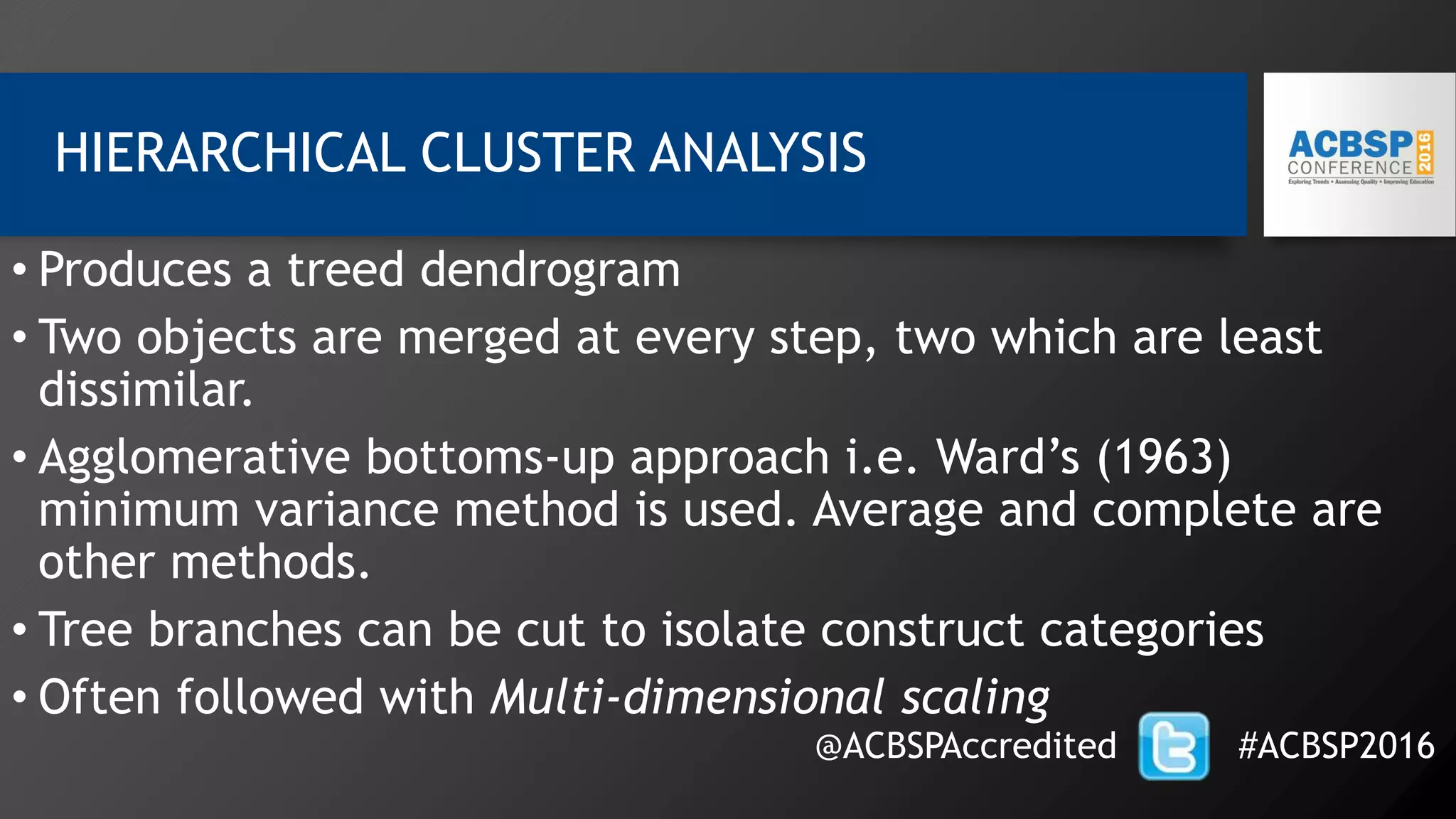
1) The document describes a study that uses text mining and content analysis techniques to analyze reflections from business students in accounting and HR courses.
