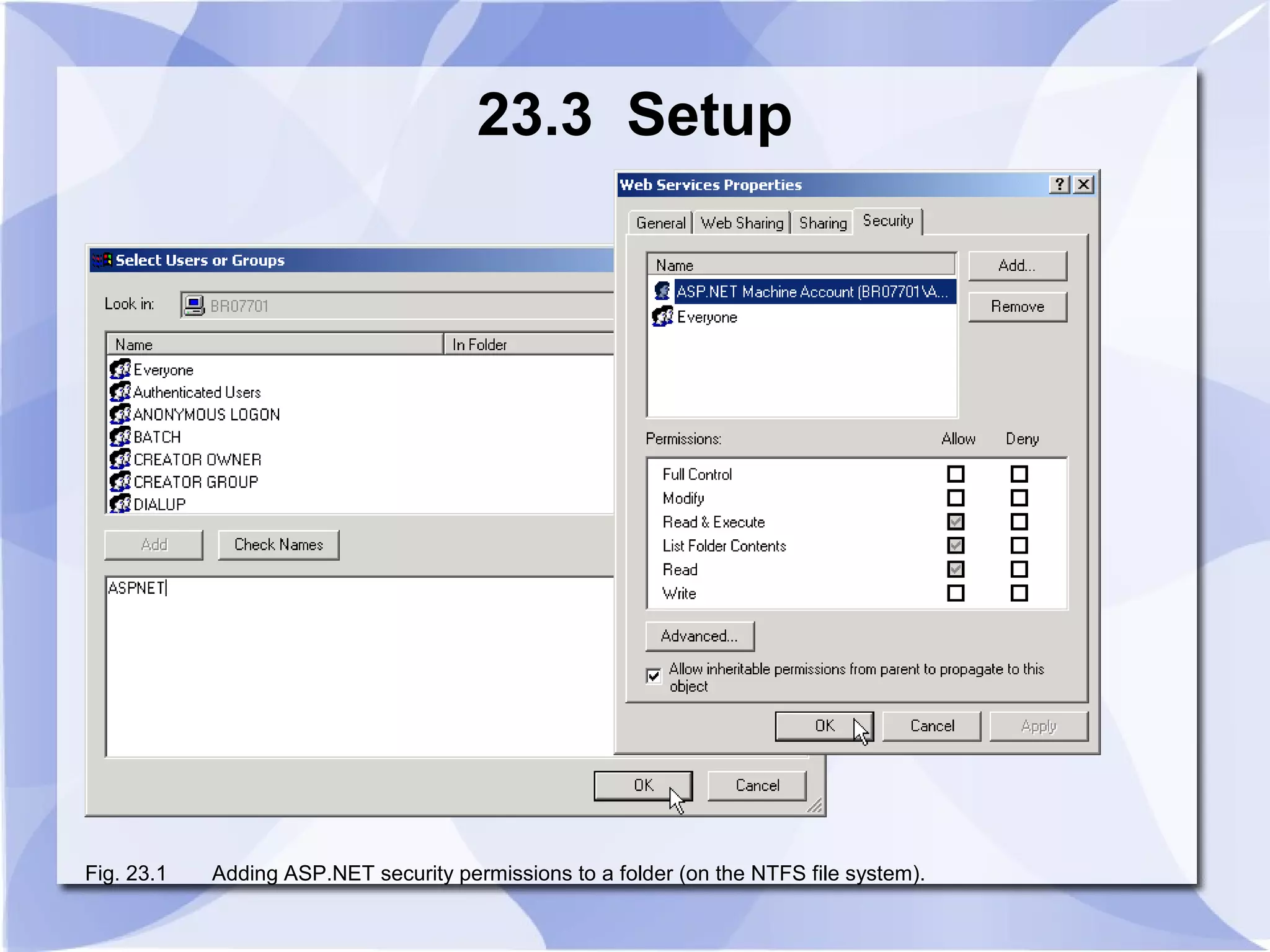
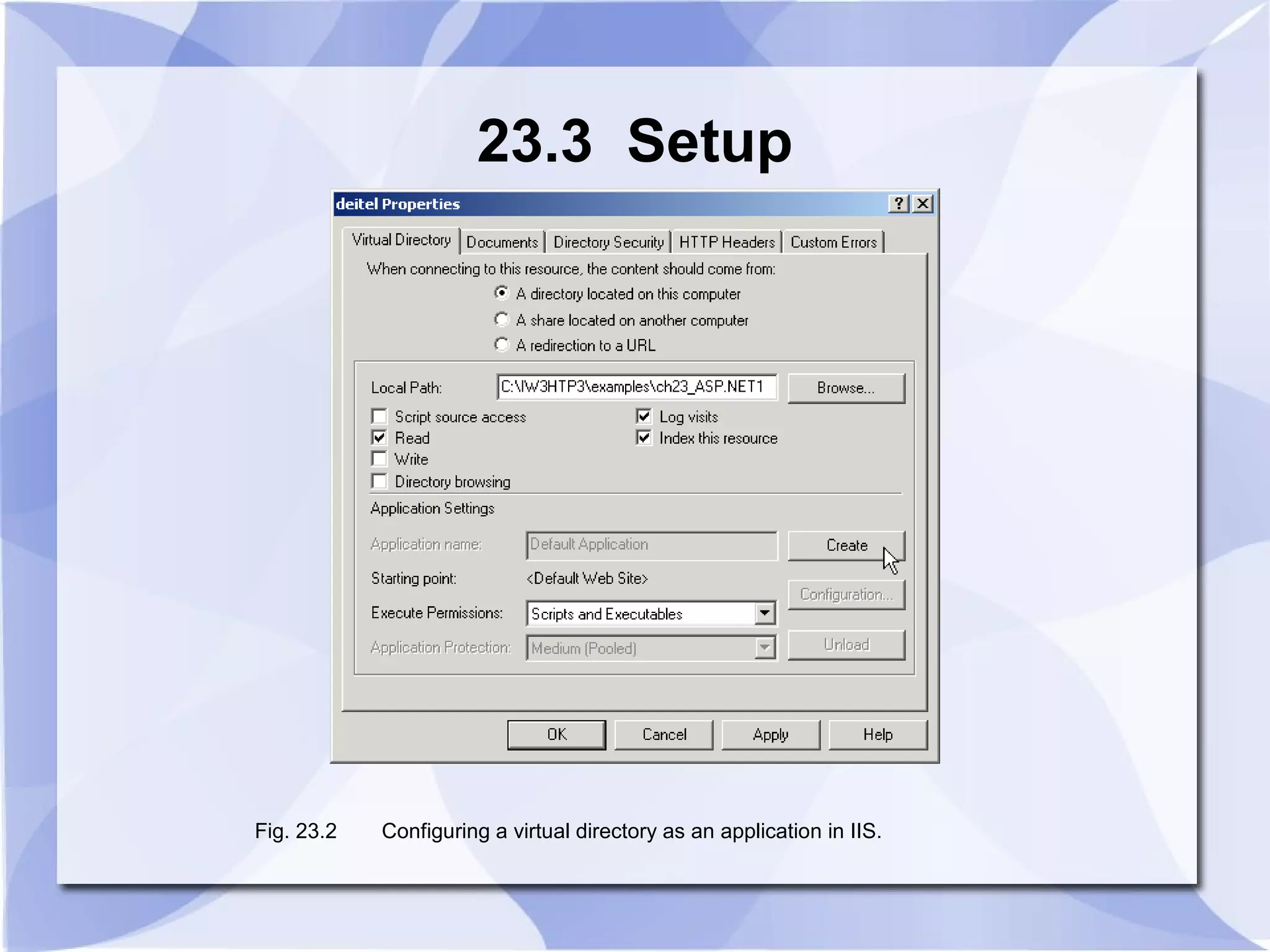
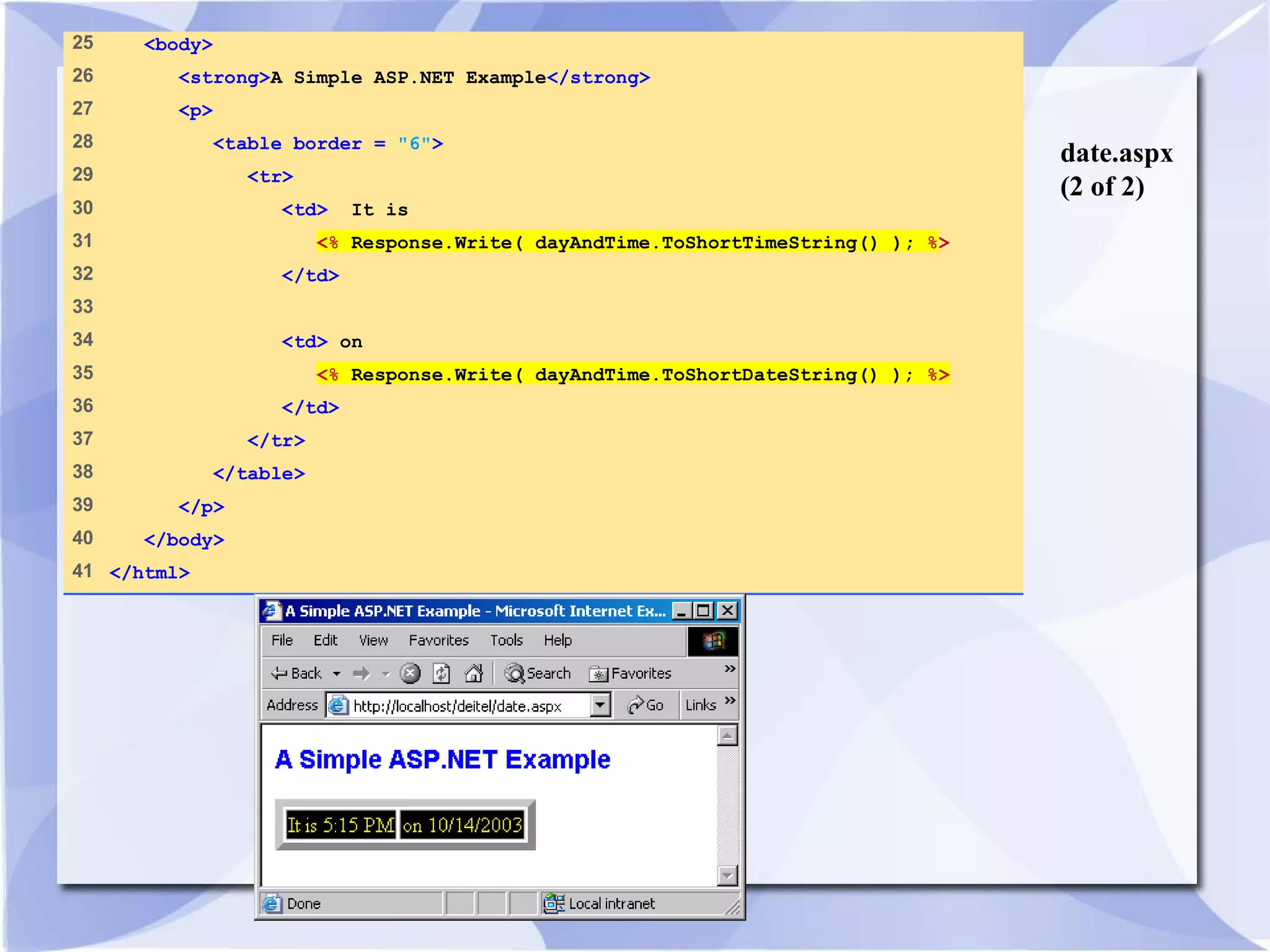
This document provides an overview and introduction to ASP.NET, including how to set it up, create simple ASP.NET pages using JScript.NET, handle server-side scripting, and access databases and XML files. It discusses key ASP.NET concepts like web forms, session tracking, and web services. An example ASP.NET page is provided that generates and displays the current date and time using server-side scripting.