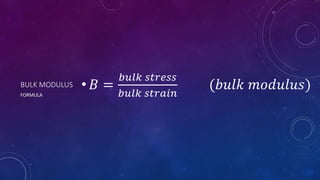The document discusses the bulk modulus, a numerical constant that describes the elastic properties of materials under uniform pressure, and explains how it measures a substance's resistance to volume changes. It provides formulas for calculating bulk modulus and compressibility and illustrates a practical application involving a hydraulic press with oil under increased pressure. The example demonstrates how to compute the decrease in volume using both bulk modulus and compressibility concepts.