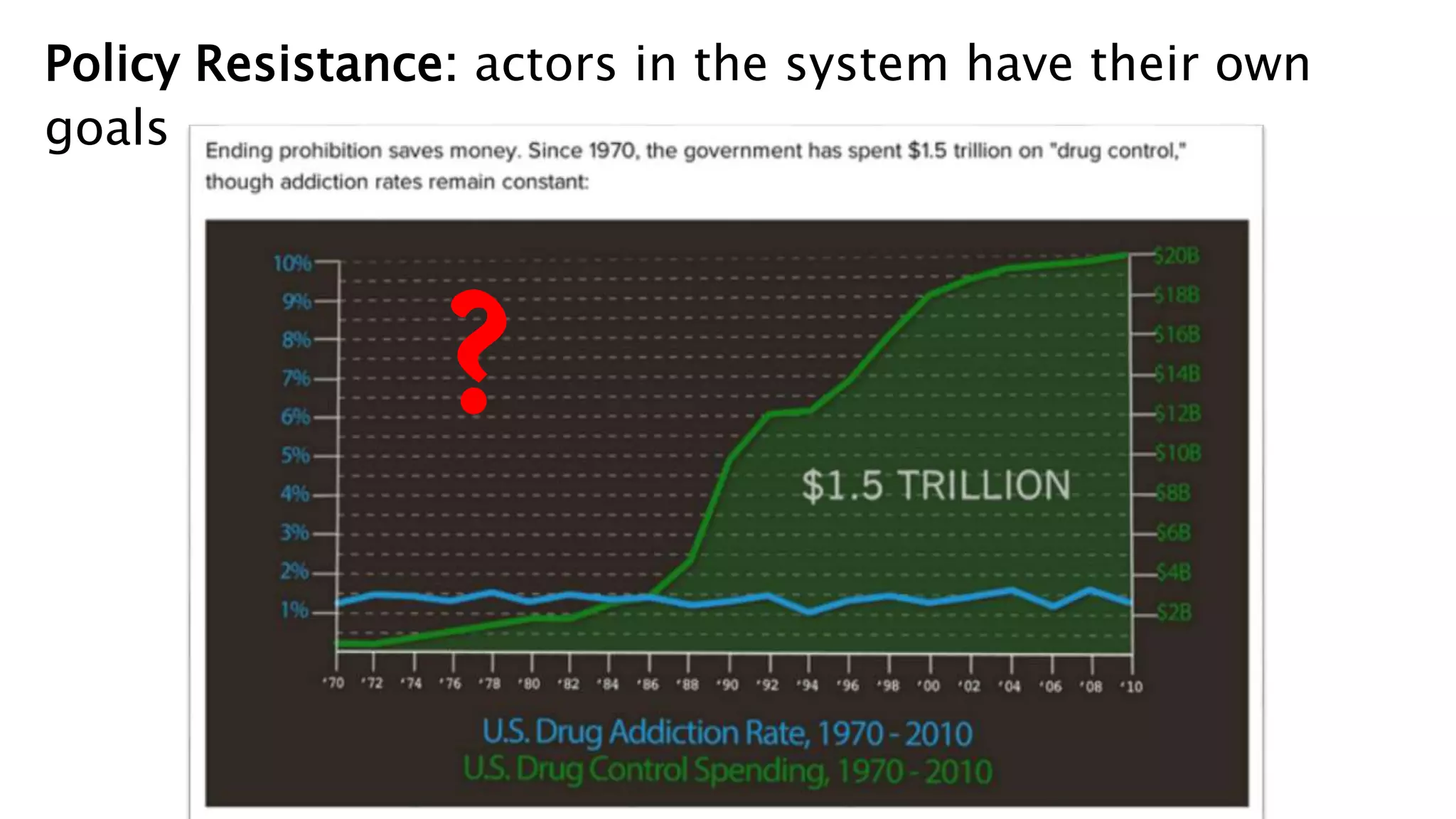
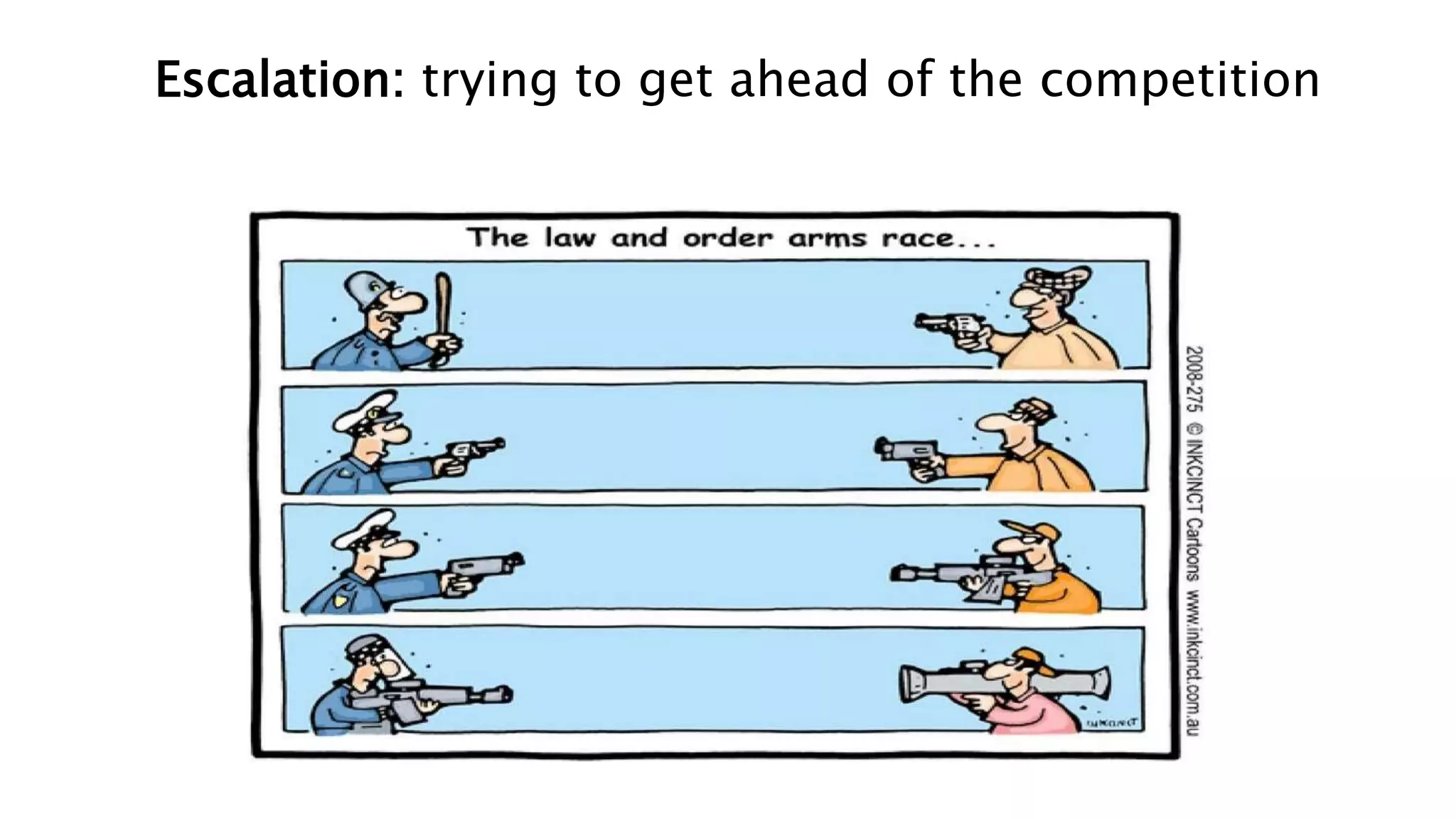
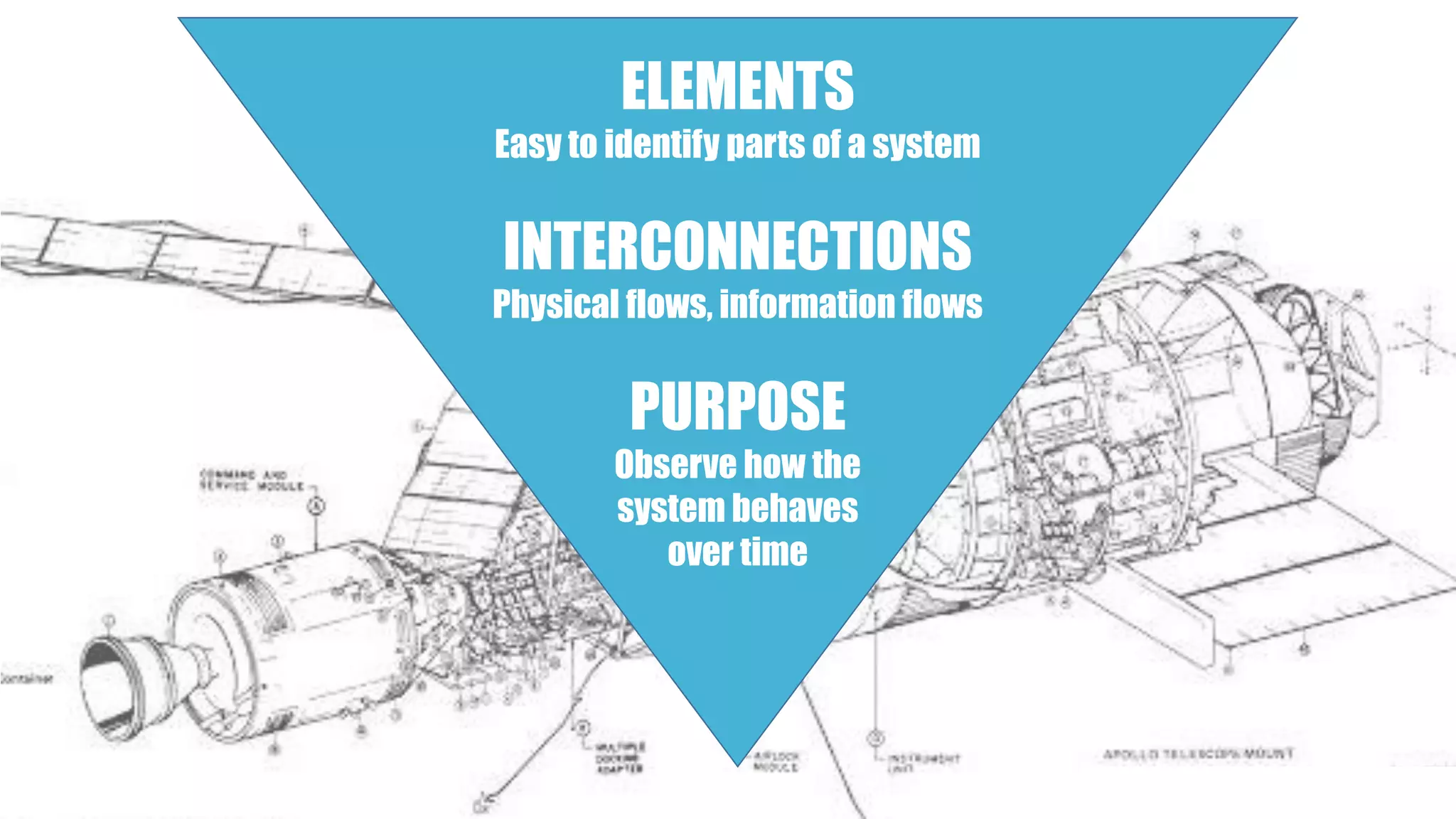
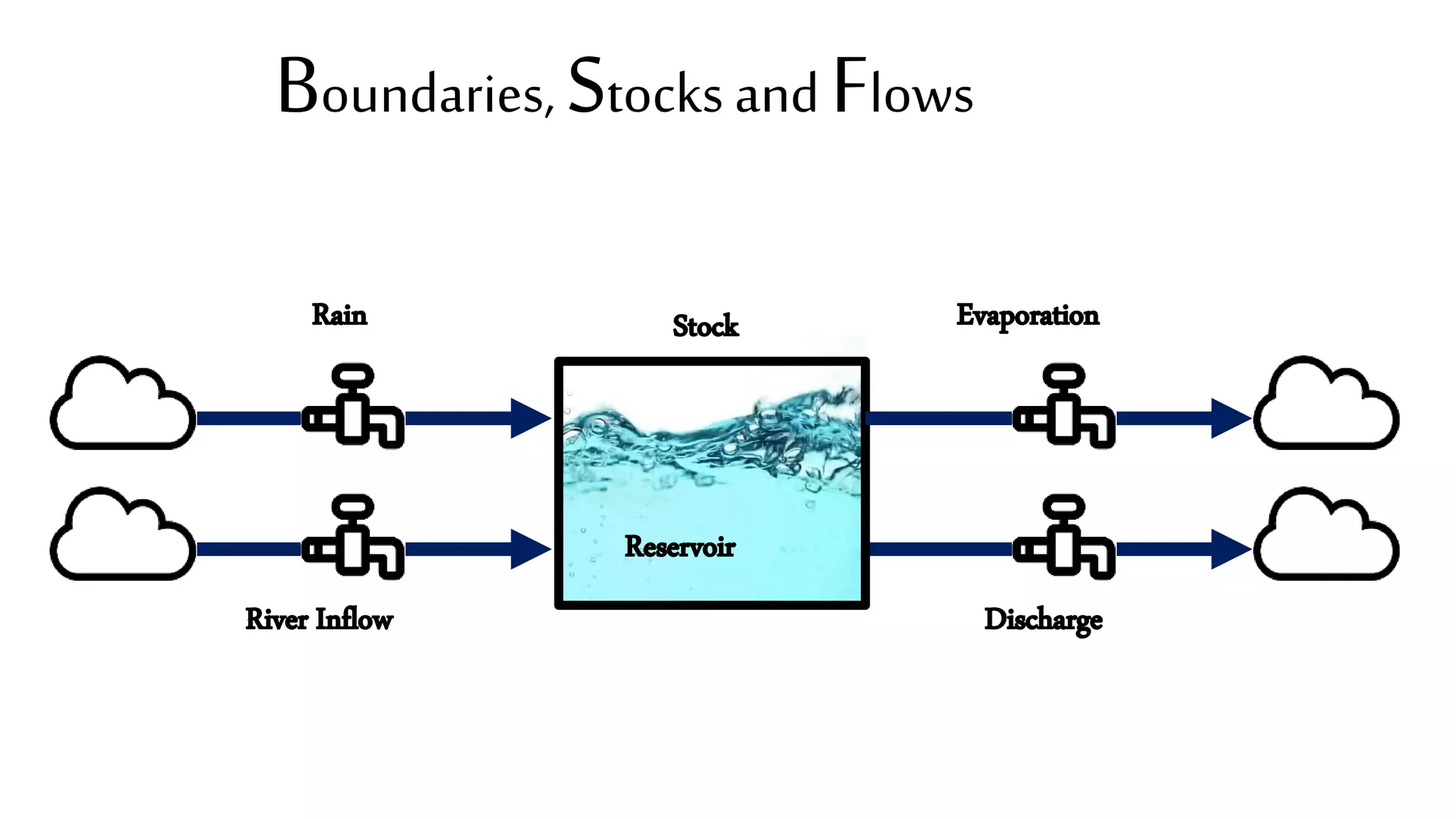