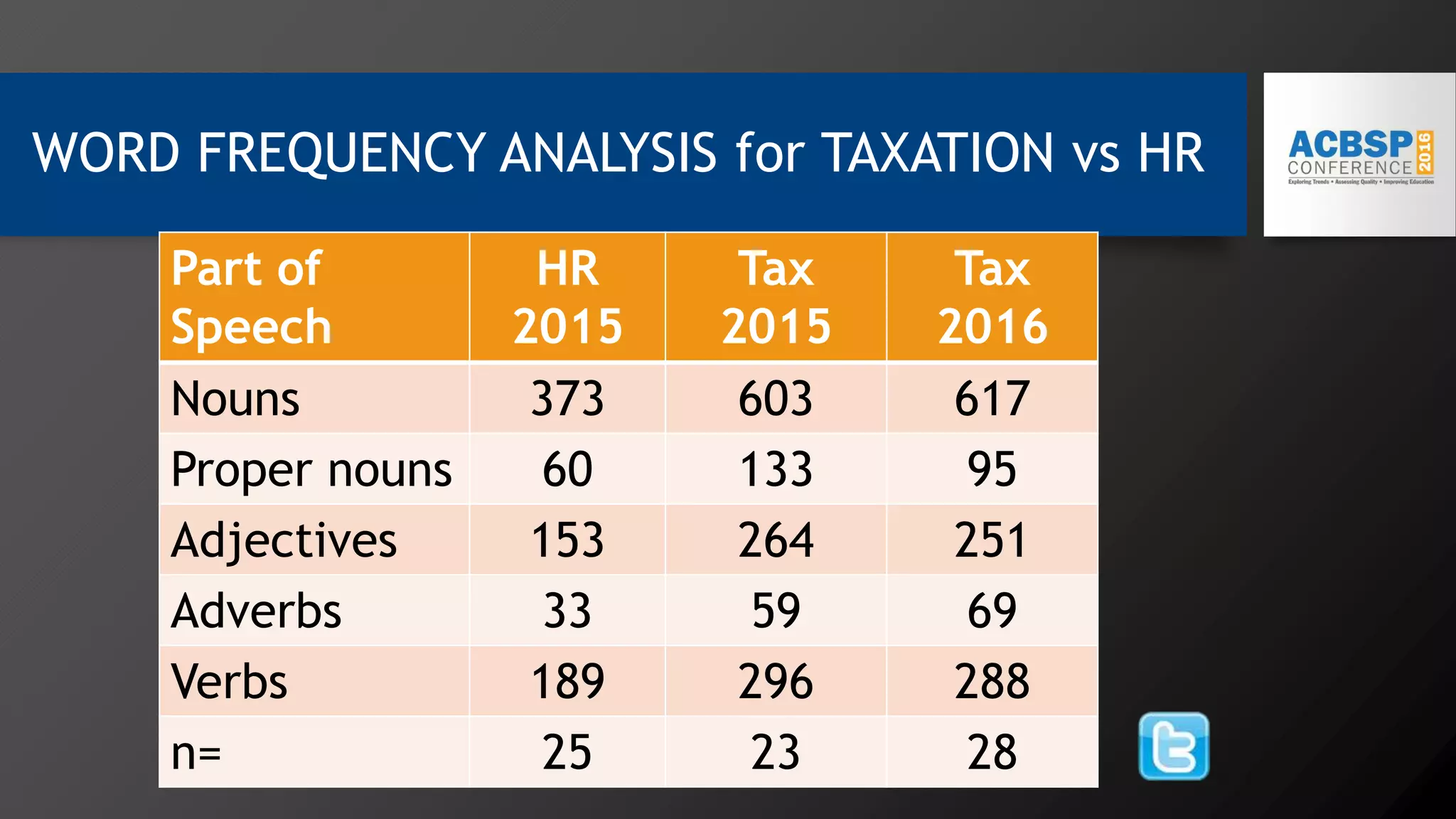
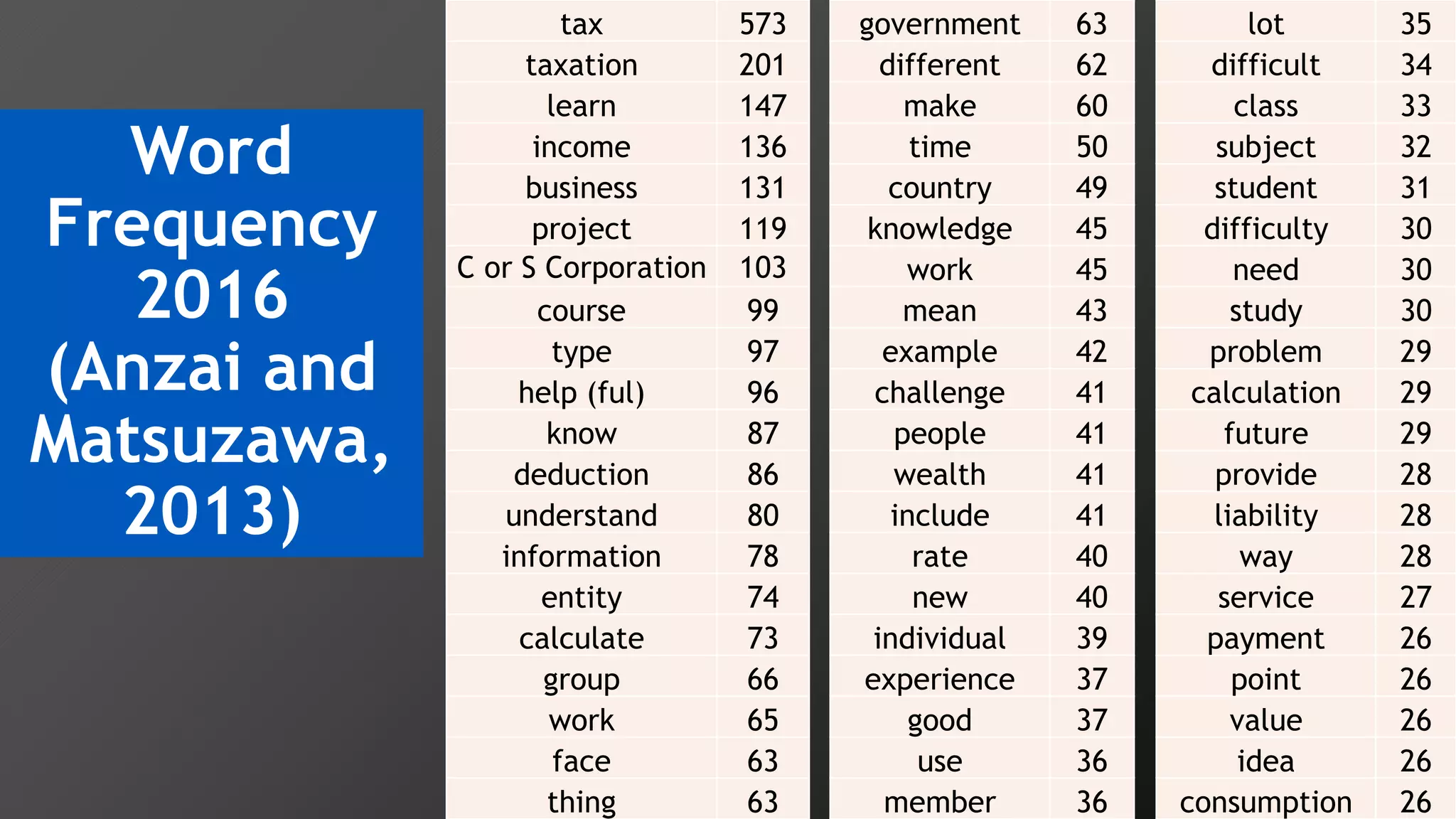
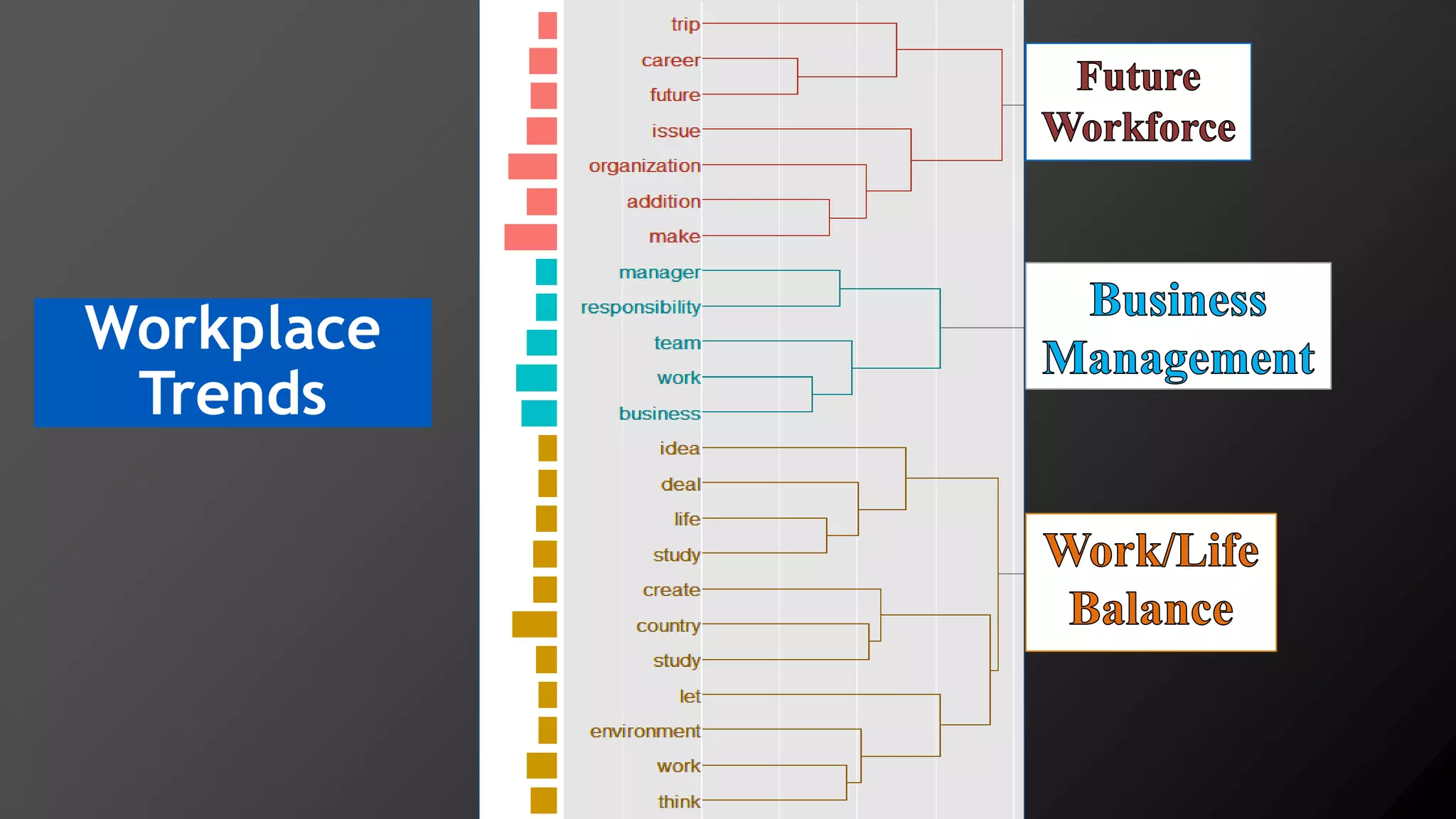
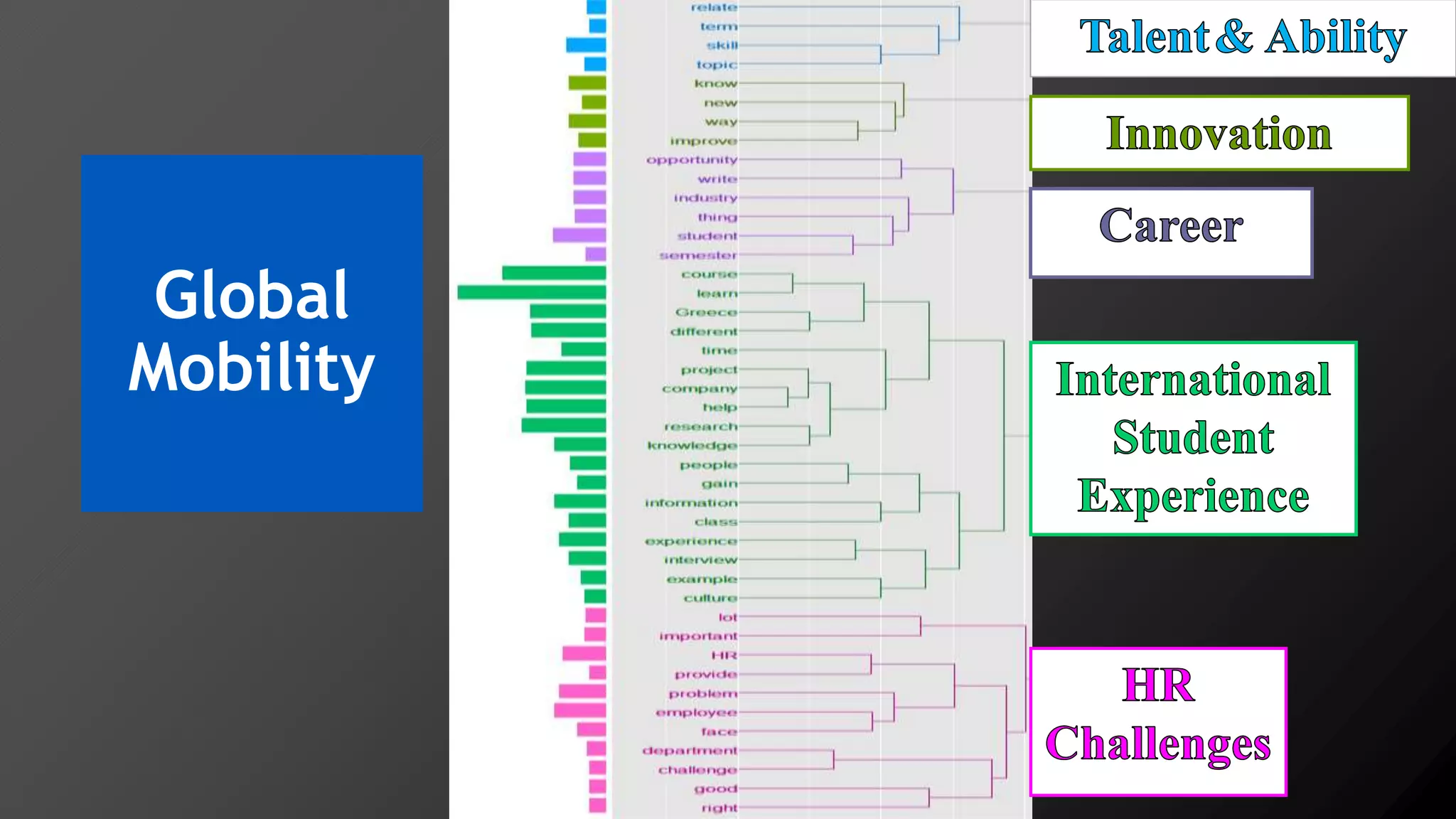
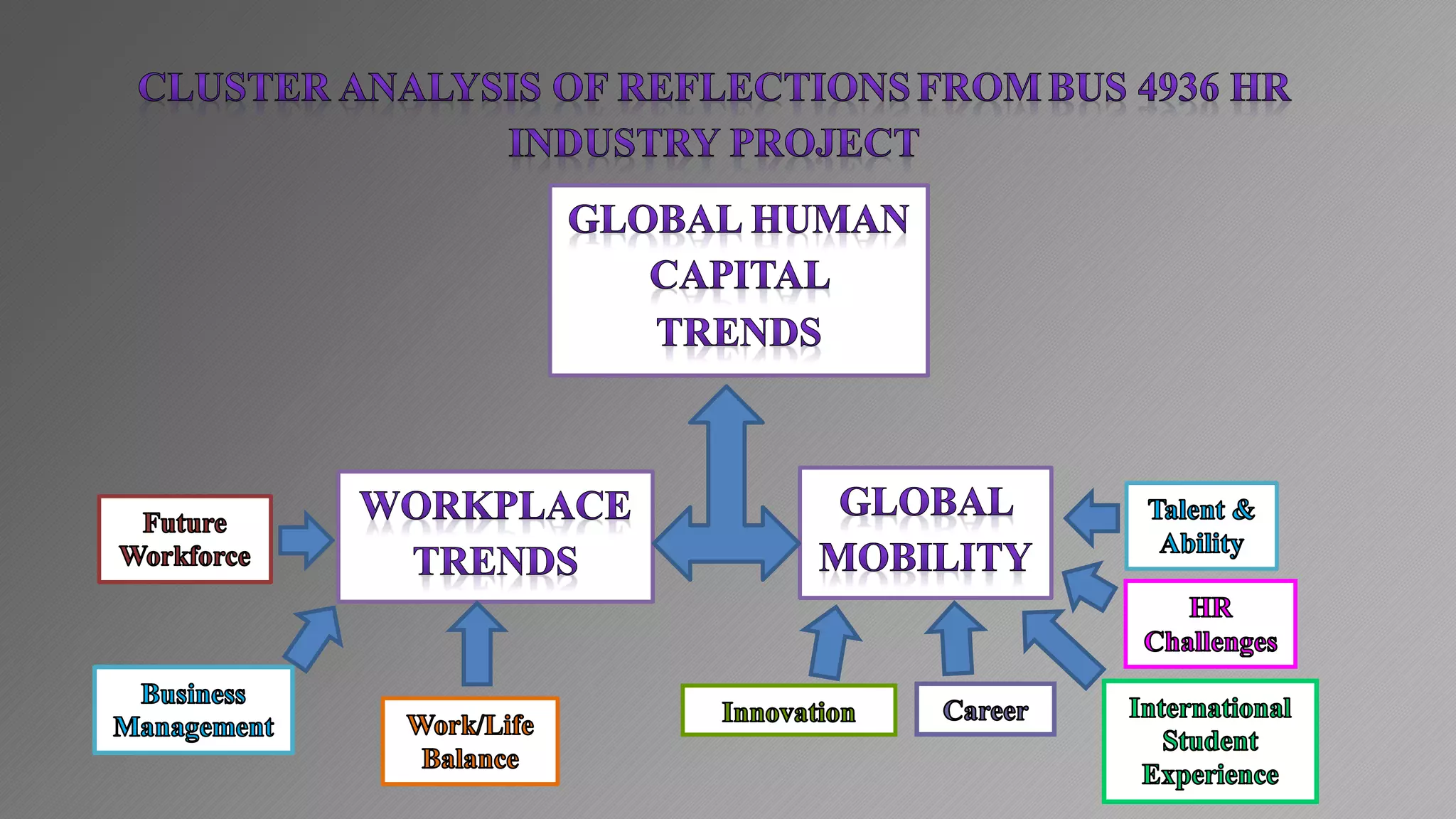
