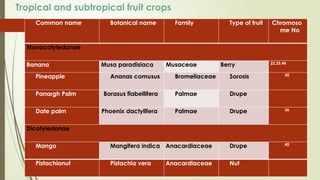
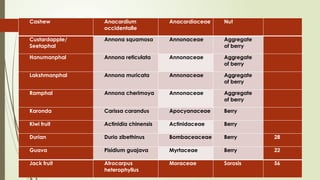
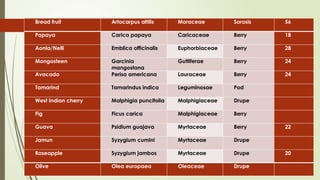
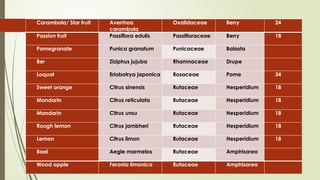
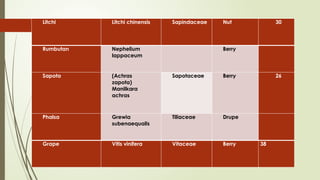
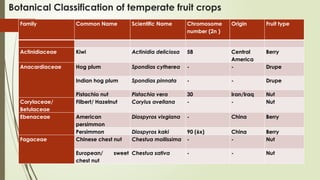
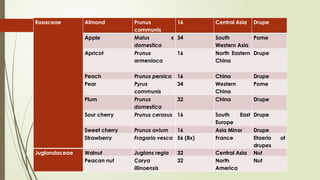
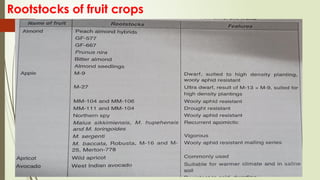
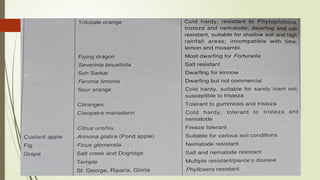
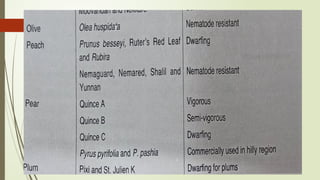
The document provides a detailed classification of various fruit crops, including both monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous fruits, along with their botanical names, families, fruit types, and chromosome numbers. It also discusses chemotaxonomy, defining it as the classification of plants based on their chemical contents, and highlights specific chemical constituents. Additionally, it introduces molecular markers as DNA fragments that identify specific genes within a genome.