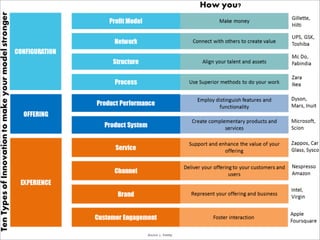
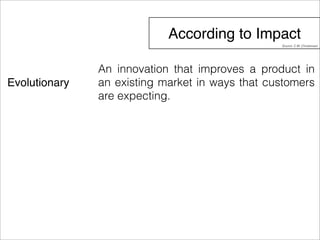
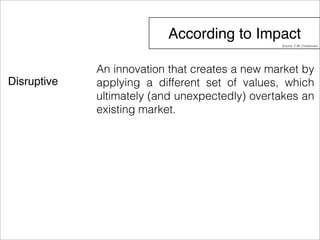
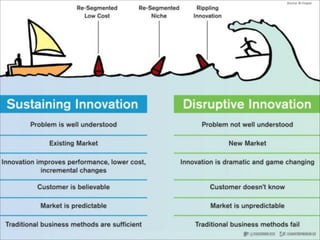
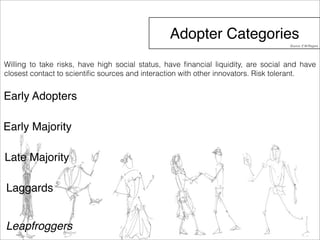
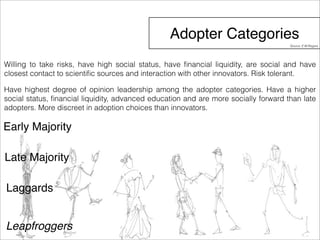
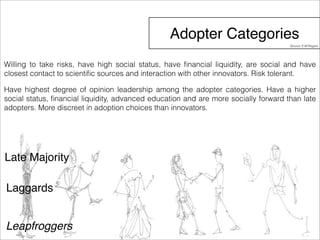
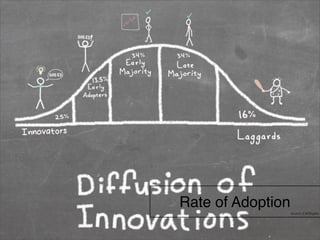
The document outlines a technology and innovation management course covering key topics such as types of innovation, including sustaining, evolutionary, revolutionary, and disruptive innovations. It describes the process of diffusion of innovation, detailing how new ideas spread, the roles of adopters, and the various stages involved in the decision-making process for adoption. The document further categorizes adopters based on their willingness to adopt innovations, highlighting characteristics of innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, laggards, and leapfroggers.