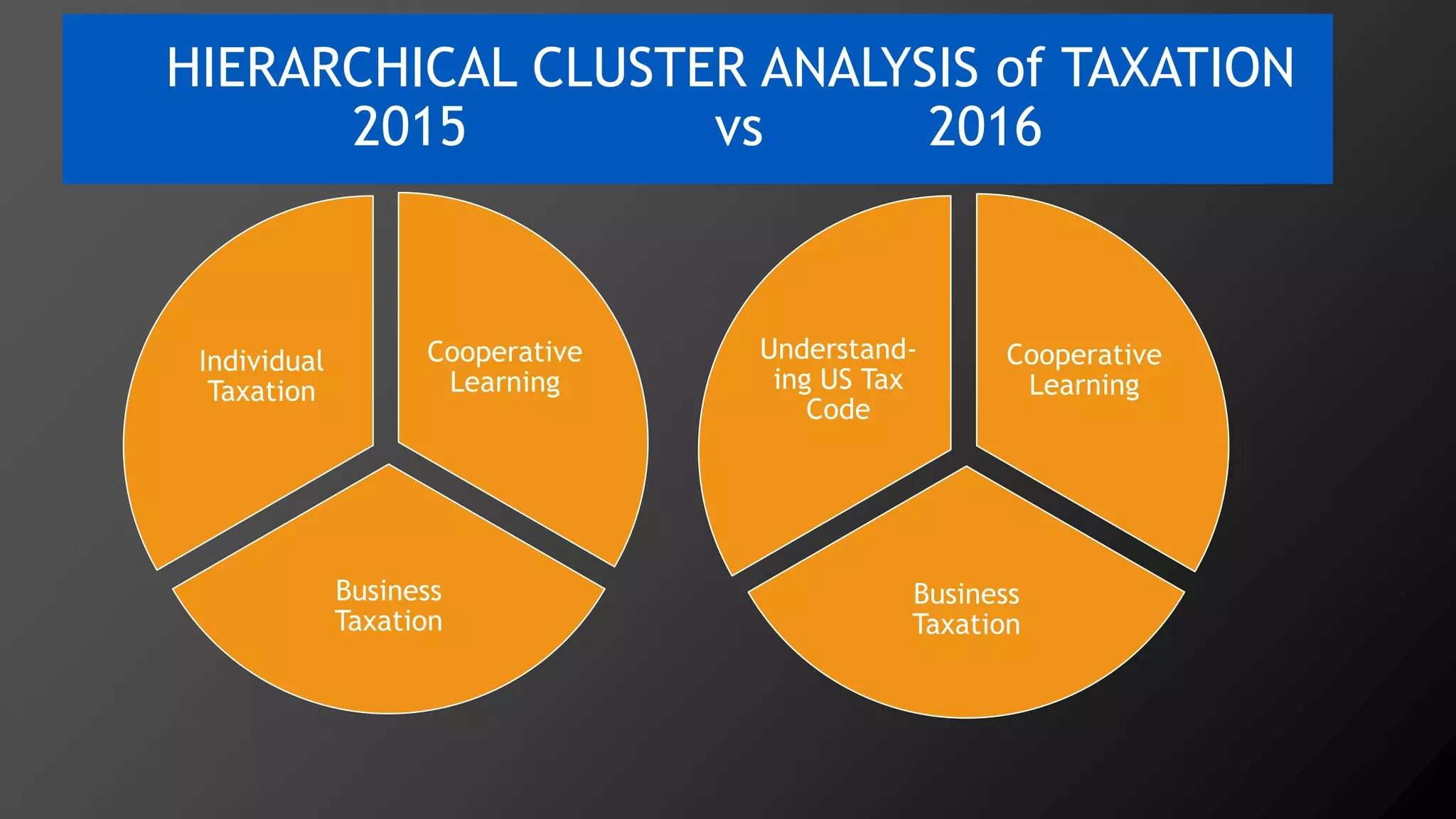
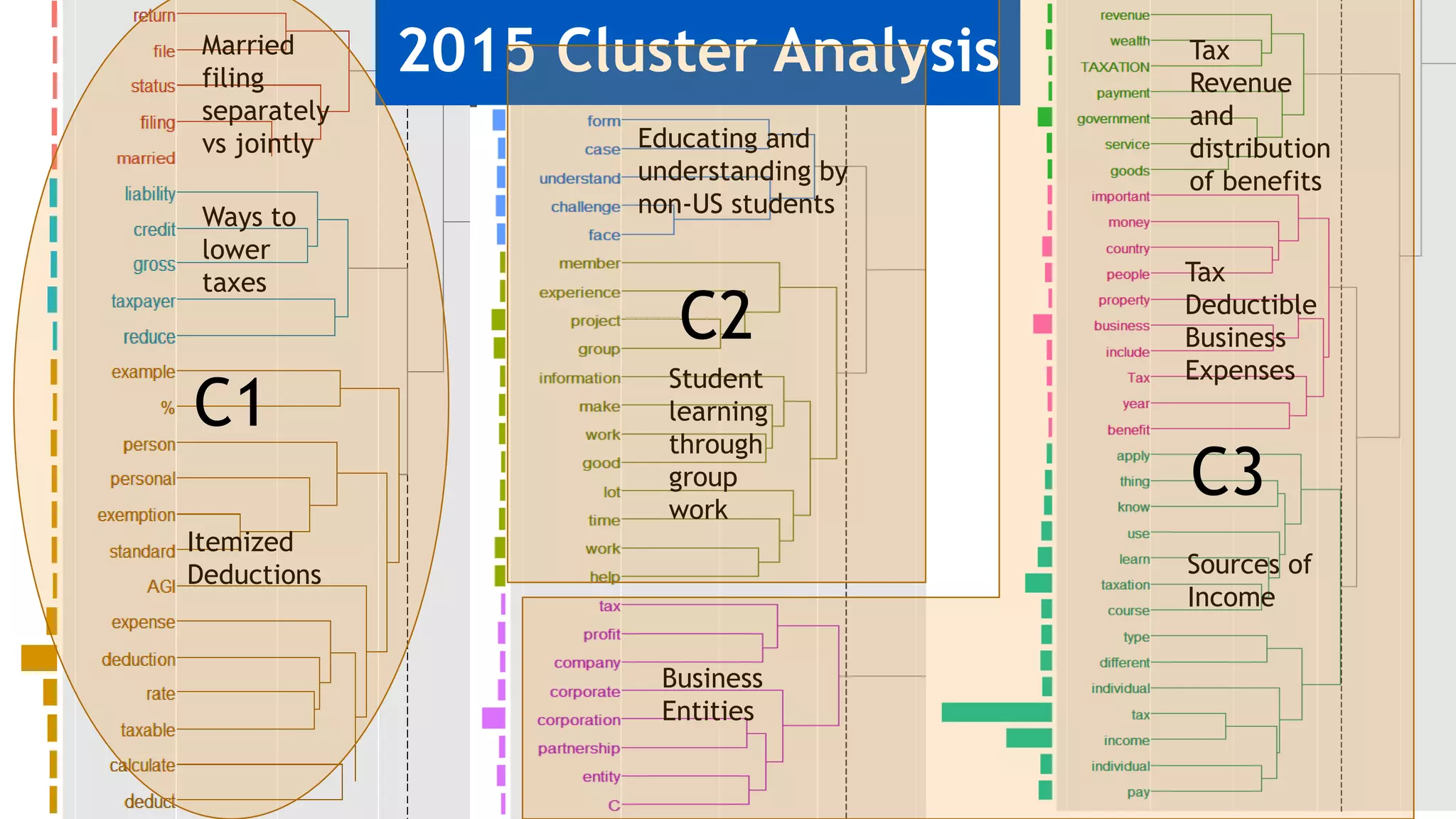
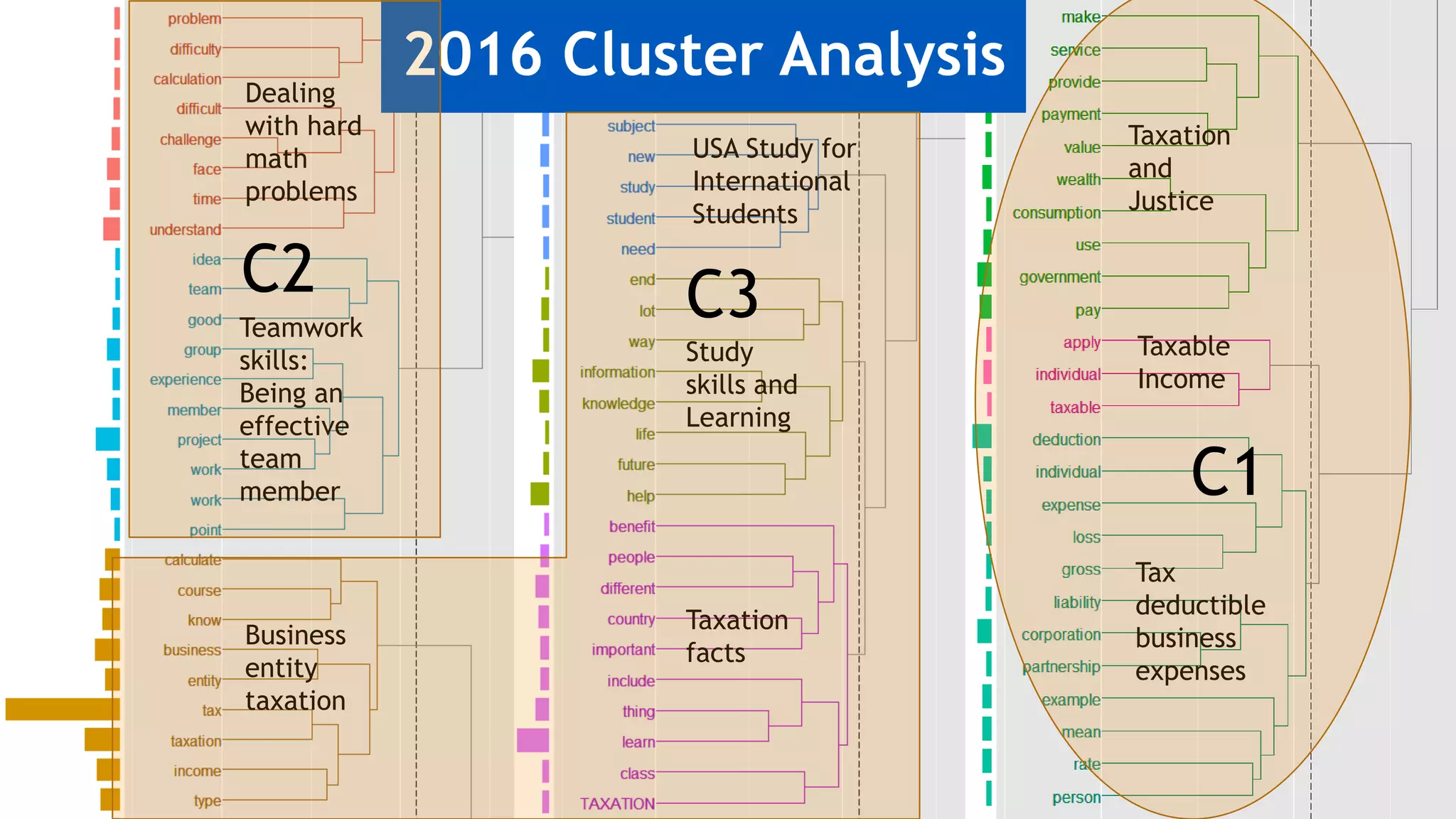
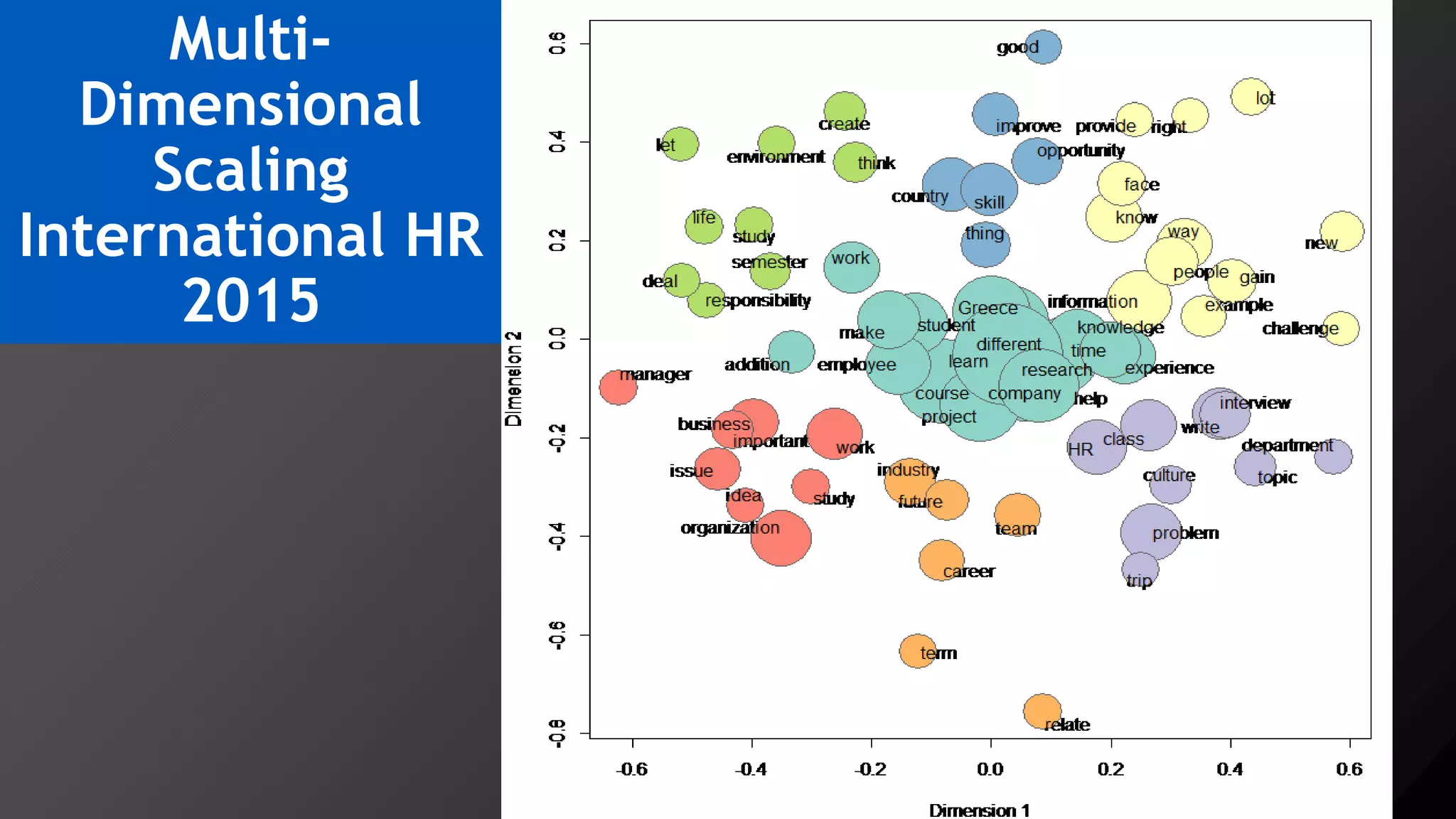
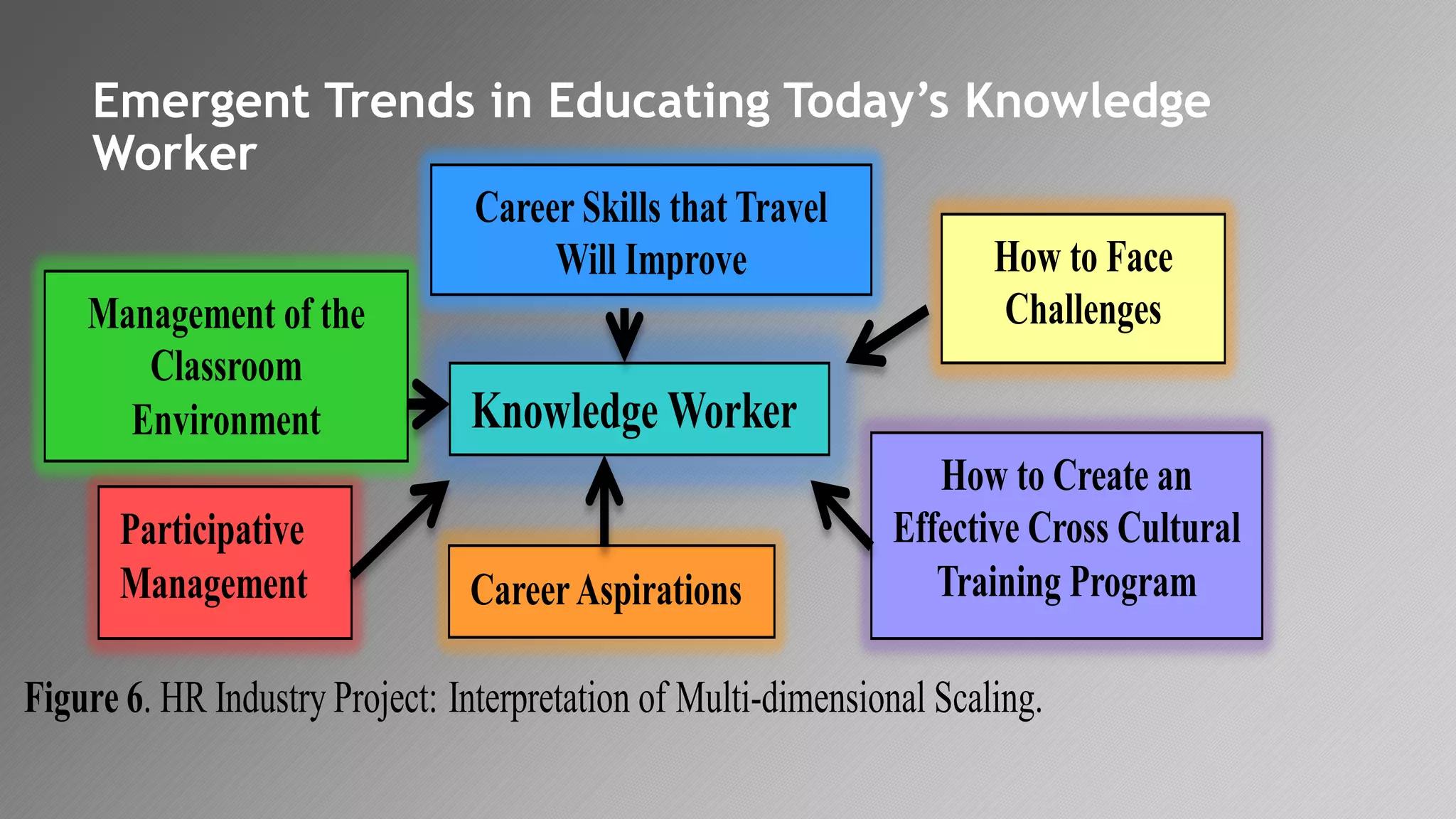
