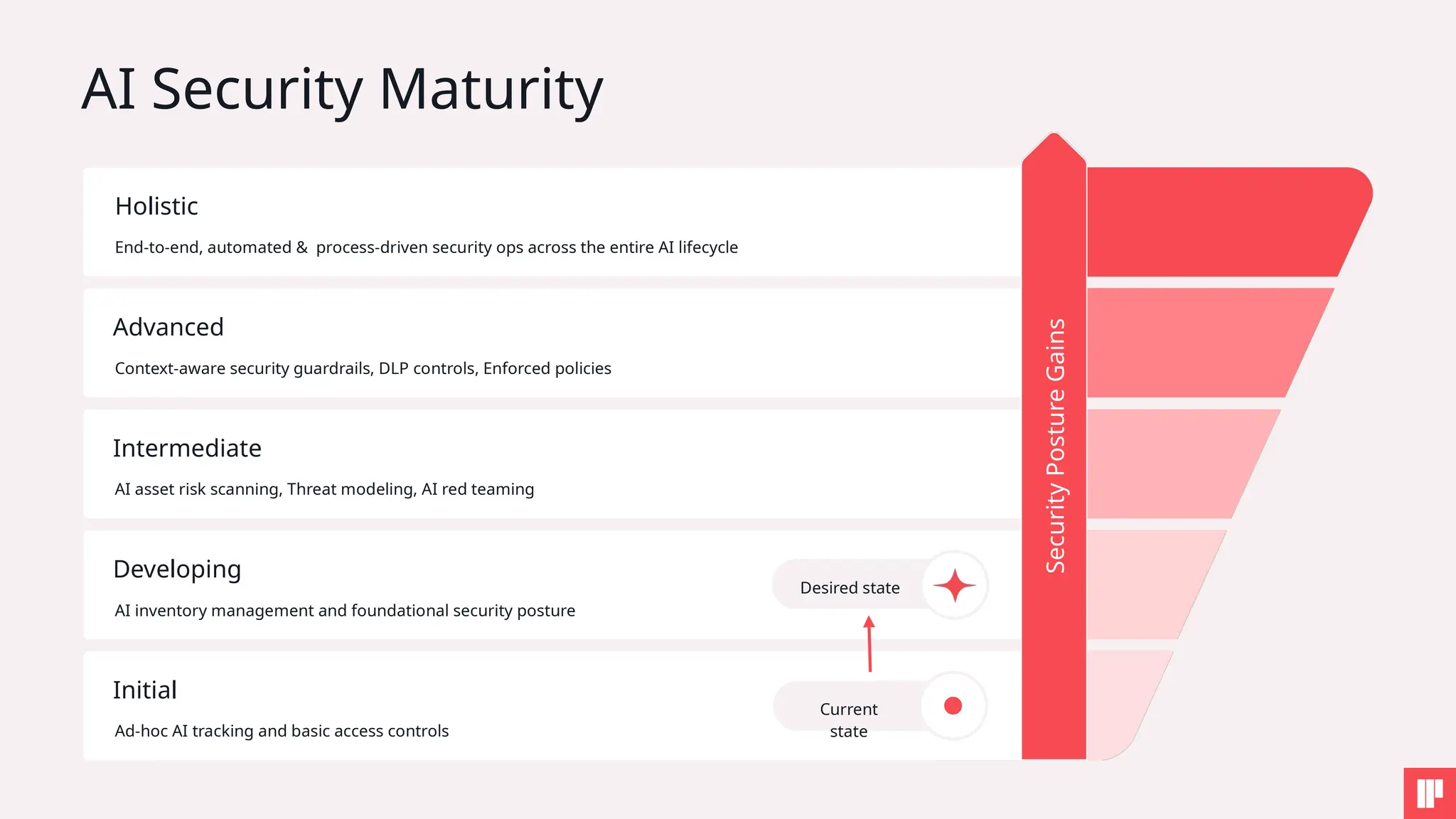
Whether you're just starting your AI security journey or looking to mature your program, you'll come away with actionable guidance on aligning innovation with security and governance.
