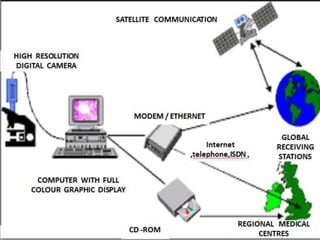
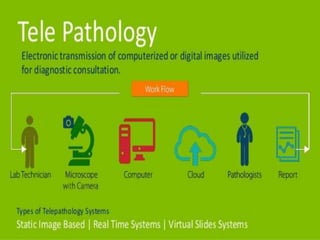
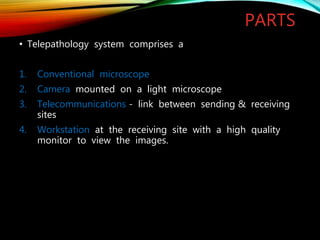
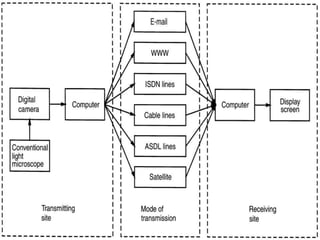
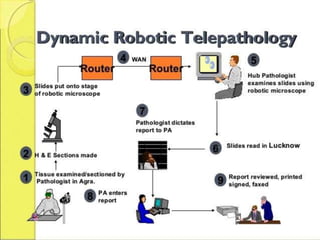
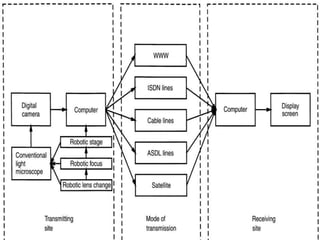
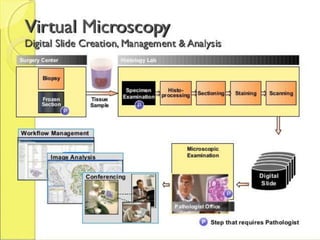
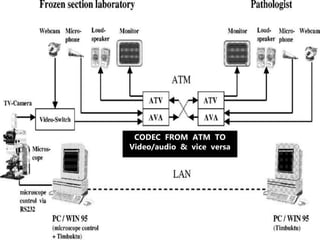
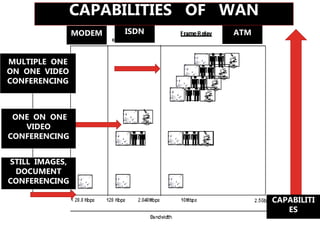
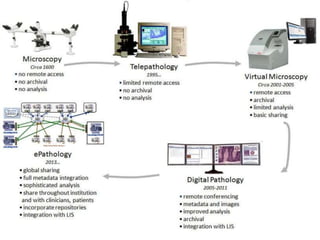
Telepathology involves the practice of pathology at a distance using digital imaging technology. There are three main types: static telepathology which uses stored images, robotic interactive pathology which allows remote control of a microscope in real-time, and virtual slide telepathology which uses high resolution whole slide imaging. The future of telepathology depends on continued improvements in digital imaging quality and pathologist skills in virtual microscopy to match conventional diagnosis under a microscope.