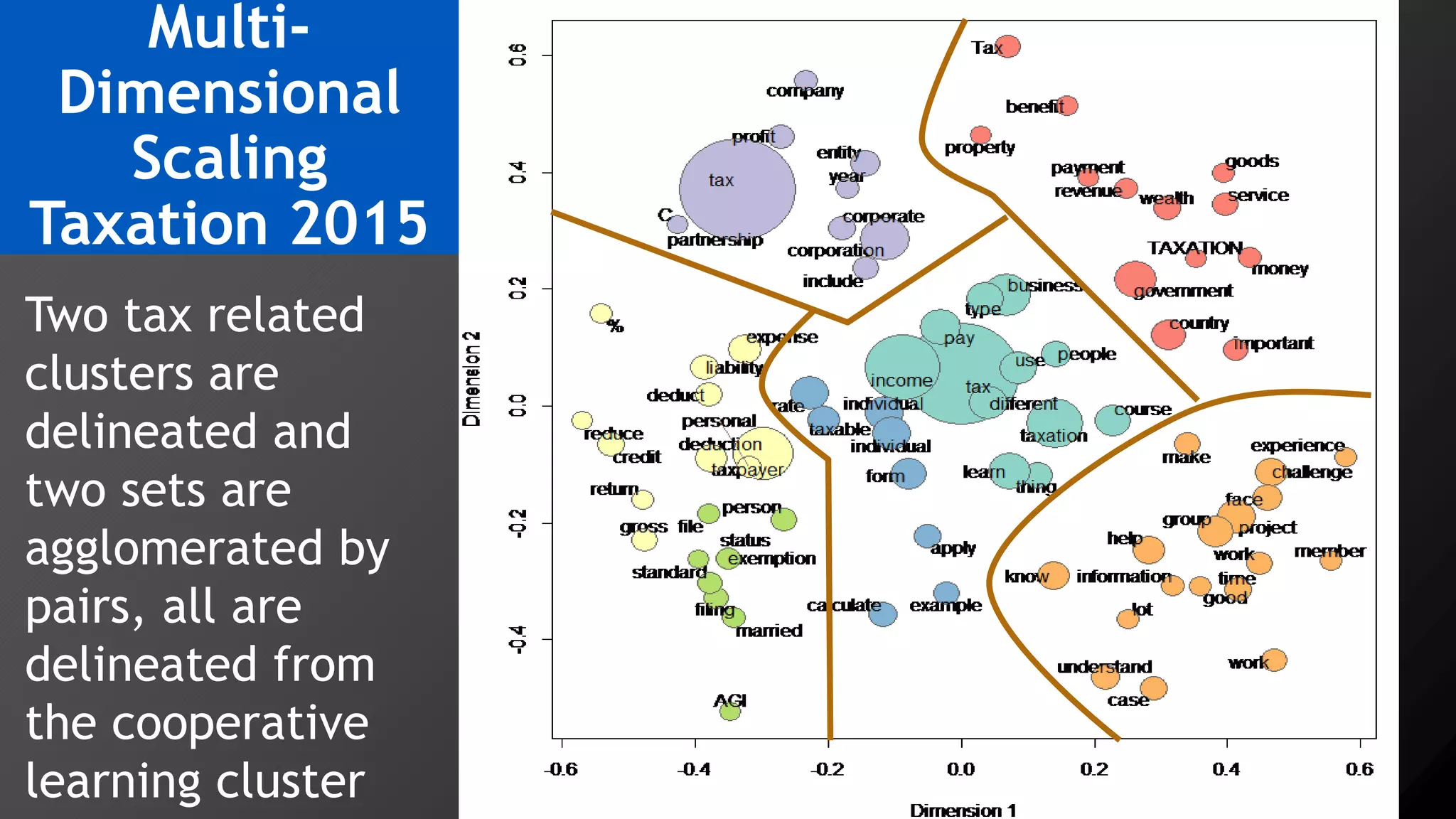
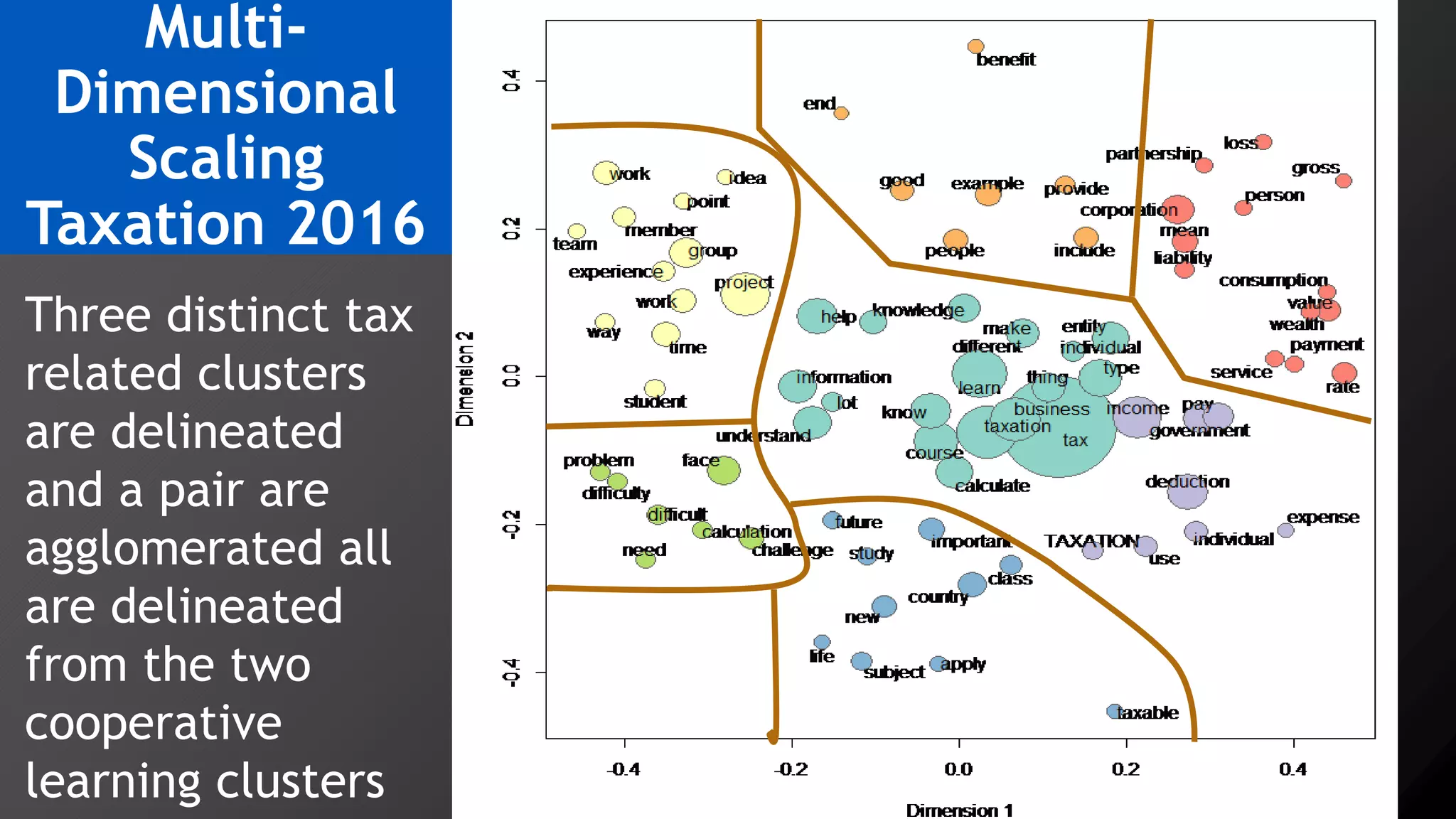
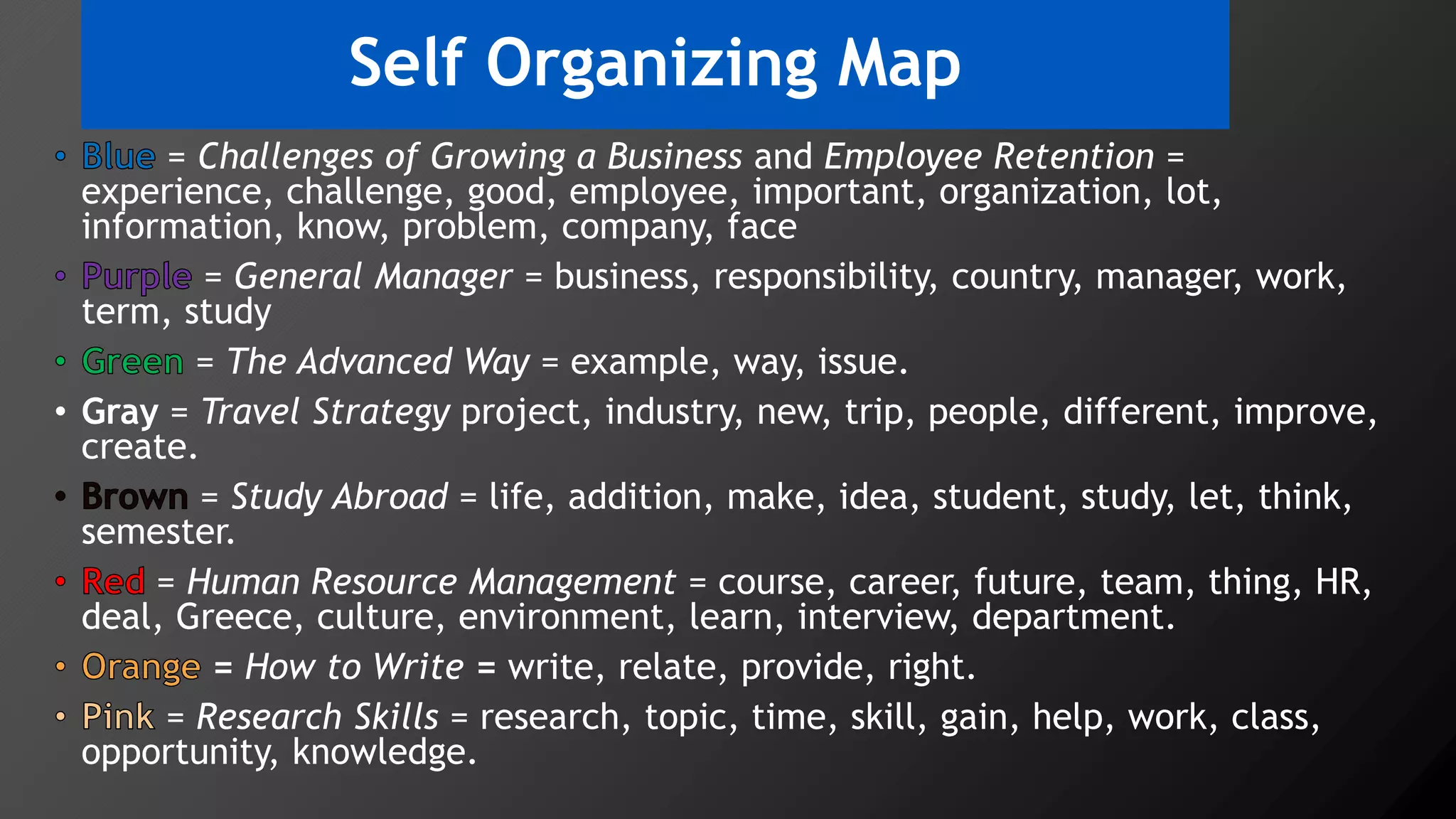
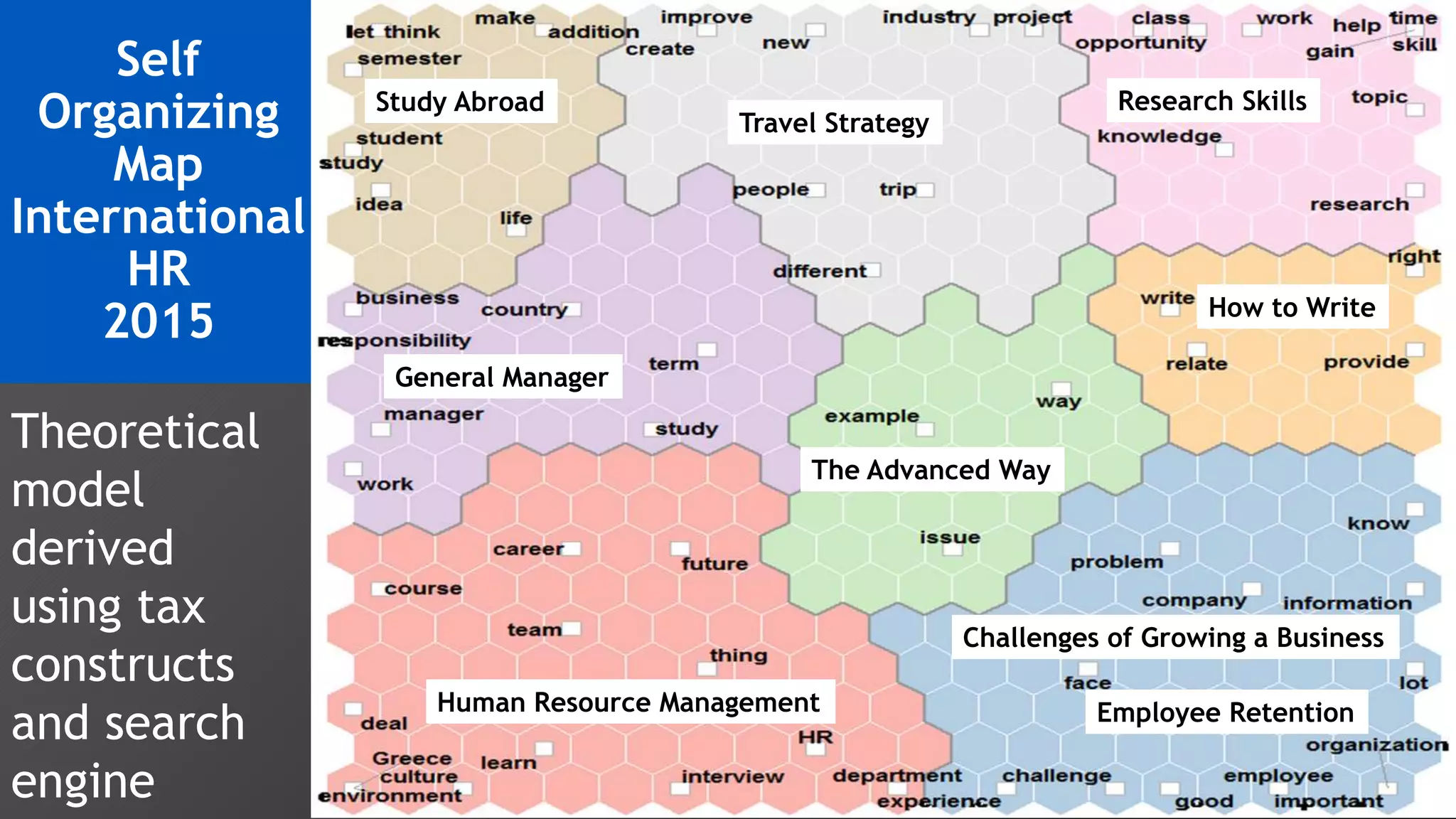
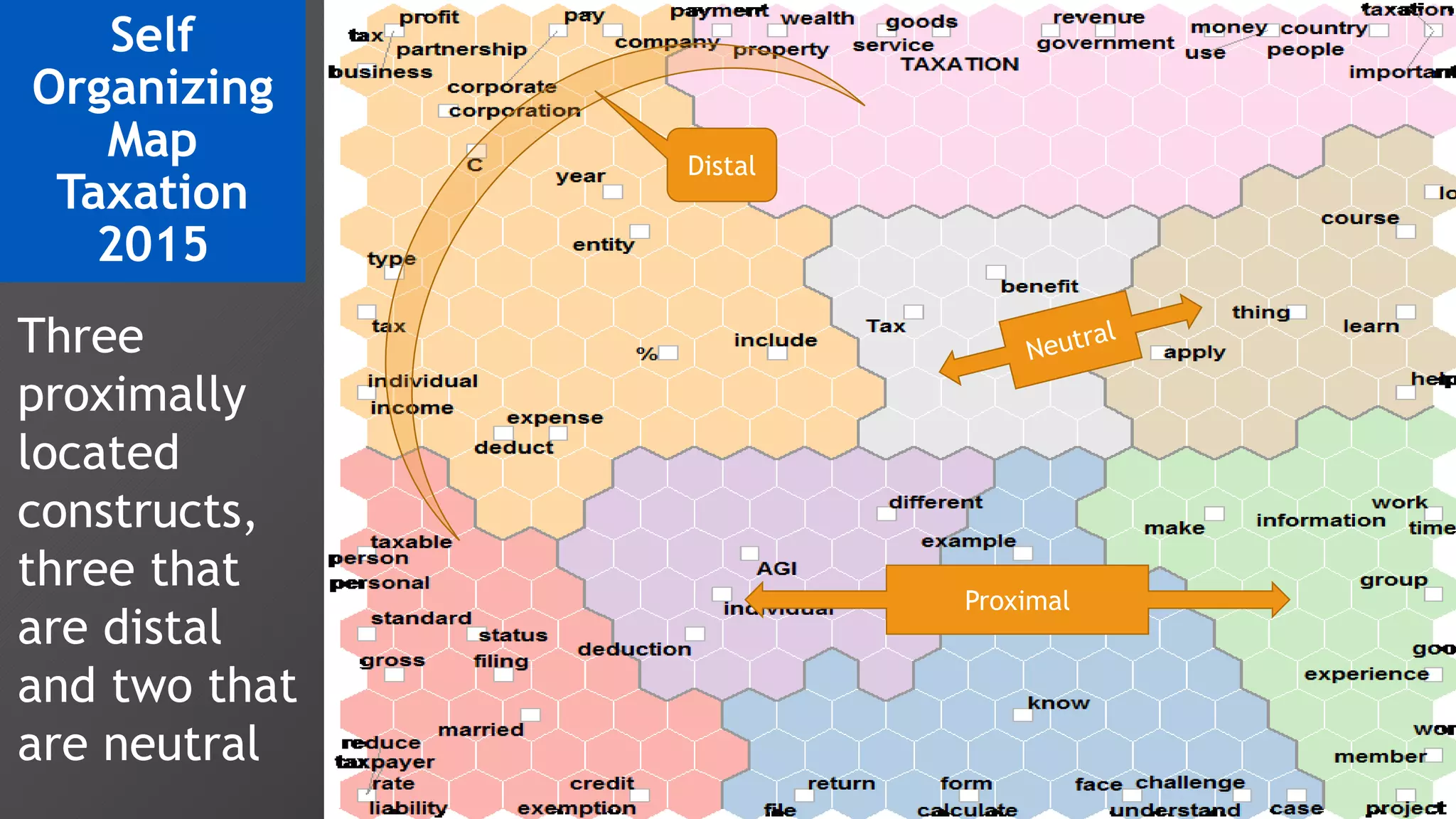
