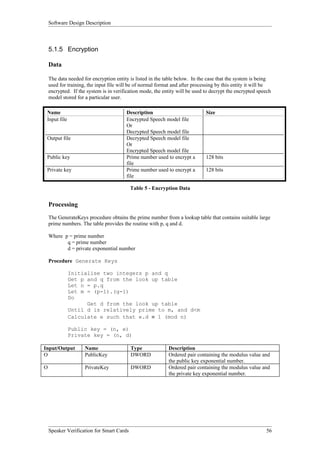
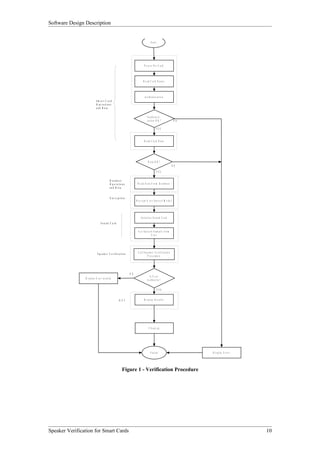
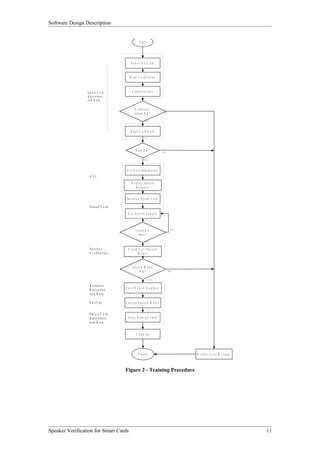
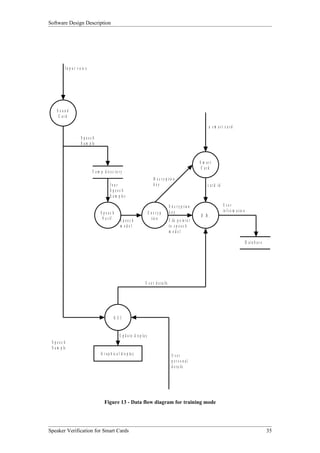
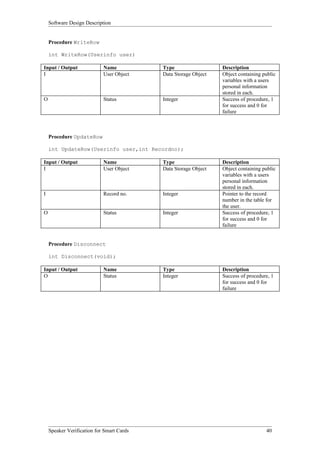
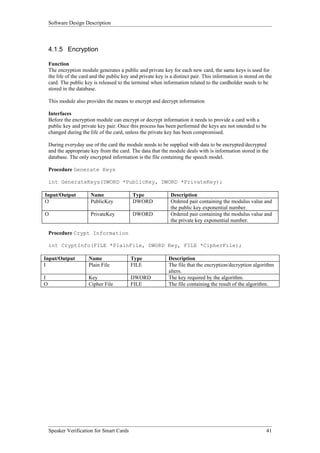
The Smart Card Operations entity provides the functionality to interface with smart cards. As shown in Figure 3, it has two subordinate entities - Initialization and Card Functionality. Initialization handles turning on the reader and card. Card Functionality contains functions to read from, write to, and authenticate smart cards.






























![Software Design Description
4.1.6 Sound card
Function
The functions of this entity include:
• Initialising the sound card
• Retrieving data samples from the sound card
Initialisation of the sound card involves telling the sound card that we require its services. We then
specify the following recording parameters:
• Samples rate ( The number of samples to be taken from the microphone per second )
• Sampling accuracy
• Stereo/Mono recording
• Number of buffers
Interfaces
The entity “Sound Card” and its methods will be encapsulated within a class in the program.
This entity interacts with other entities through the three methods:
• InitSound
• InitSoundInterrupts
• GetSpeechSample
The method InitSound has no parameters, it simply returns a success/fail result. This will be ‘1’ for
success and ‘0’ for failure.
