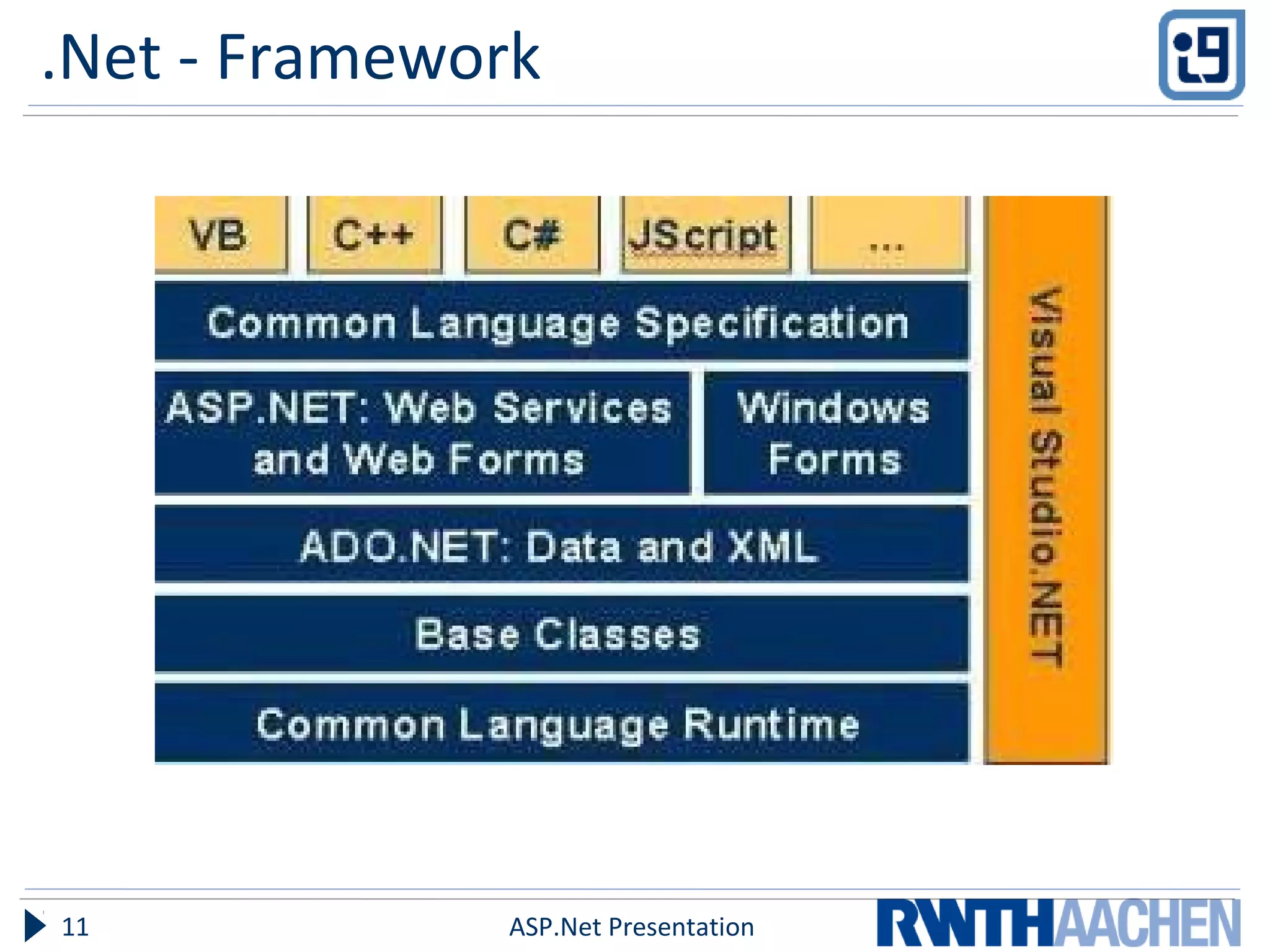