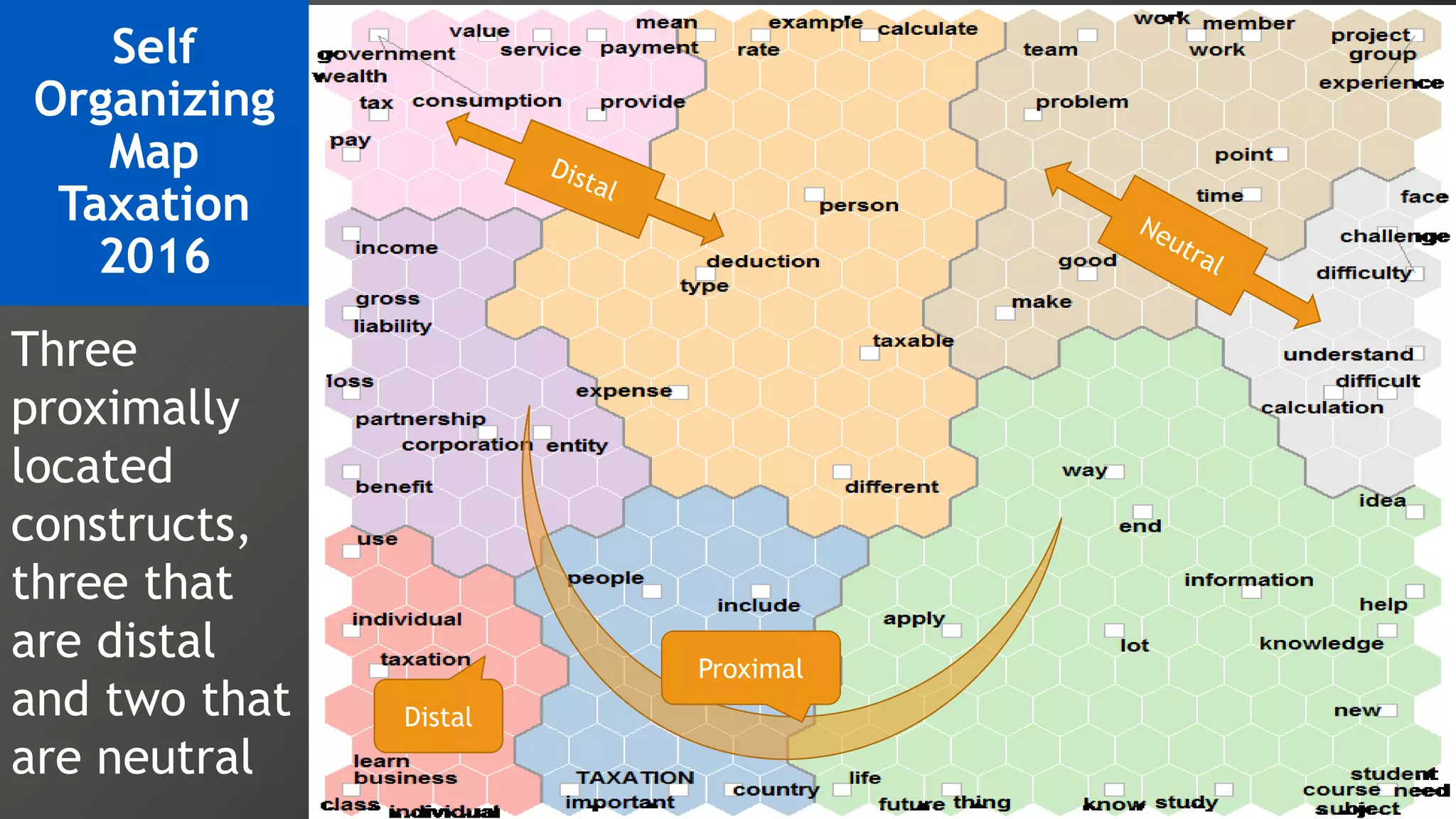
2) Key findings include identification of frequently used words and grouping of words into clusters related to topics like global mobility, workplace trends, and taxation.
