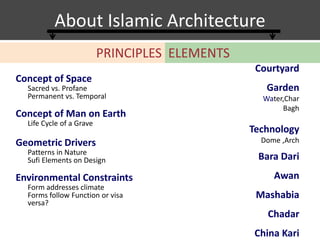
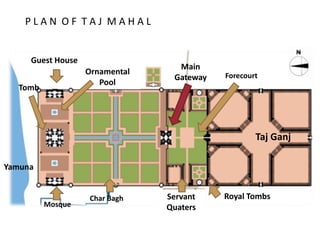
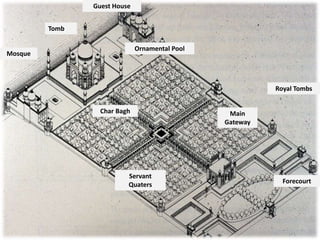
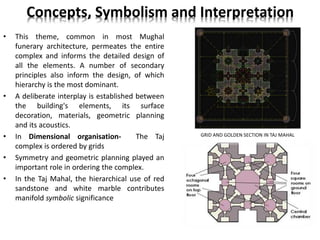
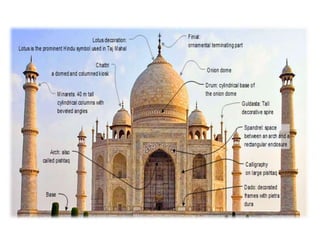
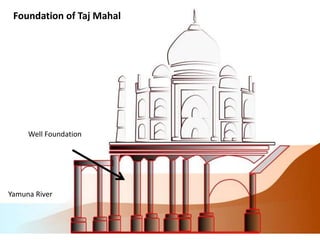
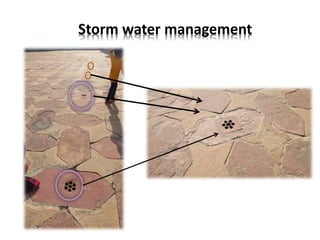
The document provides information about the Taj Mahal in Agra, India. It discusses the history and construction of the mausoleum, which was built between 1631-1653 by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan as the final resting place for his wife Mumtaz Mahal. The Taj Mahal represents the finest example of Mughal architecture, incorporating Islamic architectural elements and principles of symmetry, geometry, and hierarchy. It consists of several elements organized around a central courtyard, including the main tomb chamber, mosque, guest house, and gardens along the Yamuna River.