What You’ll Learn:
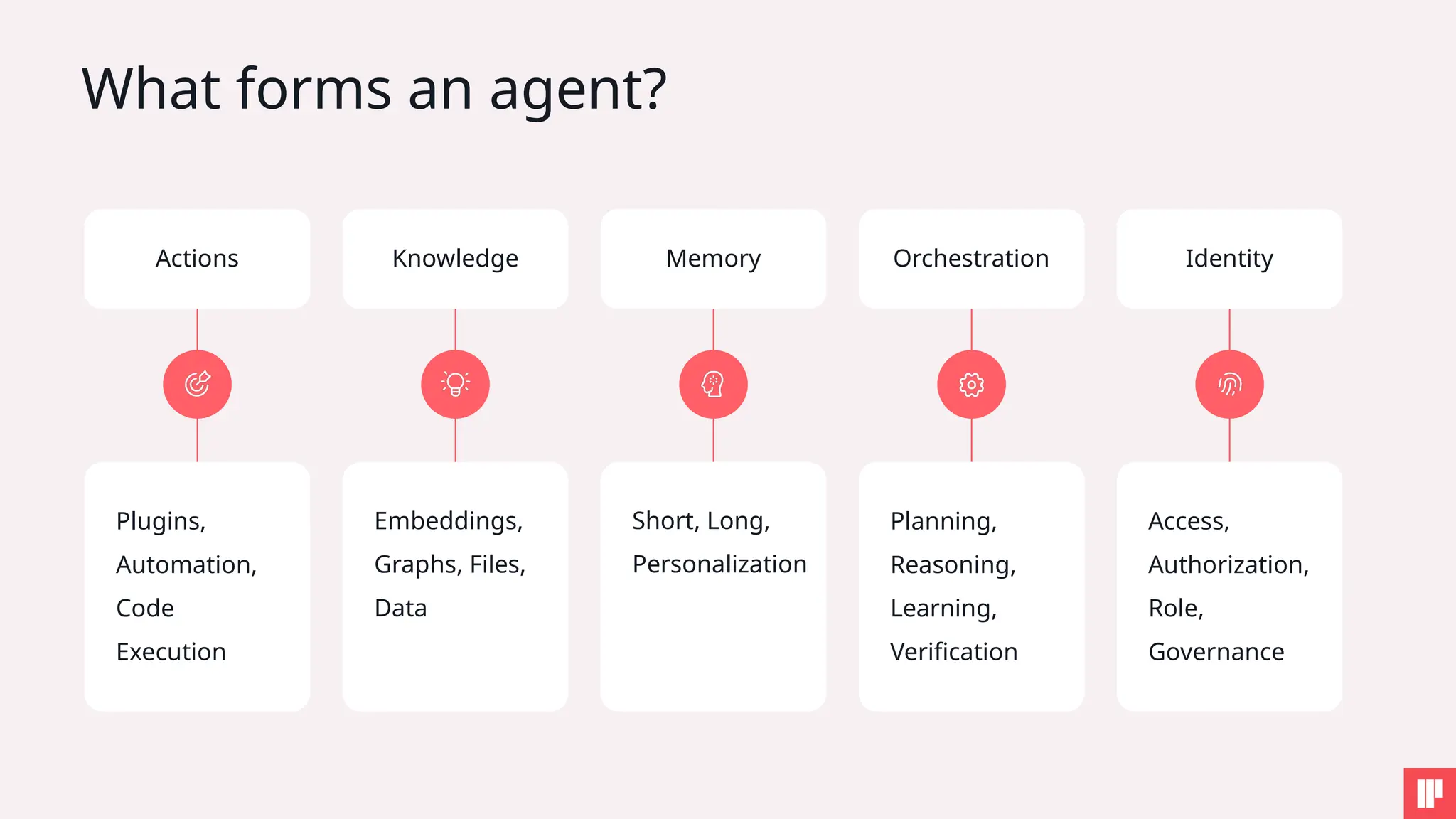
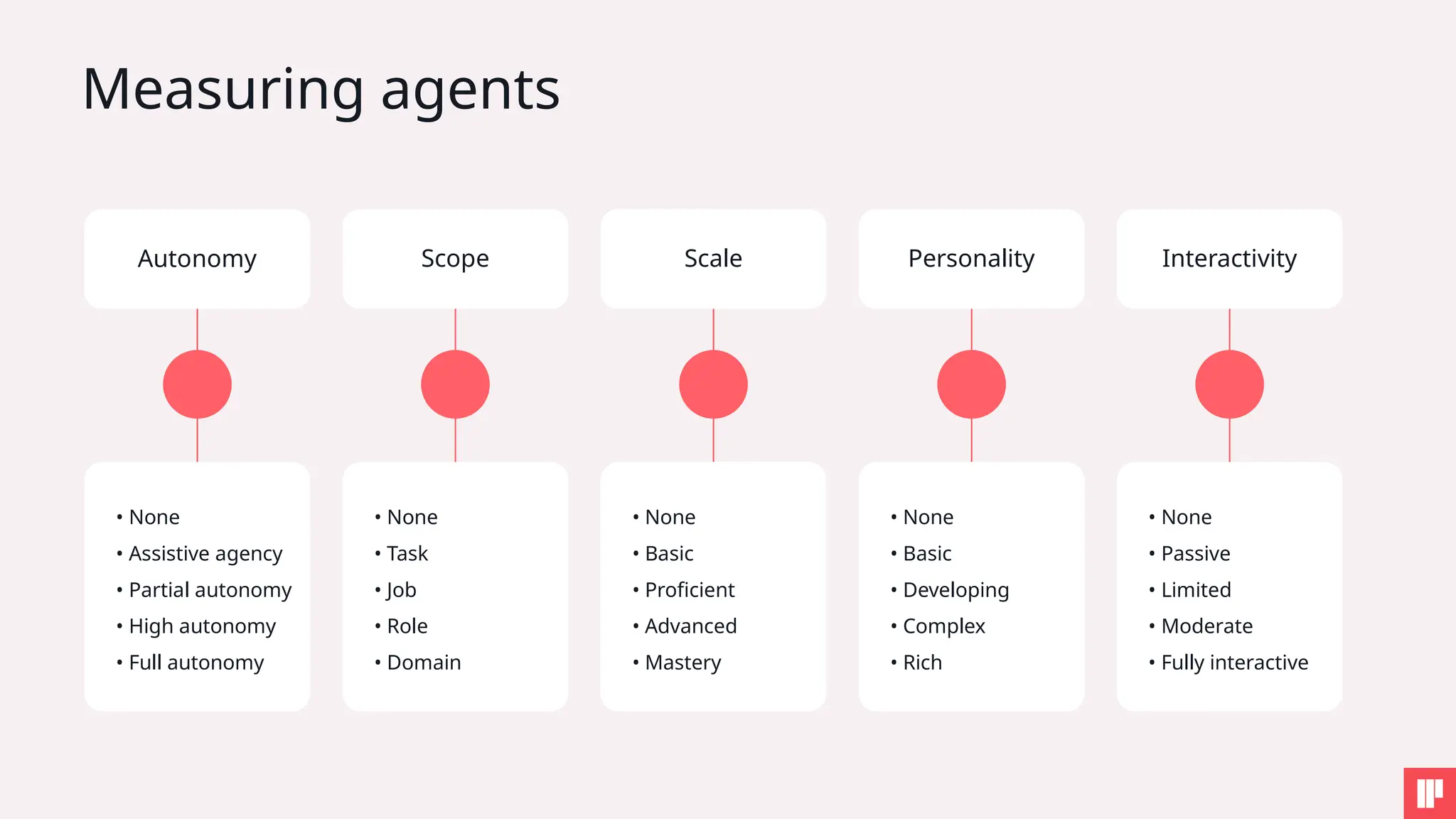