The InitSoundInterrupts method also has no parameters and it also returns a success/fail result. It
returns ‘1’ for success and ‘0’ for failure.
The method GetSpeechSample has one parameter. This will be an array of fixed length and on
completion of the method it will contain the last speech sample recorded by the sound card. The
method will also return a success/fail result. This will be ‘1’ for success and ‘0’ for failure.
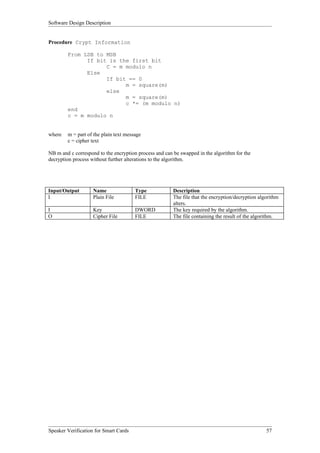
Procedure InitSound
int InitSound(void);
Input/Output Name Type Description
O Procedure int Returns 1 for success and 0 for failure
Success
Procedure InitSoundInterrupts
int InitSoundInterrupts(void);
Input/Output Name Type Description
O Procedure int Returns 1 for success and 0 for failure
Success
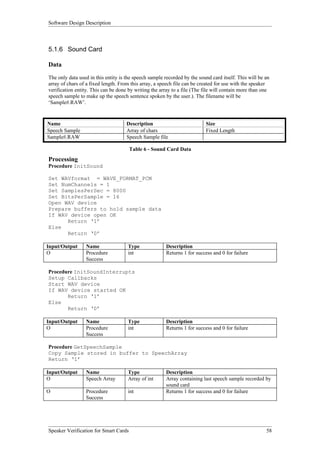
Procedure GetSpeechSample
int GetSpeechSample(int Speech[]);
Input/Output Name Type Description
O Speech Array Array of int Array containing last speech sample recorded by
sound card
O Procedure int Returns 1 for success and 0 for failure
Success
Speaker Verification for Smart Cards 42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/test24467/85/test2-42-320.jpg)

![Software Design Description
4.1.8 Speaker Verification
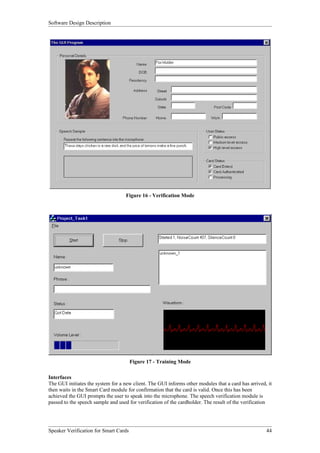
Function
This entity implements the speaker verification procedures/algorithms by comparing a user speech
model with a speech sample. It then returns a success/fail result.
This entity also has the ability to create user speech models. It does this by analysing a number of
speech samples recorded by the user, and extracting features from these speech samples. It then creates
a speech model of that user to be used in the verification process.
Interfaces
The entity “Speaker Verification” and its methods will be encapsulated within a class in the program.
This entity interacts with other entities through the two methods:
• TrainSpkrModel
Procedure TrainSpkrModel
int TrainSpkrModel(char *spkrID, char *allFileNames[],
int numFiles );
Input/Output Variable Name Type Description
I spkrID char * The name of the user
I allFileNames char * [] Array of filenames
containing the speech
samples
I numFiles int The number of filenames
listed in the above array
O Return Value int The method returns a
success/fail result:
‘1’ for success
‘0’ for failure
Upon success, this method creates a user speech model. The speech model is stored in a file called
“UserName.HMM”
• SpkrVerif
The function prototype for this method is as follows:
Procedure SpkrVerif
int SpkrVerif( char *fileName, char *spkrID );
Input/Output Variable Name Type Description
I fileName char * The name of the file
containing the speech
sample
I spkrID char * The name of the user
O Return Value int The method returns a
success/fail result:
‘1’ for success
‘0’ for failure
Speaker Verification for Smart Cards 46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/test24467/85/test2-46-320.jpg)