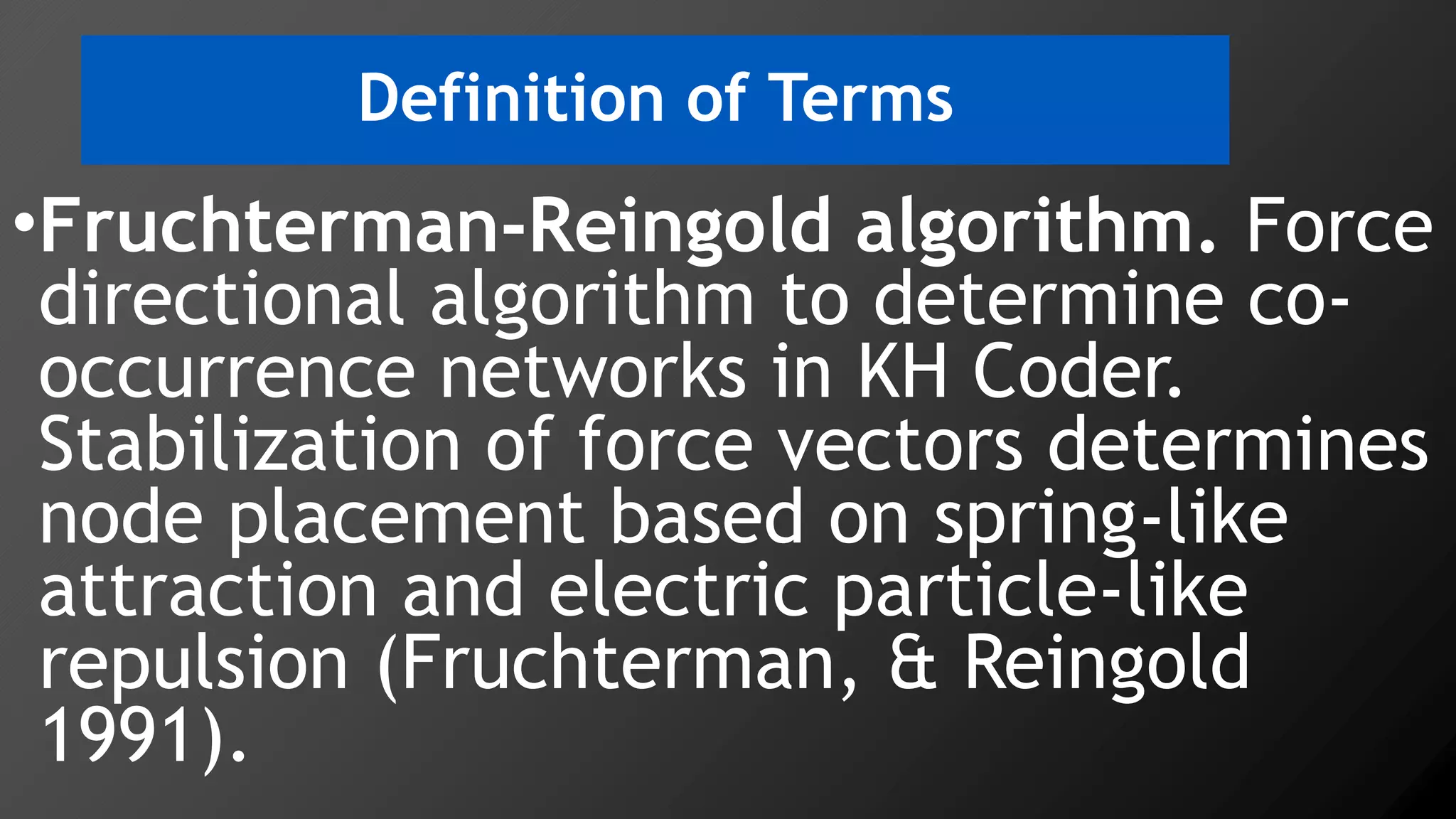
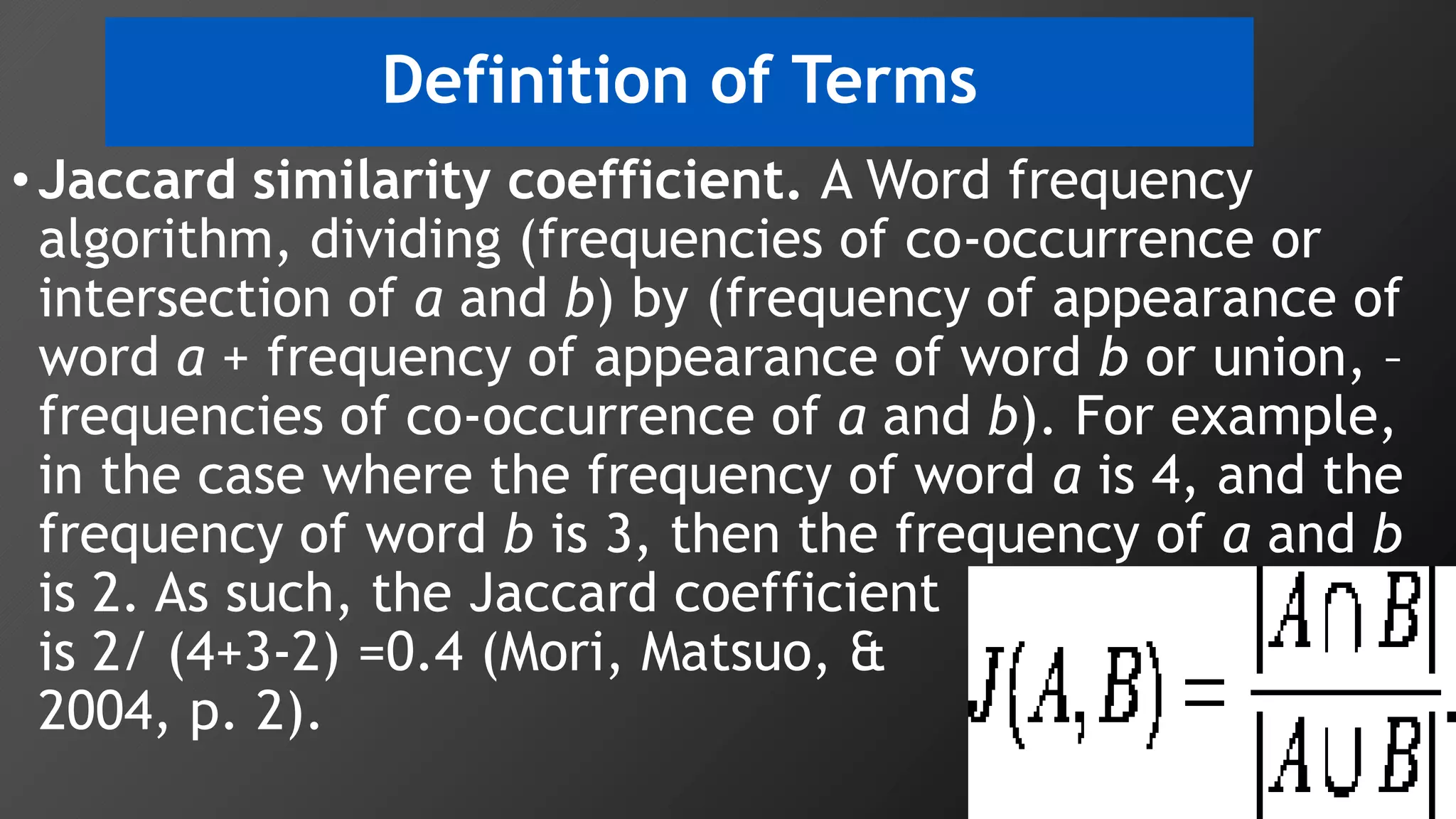
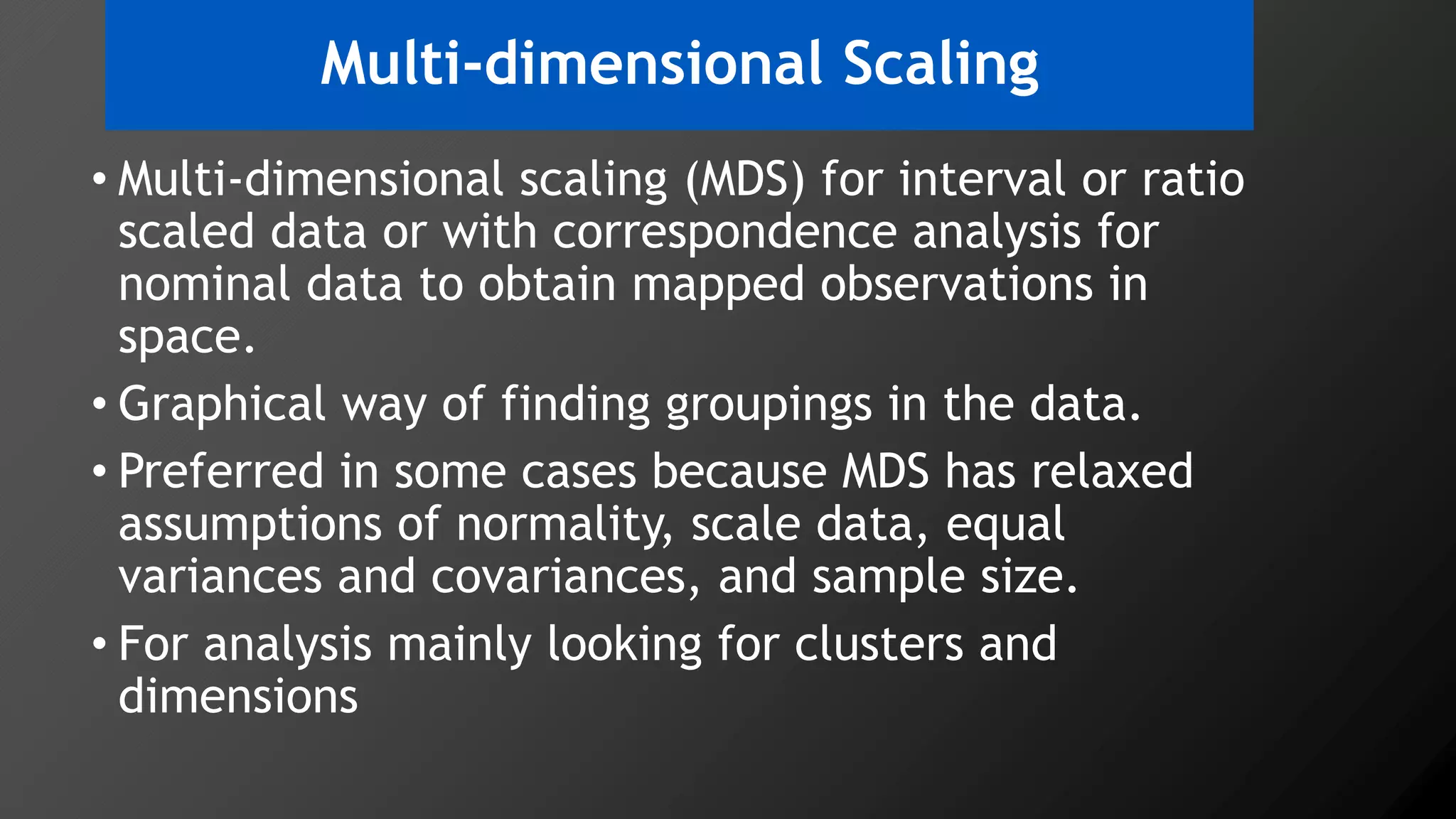
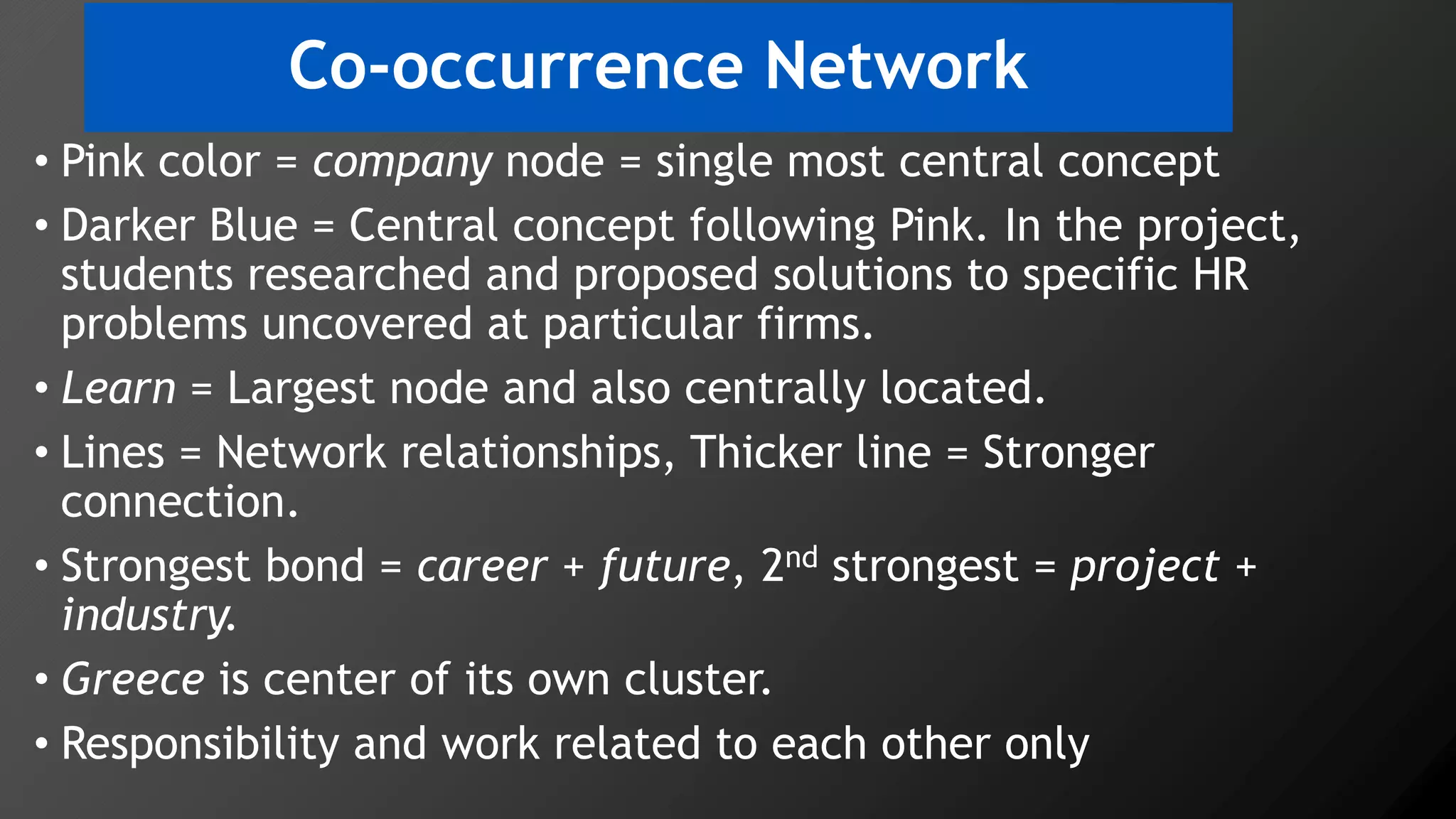
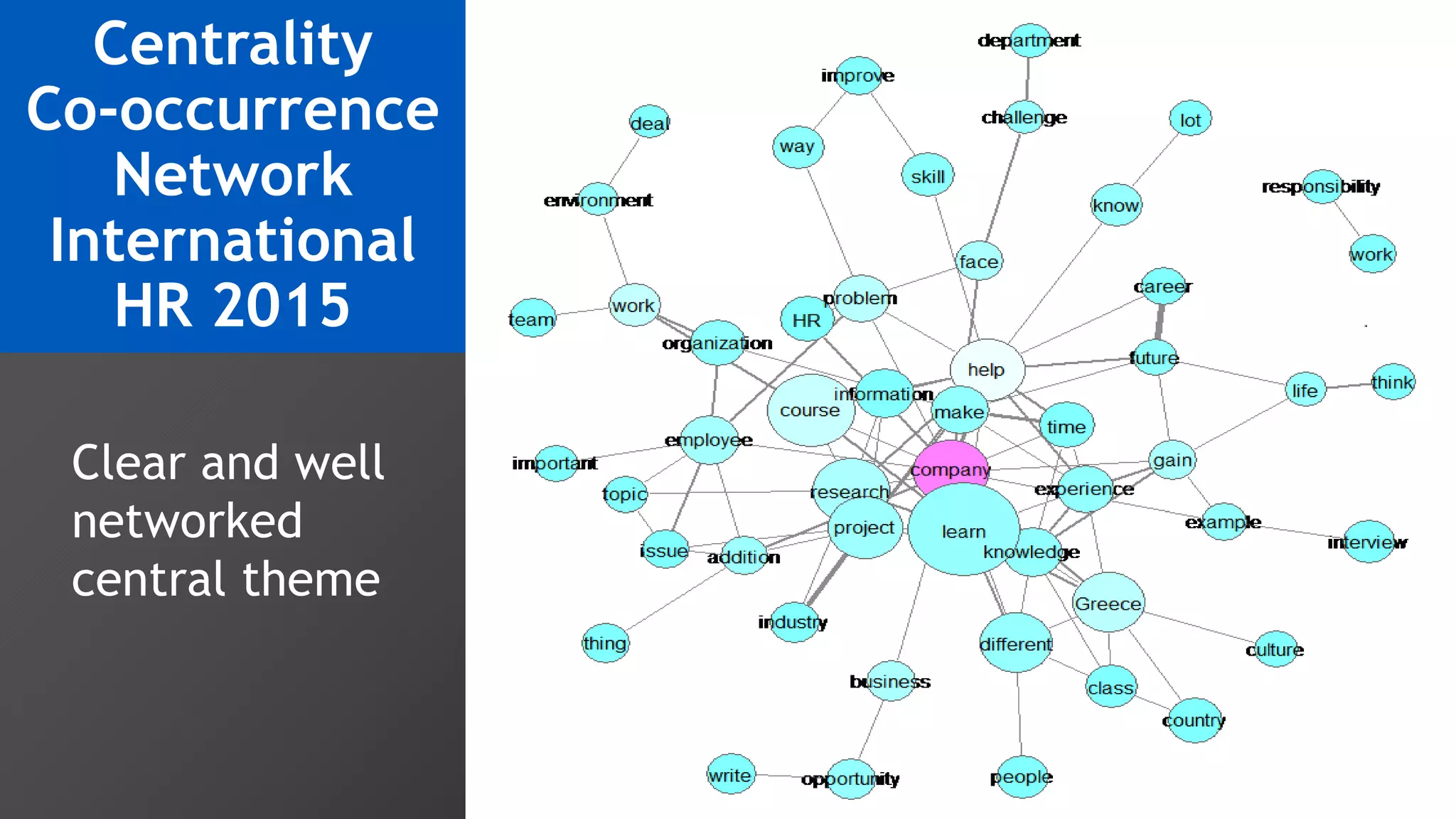
