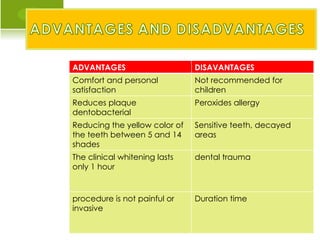
This document summarizes dental whitening materials and procedures. It discusses the intrinsic and extrinsic causes of tooth discoloration and summarizes ancient practices and modern perceptions of tooth whitening. Methods described include take-home whitening trays using carbamide or hydrogen peroxide gels or in-office whitening using higher concentration hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide gels applied with a light activator. Advantages include comfort and satisfaction while disadvantages include potential tooth sensitivity. Popular brand names and products are also mentioned.





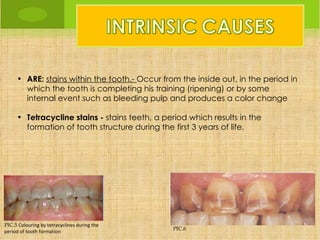



![In home:
•Molds take the patient's mouth and is made in a ferrule (flexible plastic
structure) which conform to the shape of the teeth. One for the upper teeth and
one for the lower teeth.
•They are transparent, do not bother
•It gives the patient the two braces and whitening kit containing syringes with
the bleaching product.
•Every night for 20-30 days, after brushing a small amount is deposited in the
splint, at the height of each teeth whitening, and put in mouth for 3 hours.
•After braces are removed from the mouth and cleaned with cold water to
remove residual product and inactive.
PIC. 17 whitening Gel[peroxide PIC.18 splint
hydrogen or carbamide]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expo-blanqueamentoseningles1-120507200954-phpapp02/85/teeth-whitening-13-320.jpg)


![About 15 tone, scale is easily
defined according to the
quality that
distinguish between families
of color (which is the same as
the wavelength of the PIC. 19 arranged according to hue and chroma
Light reflected from the
teeth). Chromatic color is pigmented
4 tones: 4 levels of chroma for each hue (1, 2, 3.4)
A (brown – reddish), A1, A2, A3, A4, where A1 is less saturated than
B (orange – yellowish), A4.
C (gray – greenish), y
D (gray –rose)
PIC. 20 Vita sorted by value [LIGHT-DARK AND CLEAR]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expo-blanqueamentoseningles1-120507200954-phpapp02/85/teeth-whitening-16-320.jpg)