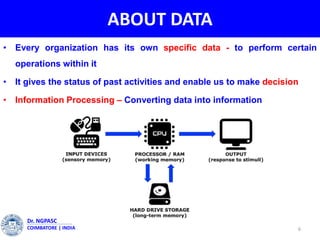
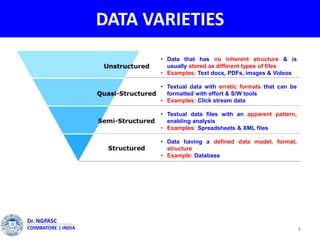
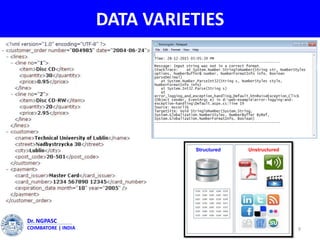
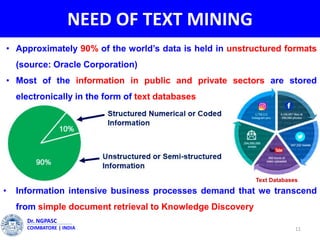
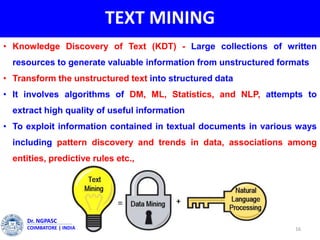
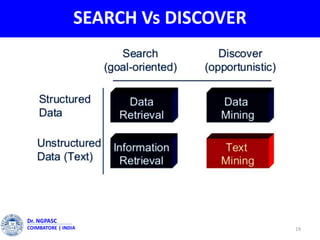
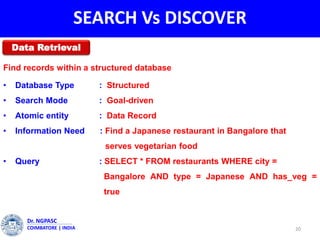
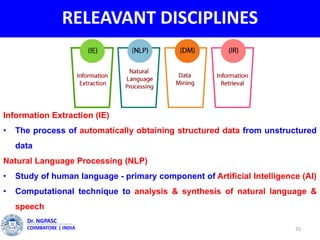
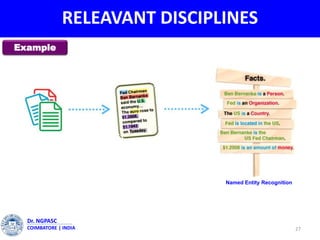
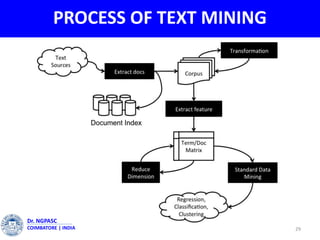
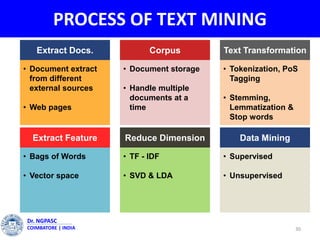
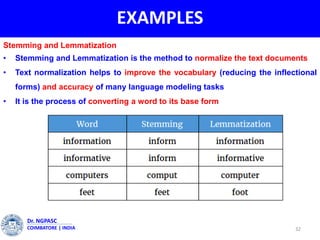
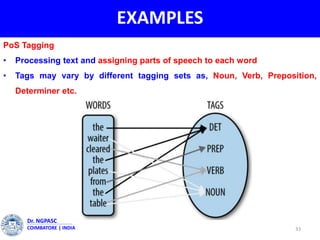
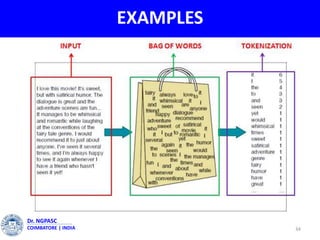
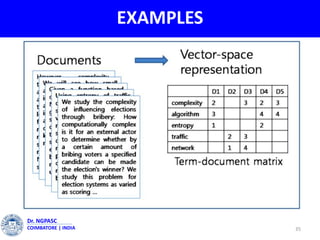
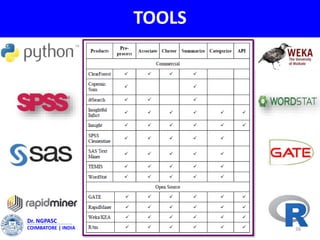
This document summarizes a webinar on text mining presented by Dr. A. Muthusamy. The webinar covered an introduction to data types and text mining, the need for text mining in analyzing large amounts of unstructured text data, the objectives and process of text mining, and applications and benefits of text mining such as knowledge discovery, predictive modeling, and information extraction. Challenges of text mining include overcoming database storage limits and handling natural language processing ambiguities.