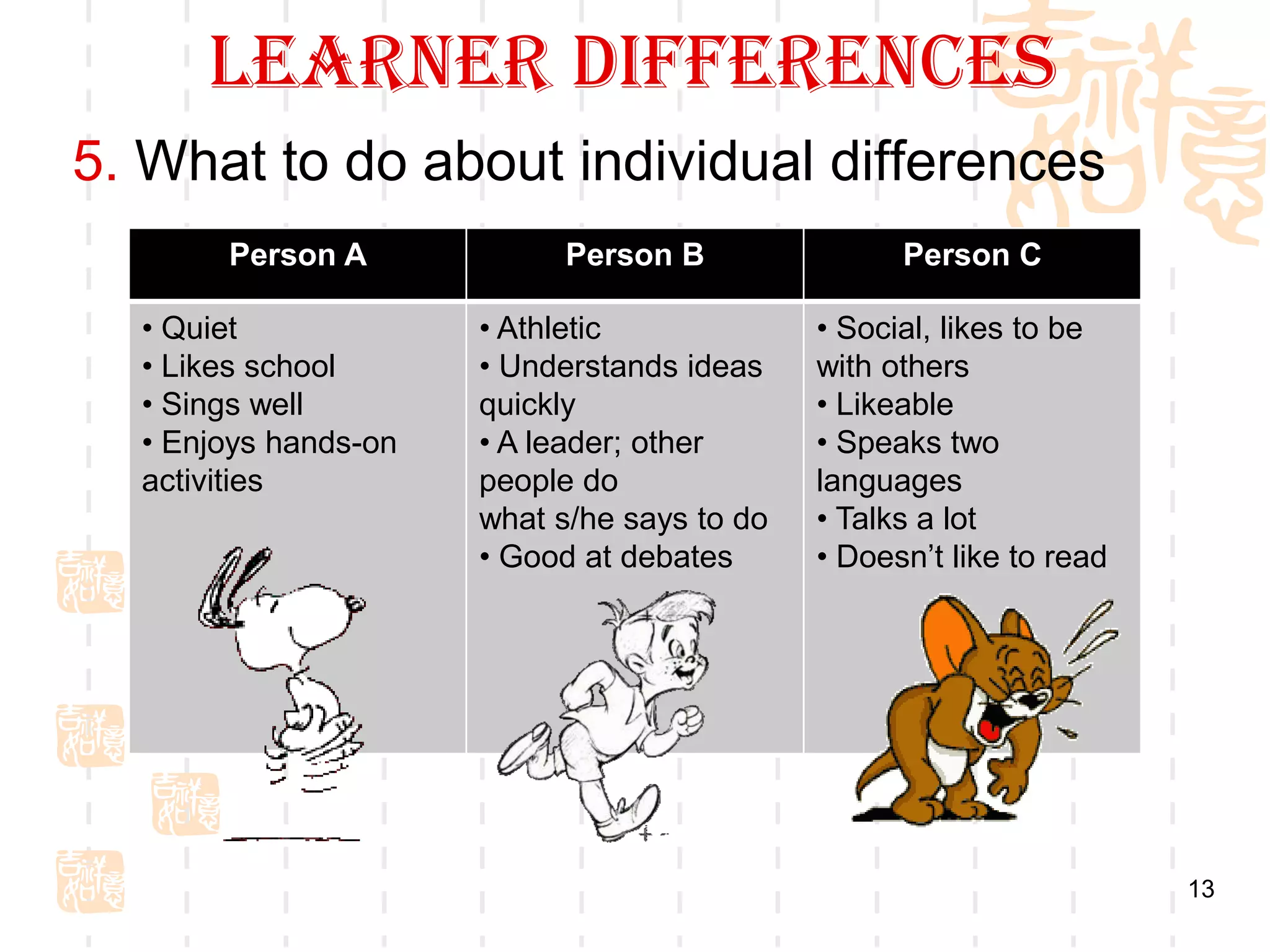
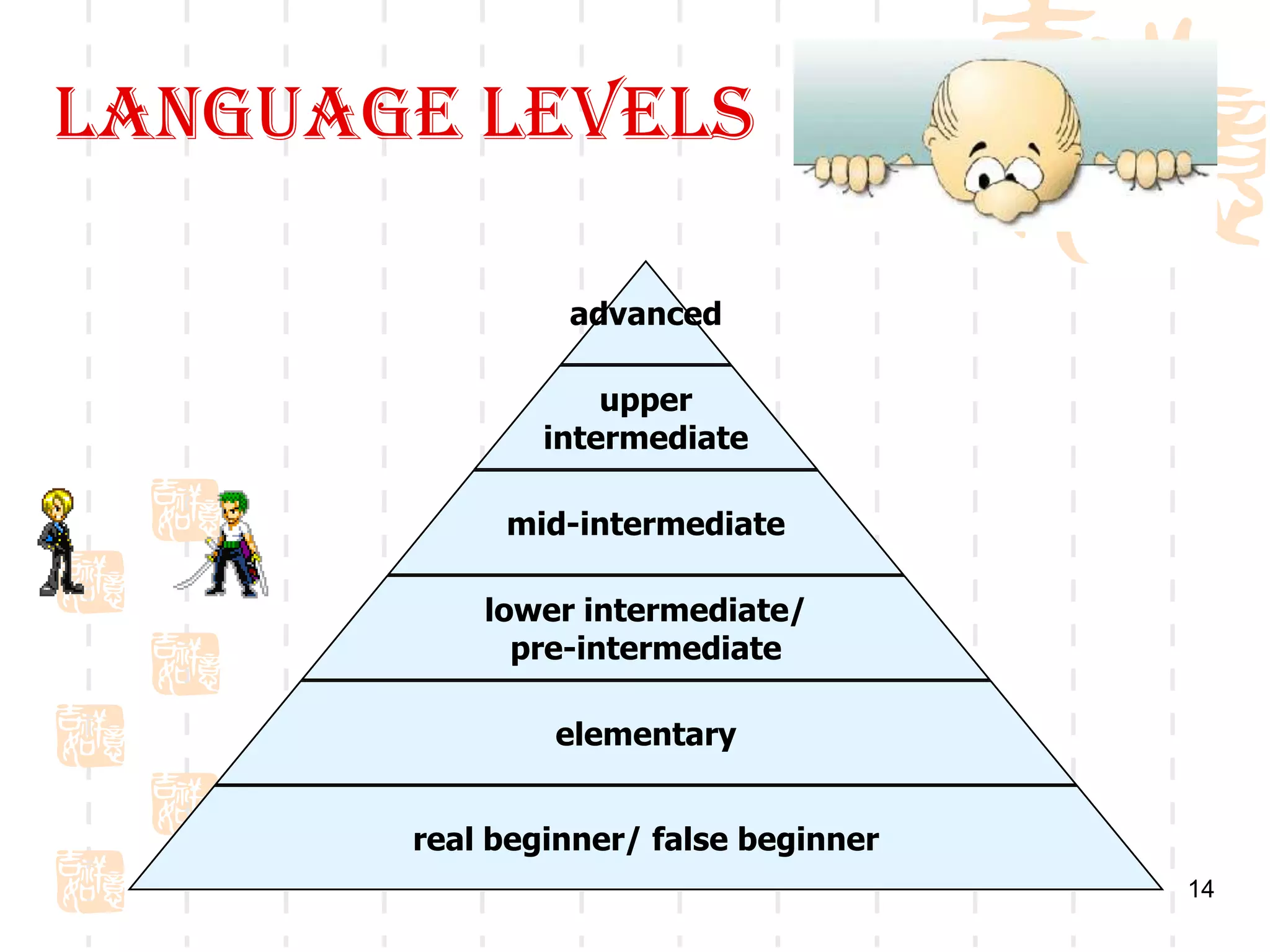
The document describes different types of language learners based on age, aptitude, learning style, and motivation. It notes that young children learn indirectly through interaction, adolescents can lack motivation but seek identity, and adults have life experiences to draw from. Learner differences include aptitude, characteristics like tolerance for ambiguity, and learning styles. Children are unique learners that may excel in areas like music, athletics, or social skills. Language levels range from beginner to advanced, and motivation can come from goals, society, relationships, or curiosity.