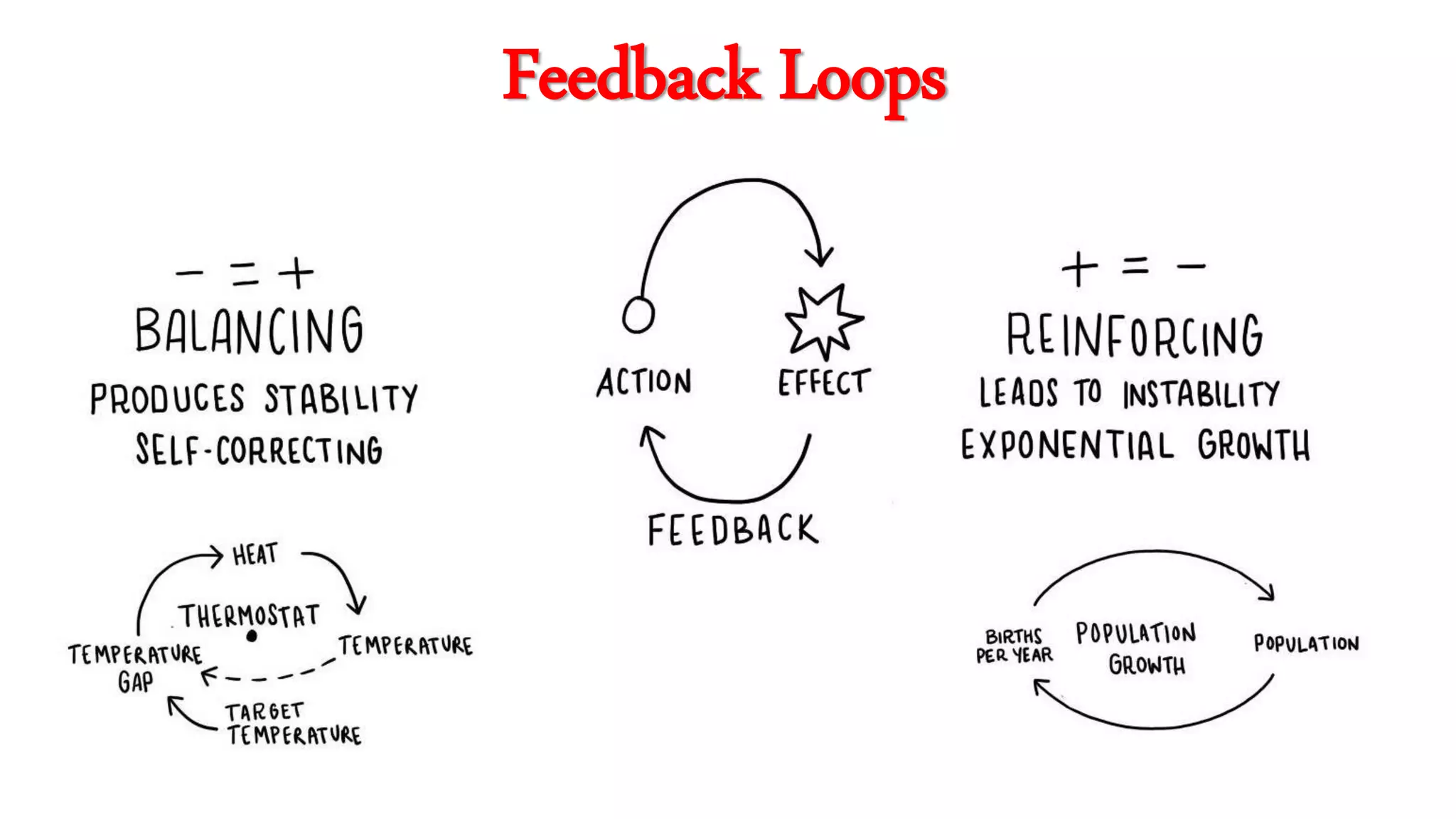
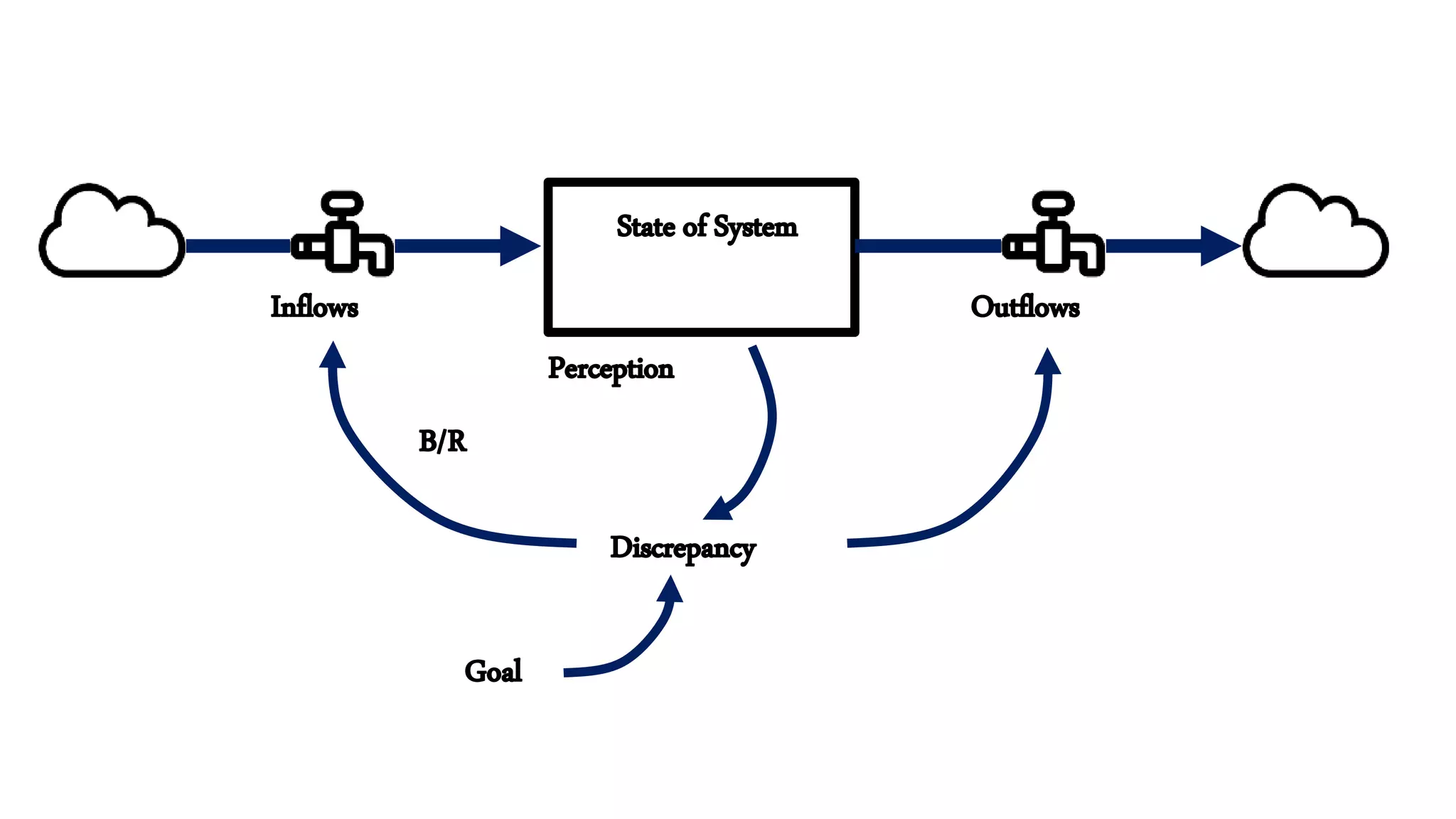
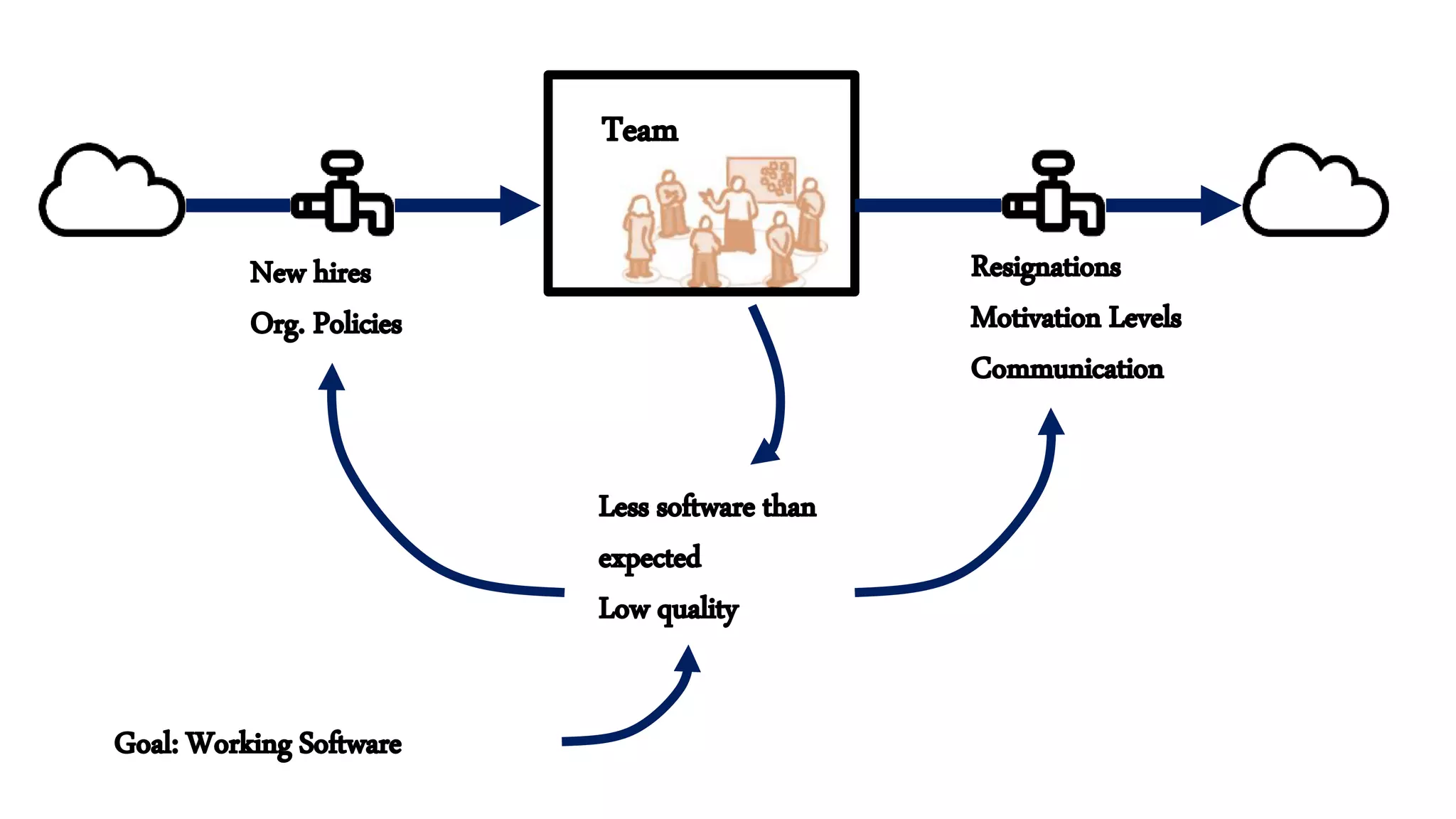
