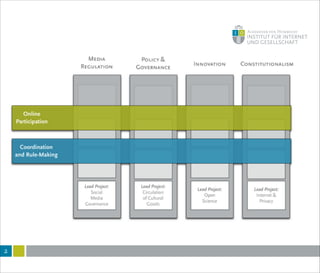
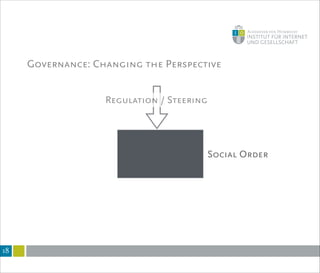
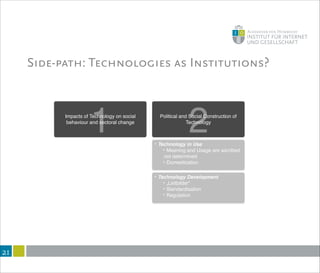
This document summarizes a lecture on internet governance and rule-making. It discusses how definitions of internet governance have evolved from a focus on policy organizations and steering to recognize decentralized and heterogeneous governance arrangements. Governance is examined through different disciplinary lenses and as a process of coordination rather than just regulation. New perspectives are needed that consider informal norms, discourses and framings, and how technologies structure communication and regulation. Internet governance involves coordination among many actors through diverse rules and mechanisms beyond just institutions.

















































![!33
!
!
Pictures
Bundestag: Times, CC-BY-SA-3.0-2.5-2.0-1.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia
Commons. URL: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Deutscher_Bundestag_Plenarsaal_Seitenansicht.jpg
DSDS, American Idol, Indian Idol: Pressematerial der Sender.
Instagram, iTunes: Eigene Screenshots der Websites.
Küche: Cornelius Jacobsen (Riksarkivet, National Archives of Norway. Archivnr: Pa1528_ua2_012. URL: http://
www.flickr.com/photos/national_archives_of_norway/6475926375/)
Laurel Hardy: Dougal McGuire CC-BY-SA 2.0. URL: http://www.flickr.com/photos/tom-margie/1535543995/)
Christian Katzenbach
!
Alexander von Humboldt Institute for Internet
and Society
Berlin, Germany
katzenbach@hiig.de
Visit our Internet Policy Review under
http://policyreview.info !
for short-form papers on !
Internet Governance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tampere-2014-guest-lecture-140328075441-phpapp01/85/Internet-Governance-beyond-Institutions-Rethinking-Rule-Making-in-the-Digital-53-320.jpg)