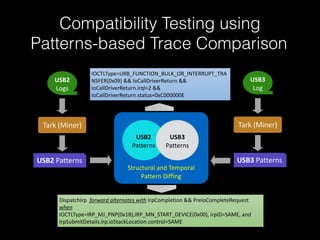
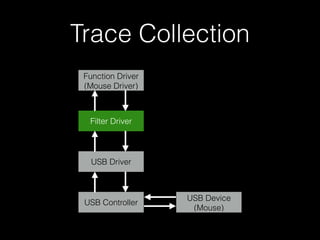
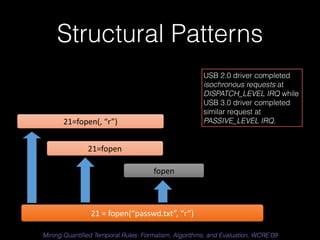
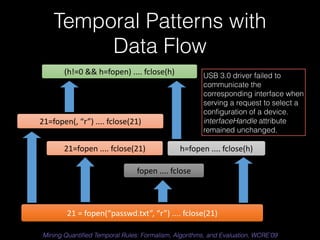
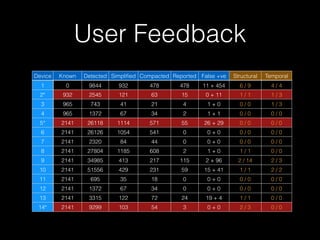
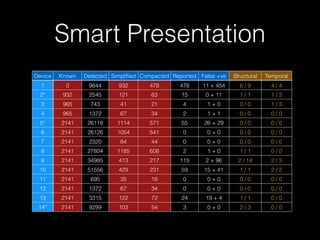
The document discusses a patterns-based trace comparison approach for compatibility testing, focusing on how USB drivers behave across different versions of Windows. It highlights challenges such as semantic incompatibilities and the complexity of regression testing. Key takeaways include the effectiveness of using structural and temporal patterns for identifying compatibility issues and the importance of domain knowledge in testing practices.