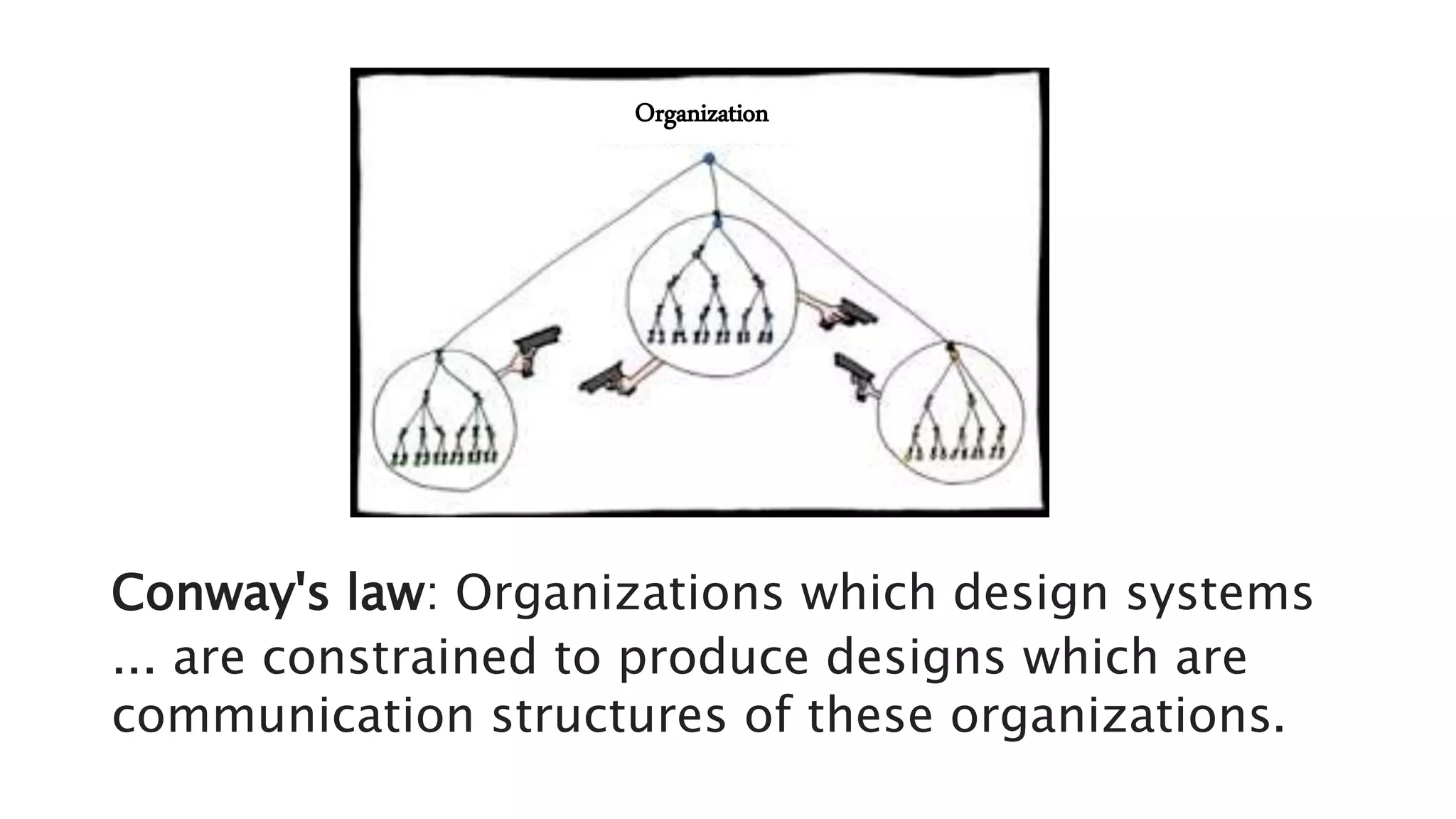
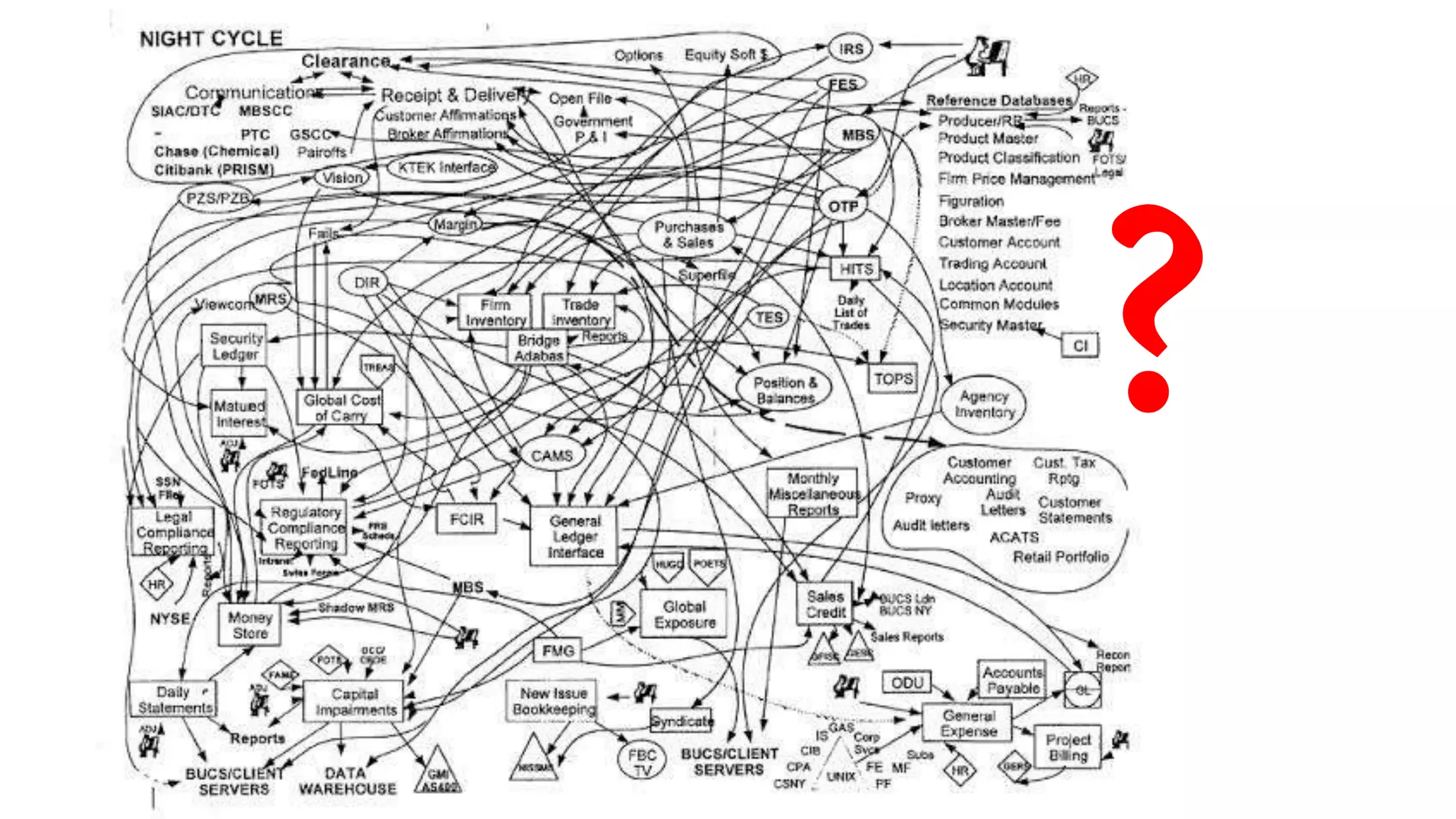
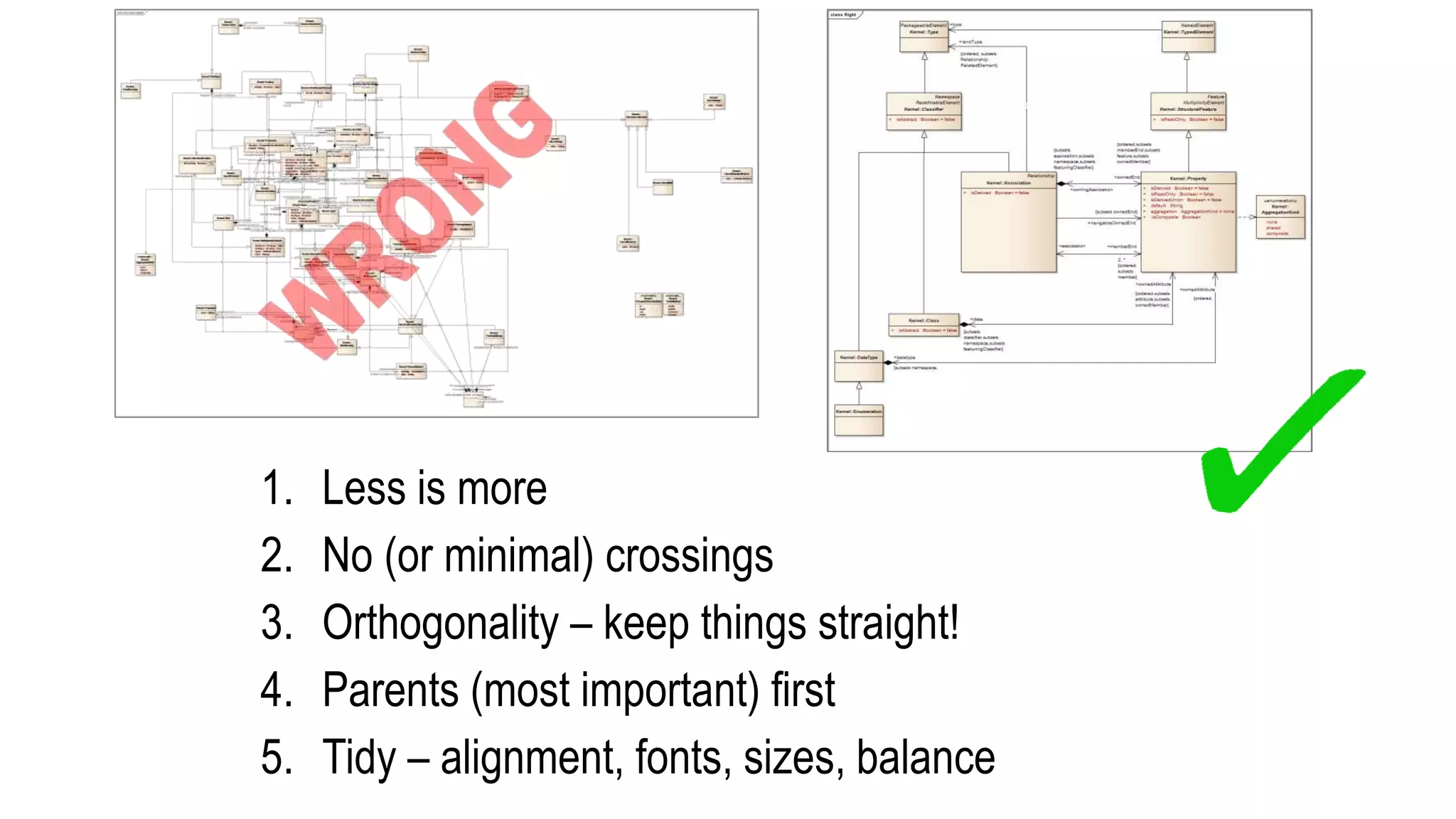
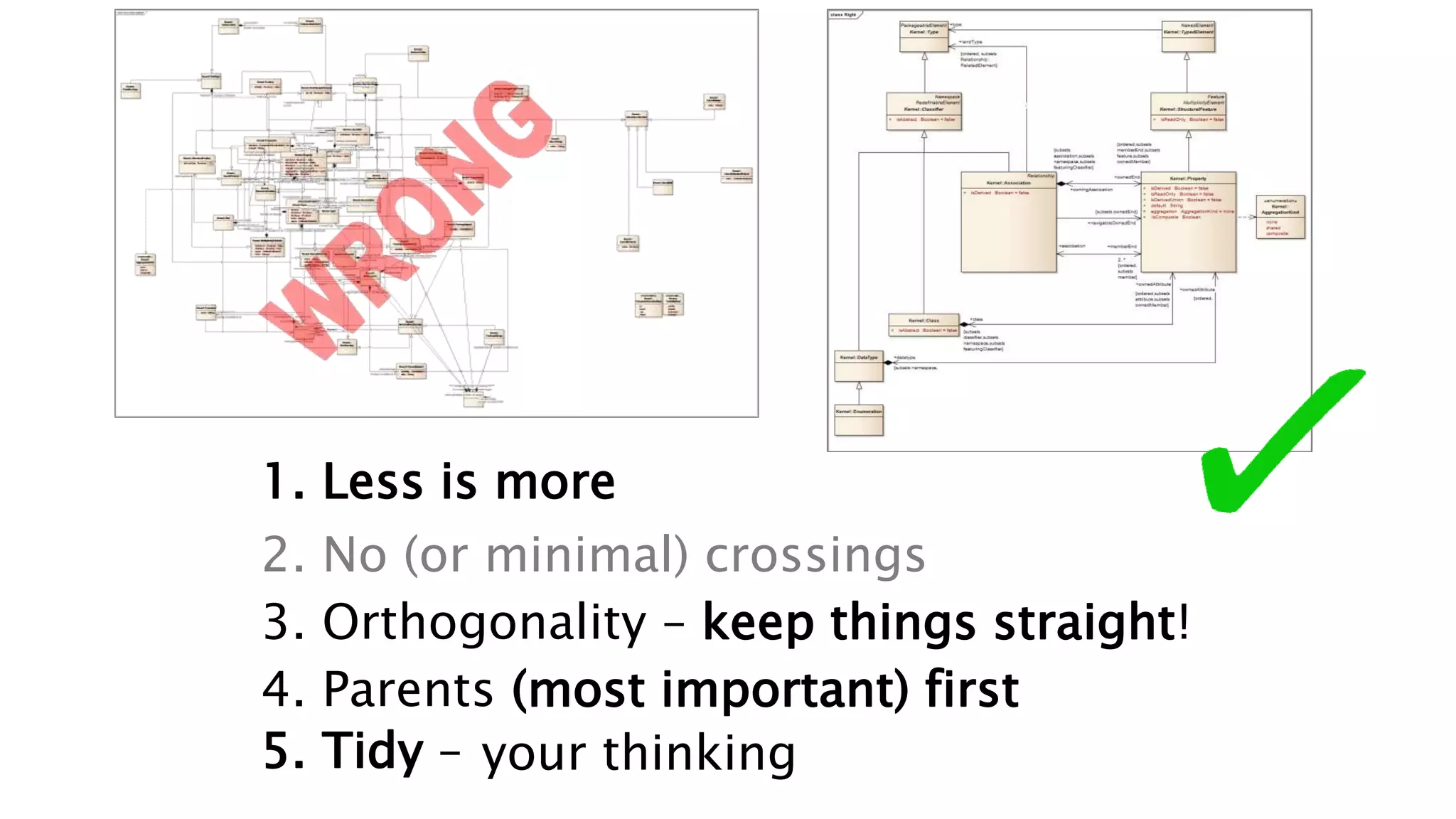
This document summarizes a presentation on systems thinking and simplification. It discusses common systems archetypes like escalation, the tragedy of the commons, and shifting the burden. It explains that systems have elements, interconnections and a purpose. The purpose of a university is discussed as an example. It also discusses modeling systems using basic diagrams of boundaries, stocks, and flows. The presentation emphasizes simplifying systems thinking by focusing on the important factors, avoiding unnecessary complexity, and following principles like Occam's razor. Resilience and the ability to adapt are discussed. The overall message is that systems can be redesigned to behave as intended rather than just as designed.