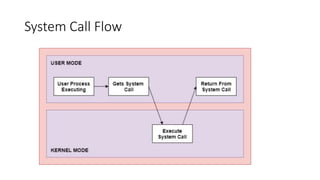
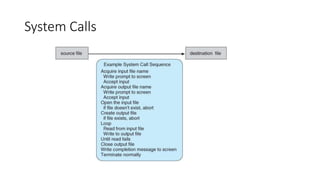
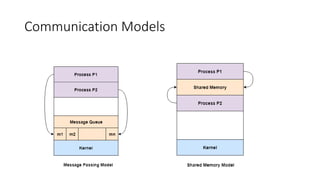
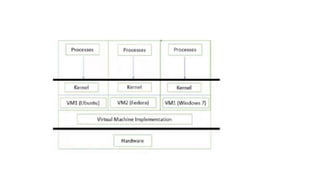
This document discusses system calls, inter-process communication models, system programs in operating systems, and virtual machines. It describes how system calls provide an interface for processes to request services from the operating system, including process control, file management, device management, and communication. It explains the shared memory and message passing models for inter-process communication. It outlines different types of system programs for file management, status information, file modification, programming language support, program loading and execution, and communications. Finally, it describes how virtual machines allow multiple operating systems to run concurrently and isolated on the same physical computer.