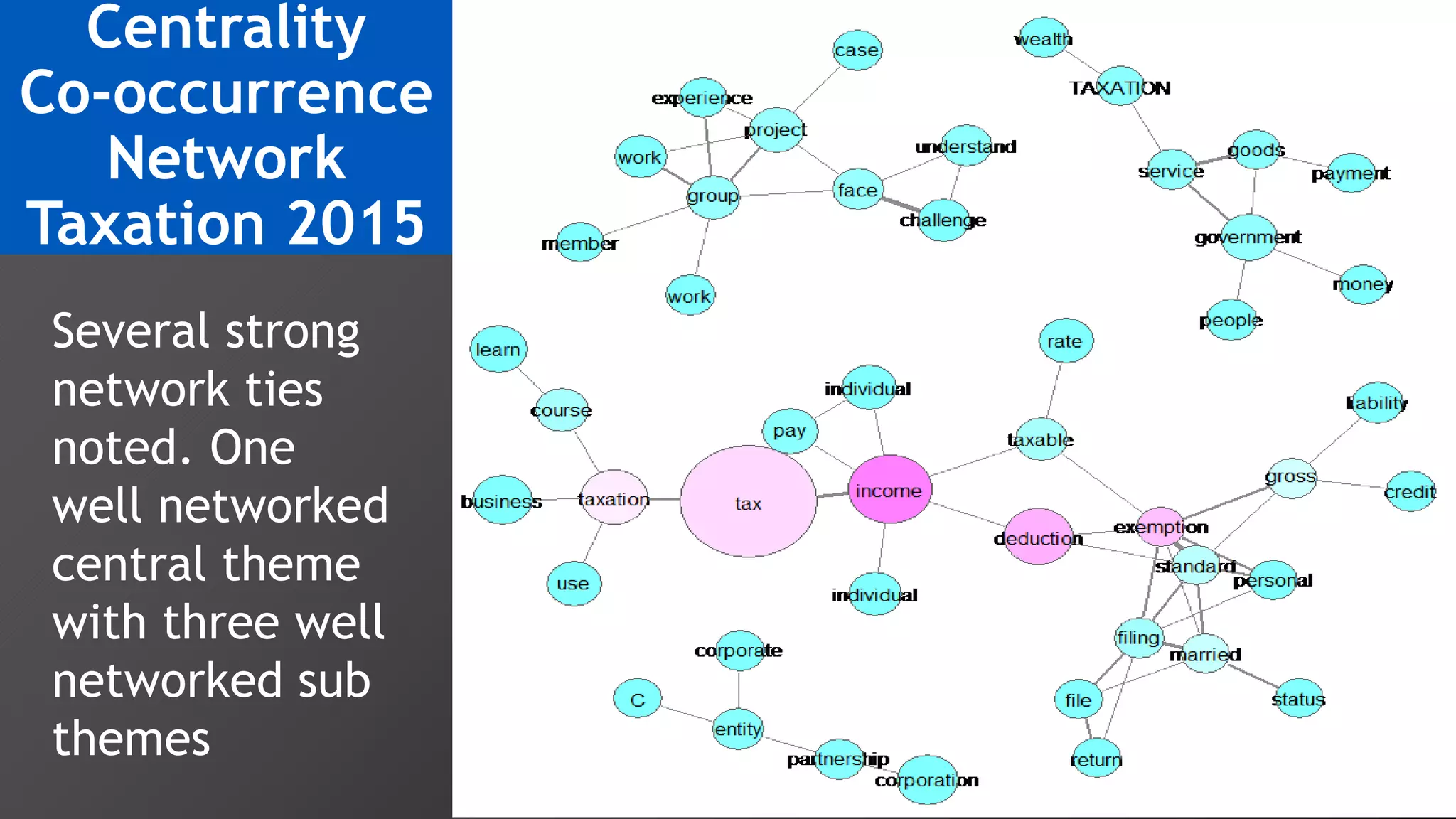
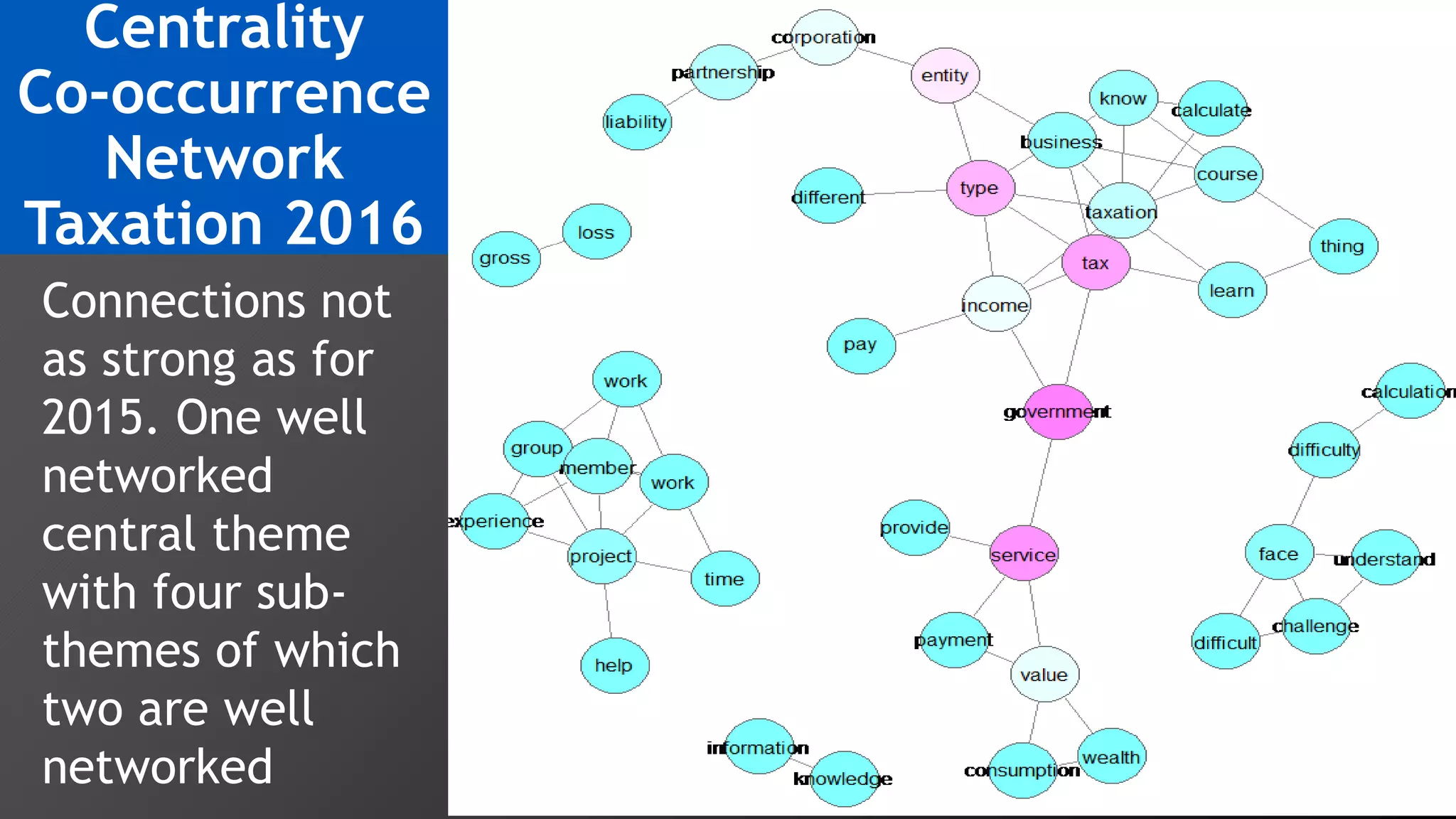
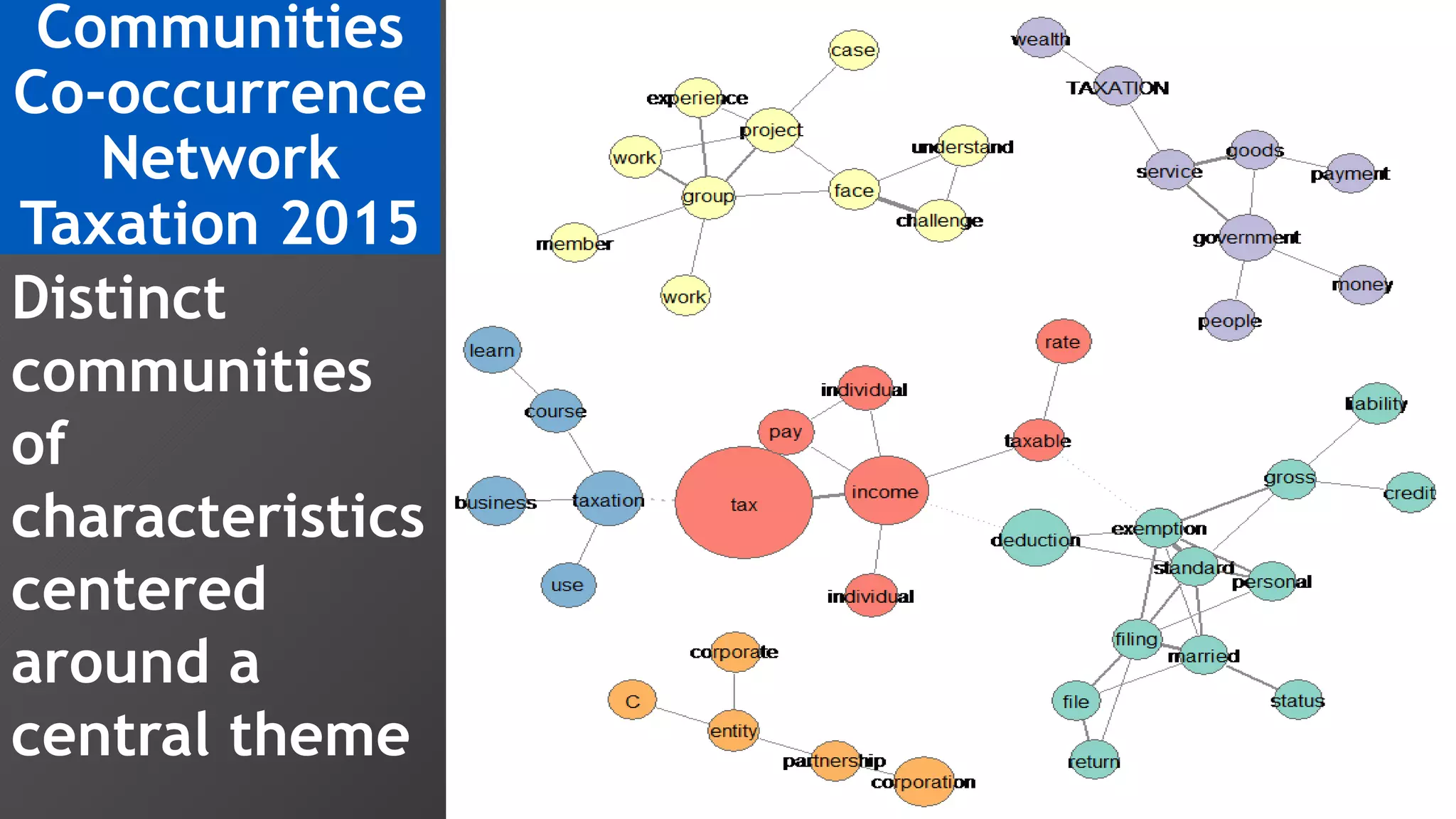
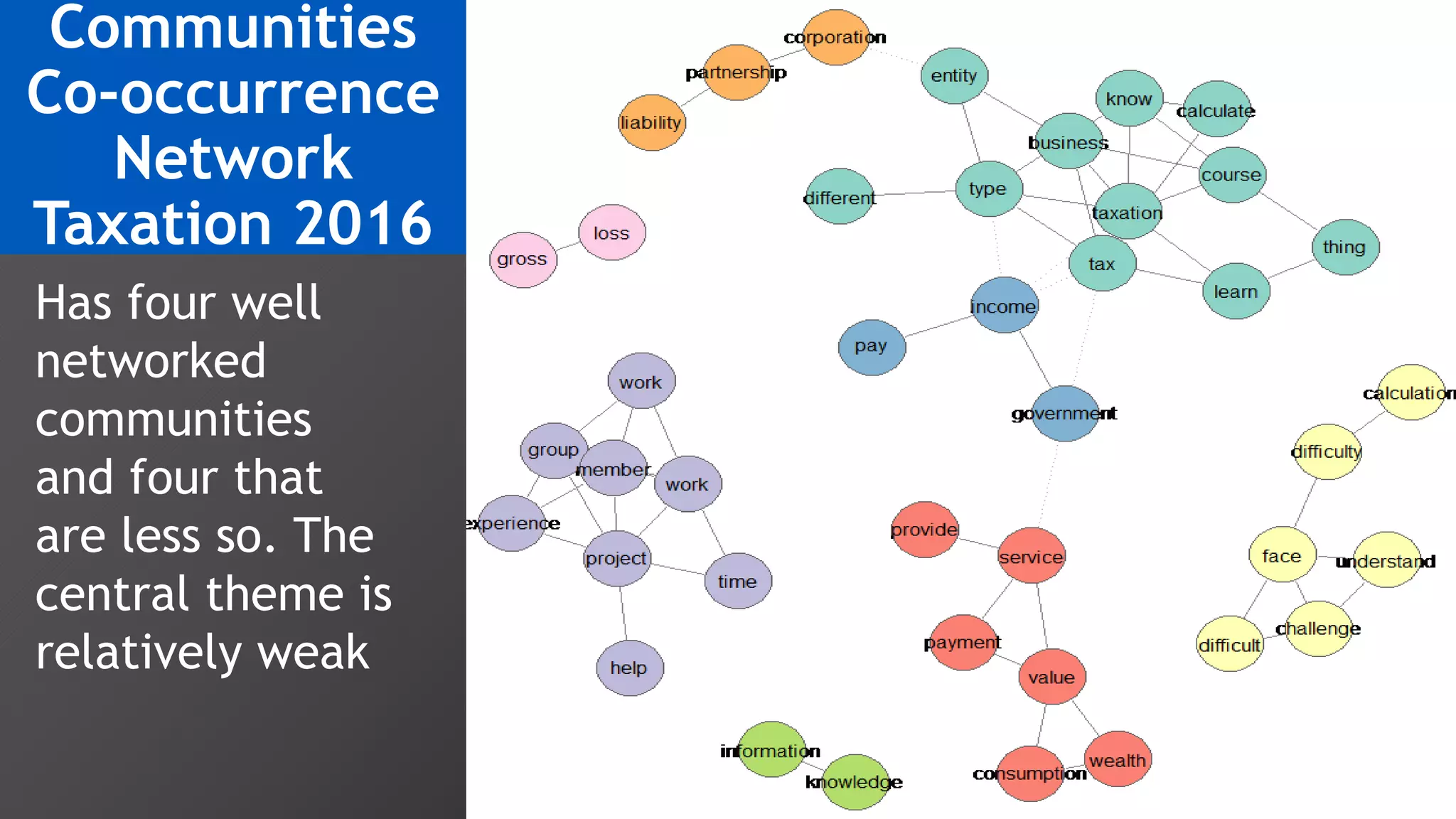
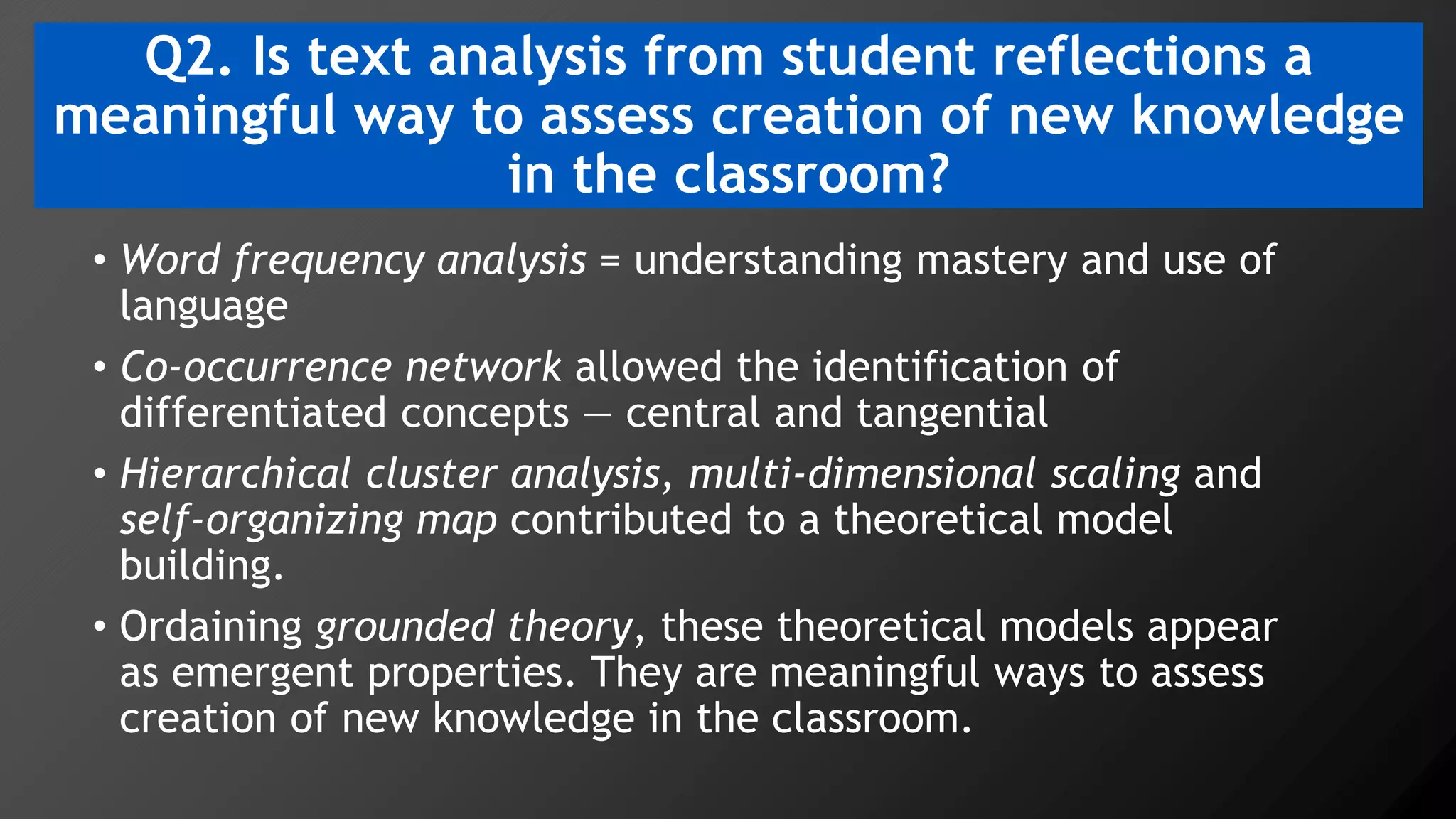
3) Multi-dimensional scaling and co-occurrence networks were used to visualize relationships between words and concepts within and between the two disciplines. The analysis aimed to explore how these techniques could assess knowledge creation in the classroom.