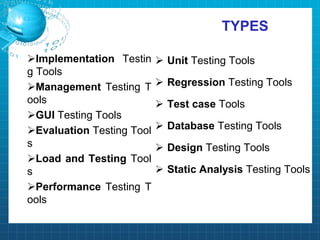
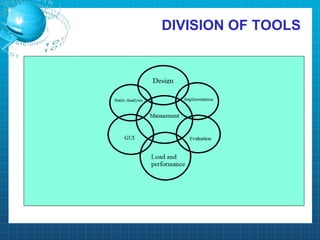
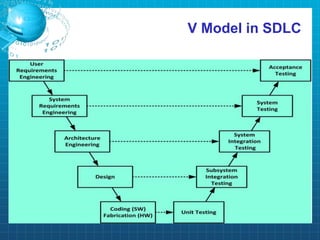
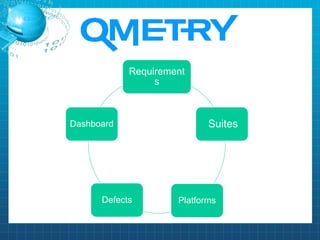
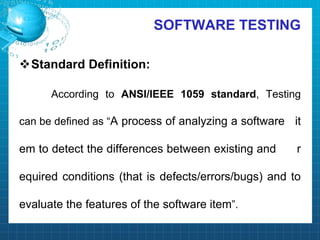
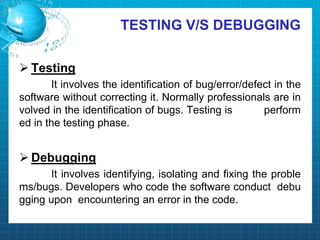
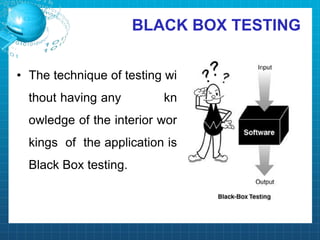
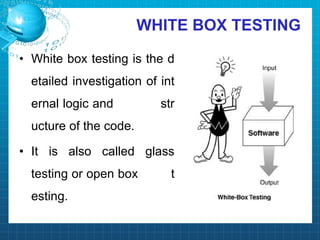
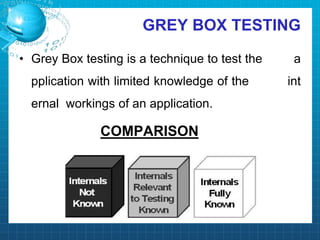
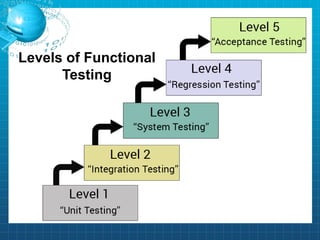
This document discusses software testing. It begins by introducing the group members - Hamza Wilayat, Ali Raza Saleem, and Hafiz Ali Raza. It then defines testing and differentiates it from debugging. It also discusses verification and validation. The main types of testing covered are black box, white box, and grey box testing. The document also discusses different levels of testing including unit, integration, system, regression, and acceptance testing. It covers functional testing and non-functional testing, specifically performance, portability, and security testing. Finally, it briefly introduces software testing tools.

















![NON-FUNCTIONAL TESTING cont..
• Portability Testing
• Tests Re-usability of software.
• Tests on Transferring the installed software.
• Security Testing
• Identify any Gaps from security point of view.
• Secures from unknown Vulnerability.
• Ensures Authentication and Availability.
• Remove Injections Flaws [if any].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwaretesting-180503210817/85/Software-Testing-levels-Techniques-Tools-24-320.jpg)