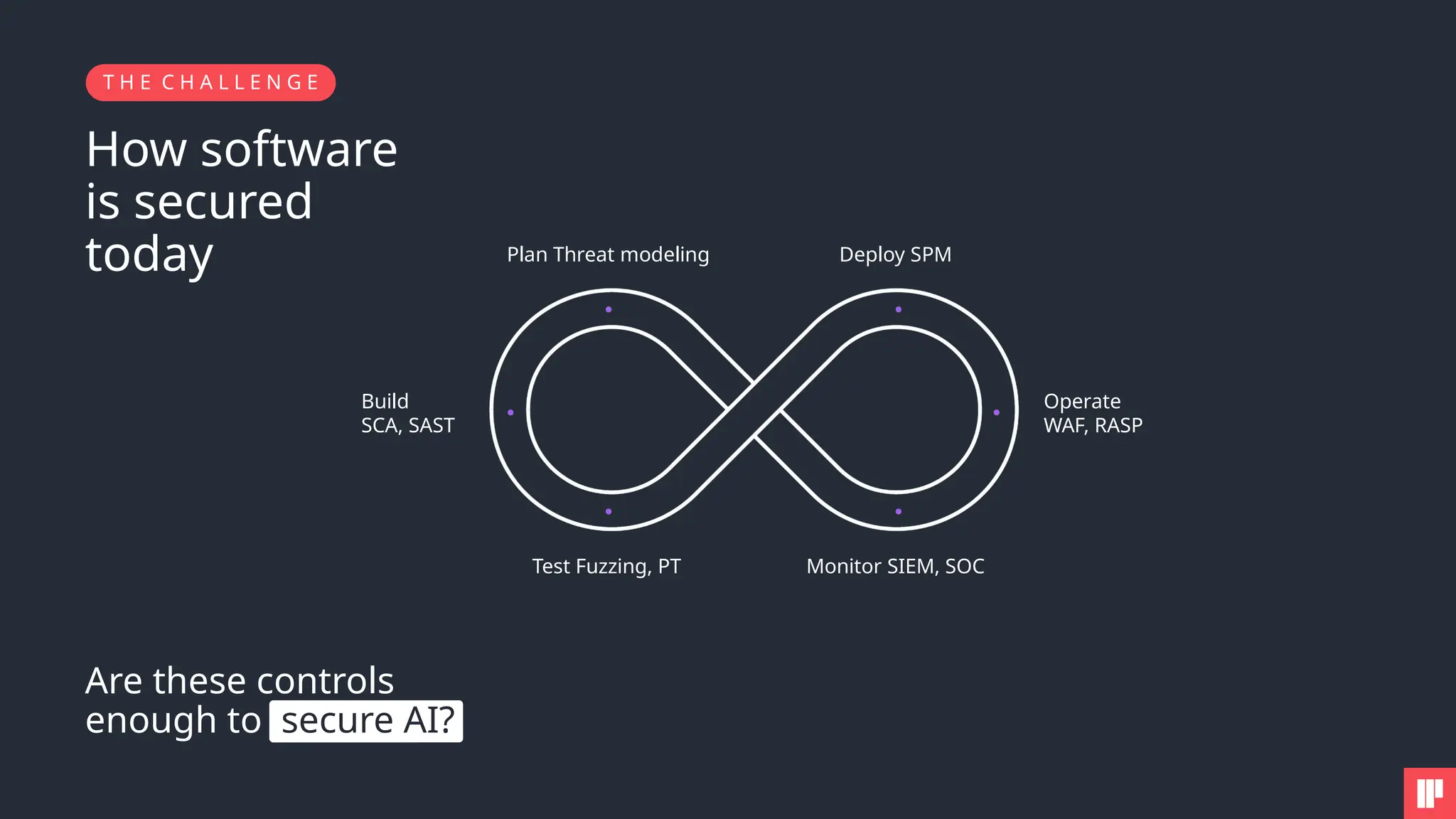
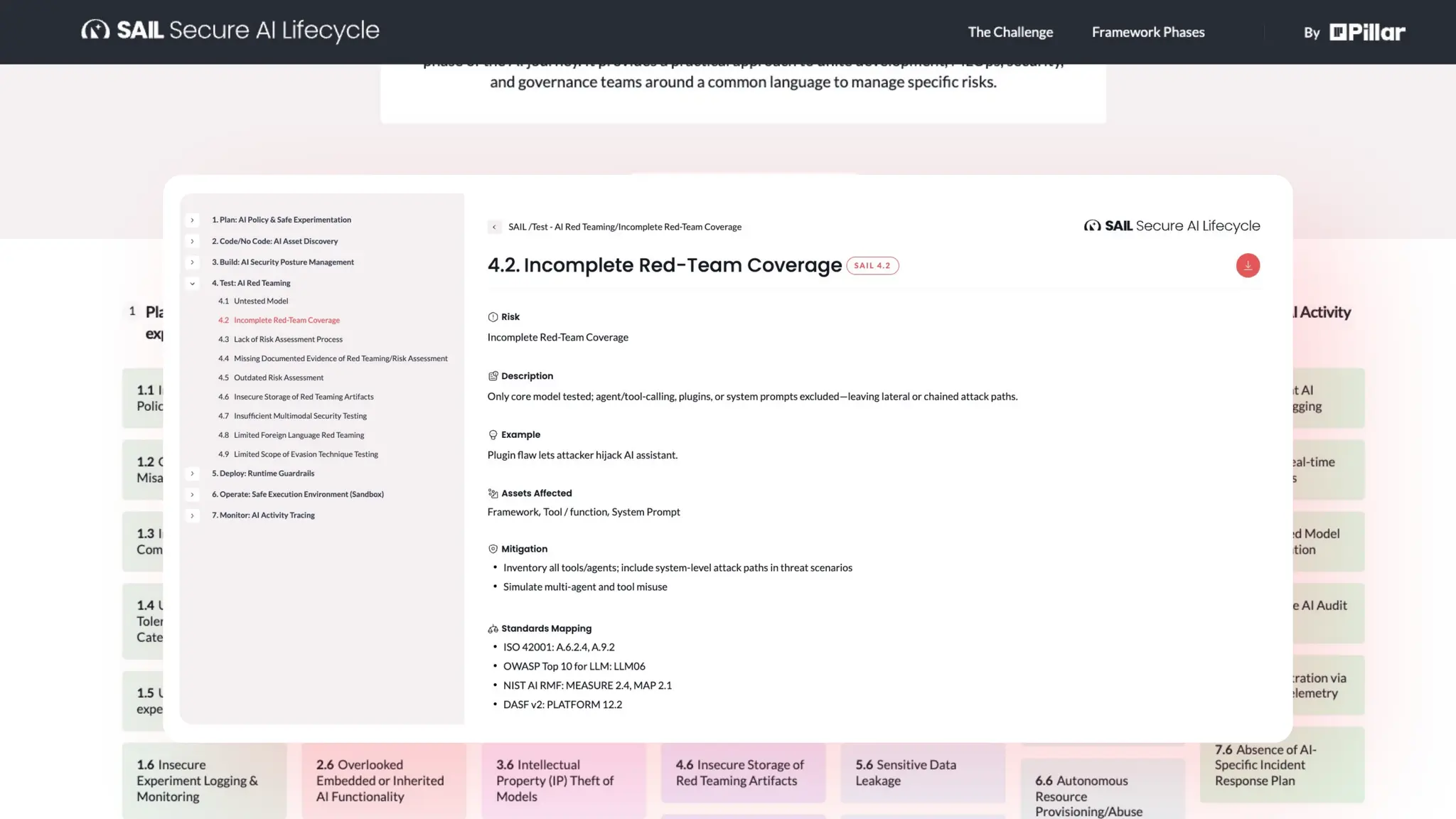
