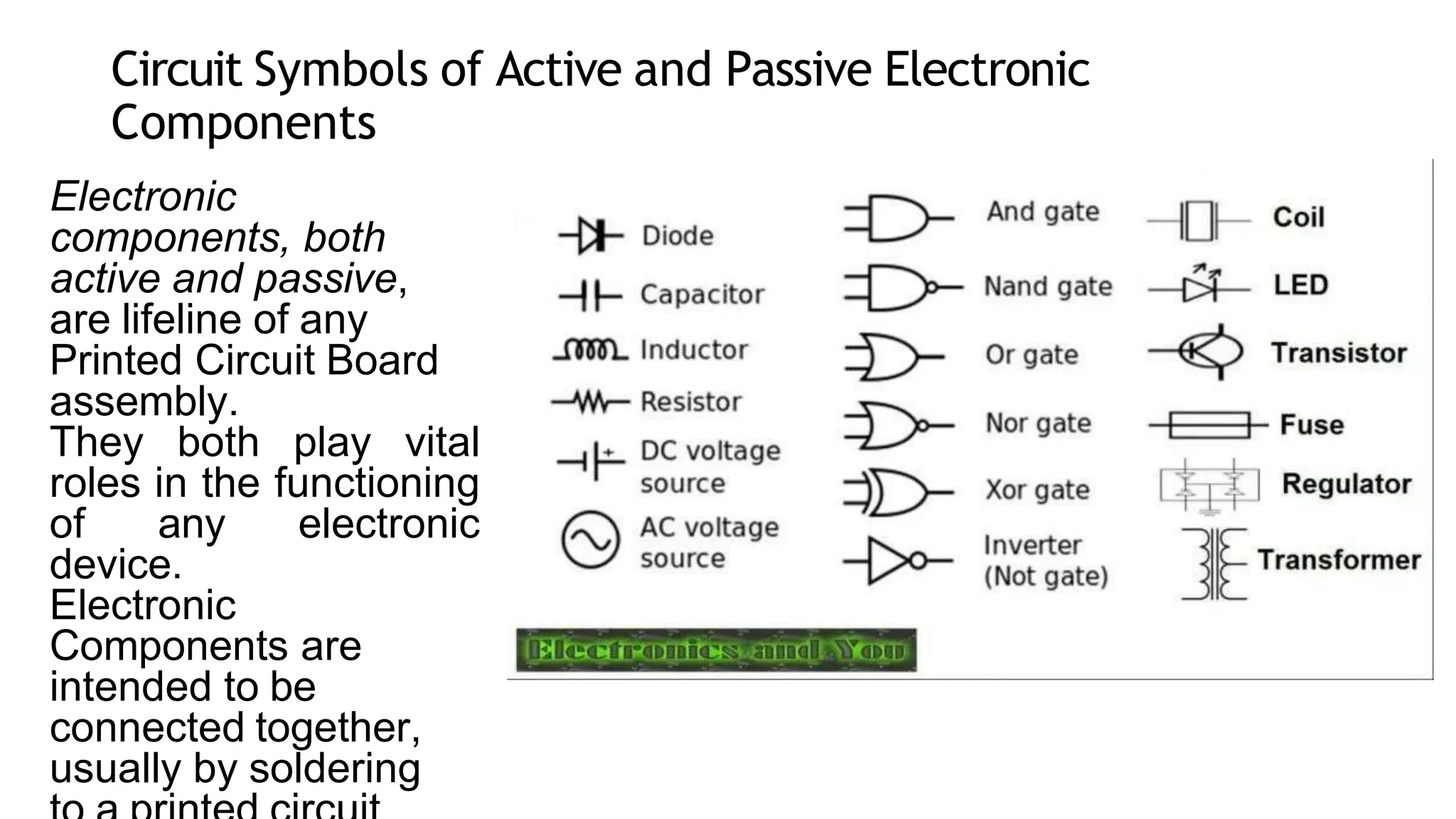
The document discusses passive electronic components, which do not control electric current with another signal, and includes examples like capacitors and resistors. It emphasizes the importance of both active and passive components in electronic devices and details various testing strategies, including dynamic, mechanical, and in-circuit testing. In-circuit testing is highlighted as a crucial method to identify manufacturing faults in printed circuit board assemblies using specialized testers and fixtures.