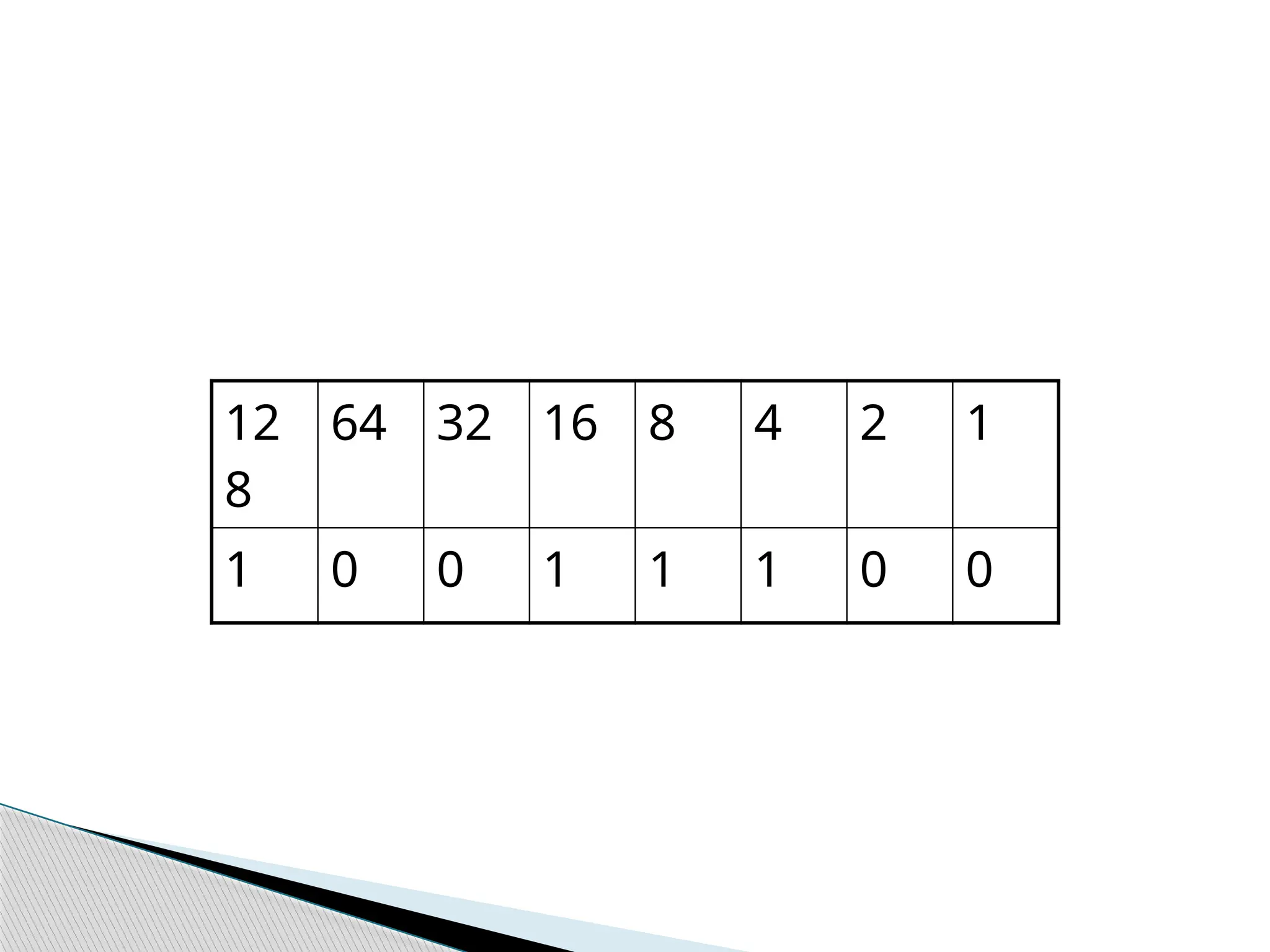
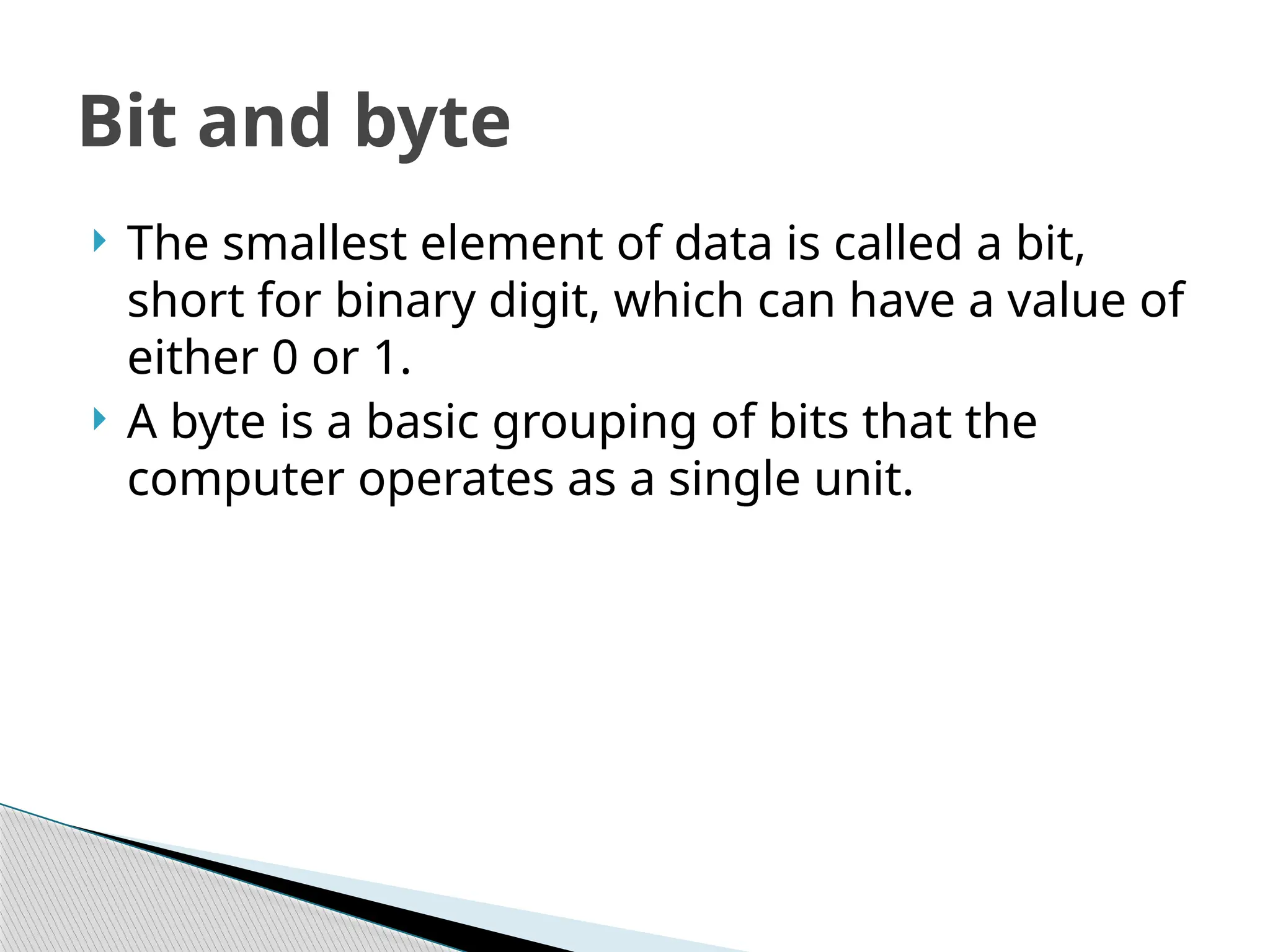
The document explains the basics of binary conversion and how computers process data using bits and bytes. A bit is the smallest unit of data, representing a value of 0 or 1, while a byte consists of eight bits. The text also details how to convert decimal numbers to binary, illustrating the process with examples.





![ 00000000 [0] 0*0
00000001 [1] 1*0
00000010 [2] 2*1
00000100 [4] 2*2
00001000 [8] 2*2*2
00010000 [16] 2*2*2*2
00100000 [32] 2*2*2*2*2
01000000 [64] 2*2*2*2*2*2
10000000 [128] 2*2*2*2*2*2*2
Binary Conversion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerstoragefundamentals-250115114415-132efcc0/75/The-fundamentals-of-Computer-Storage-System-11-2048.jpg)
![ 00000011 [3]
00000111 [7]
00001111 [15]
00011111 [31]
00111111 [63]
01111111 [127]
11111111 [255]
Binary Conversion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerstoragefundamentals-250115114415-132efcc0/75/The-fundamentals-of-Computer-Storage-System-12-2048.jpg)