1. How to tackle AI security challenges from planning through runtime
2. Real-world use cases, risks, and solutions from top AI security leaders
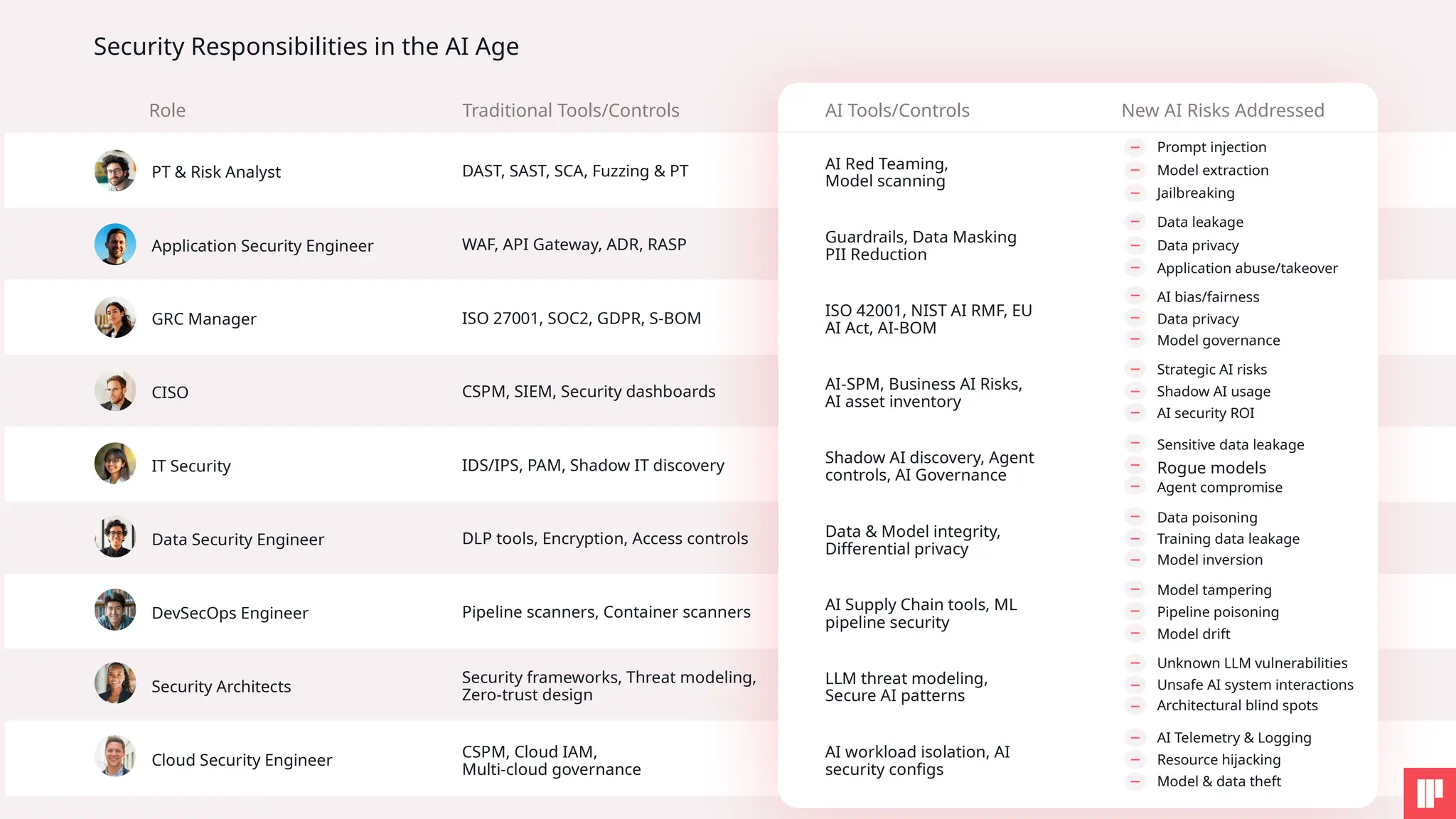
3. How to embed AI security into your organization’s DNA
4. Key SAIL Framework principles in action