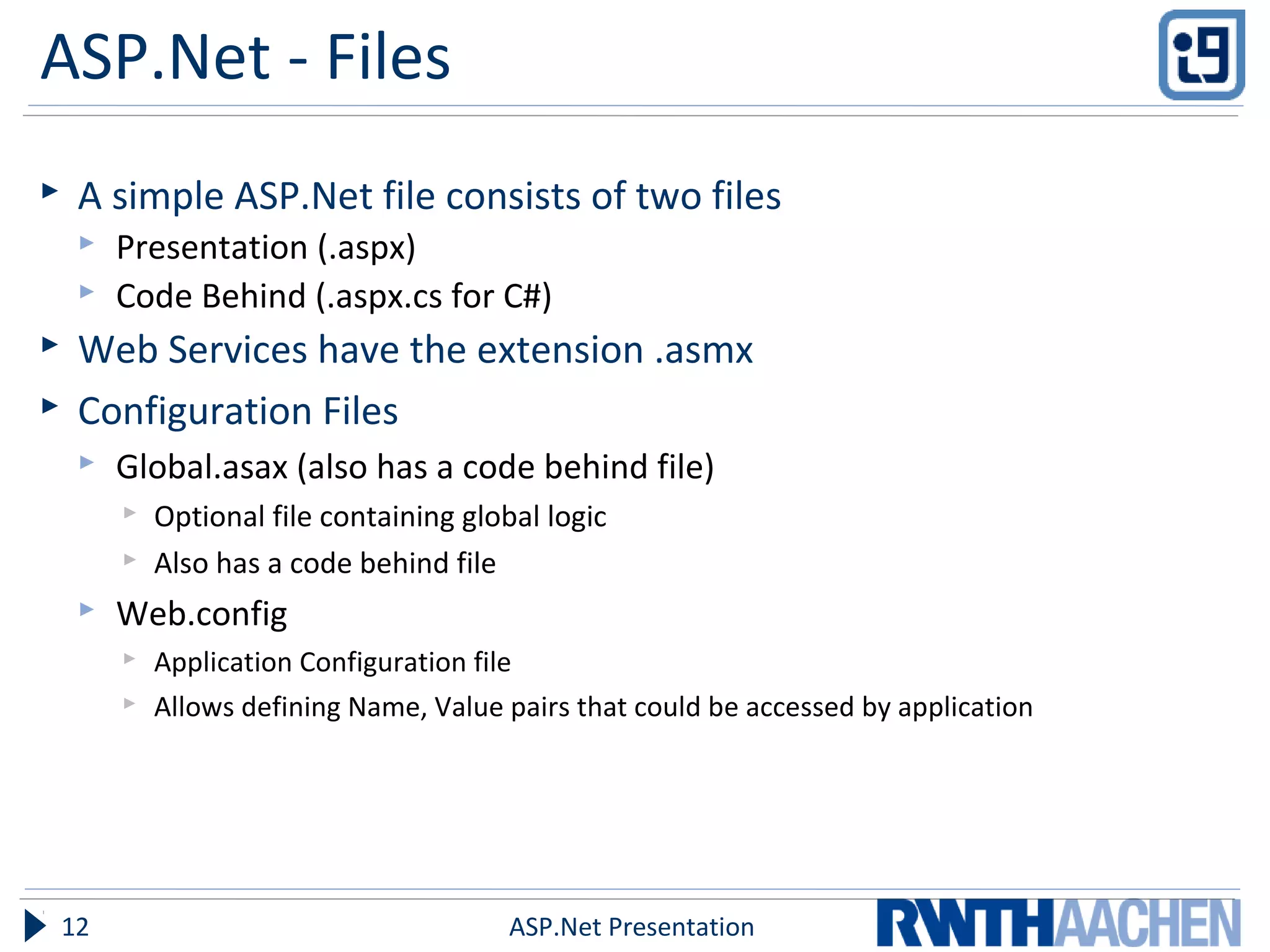
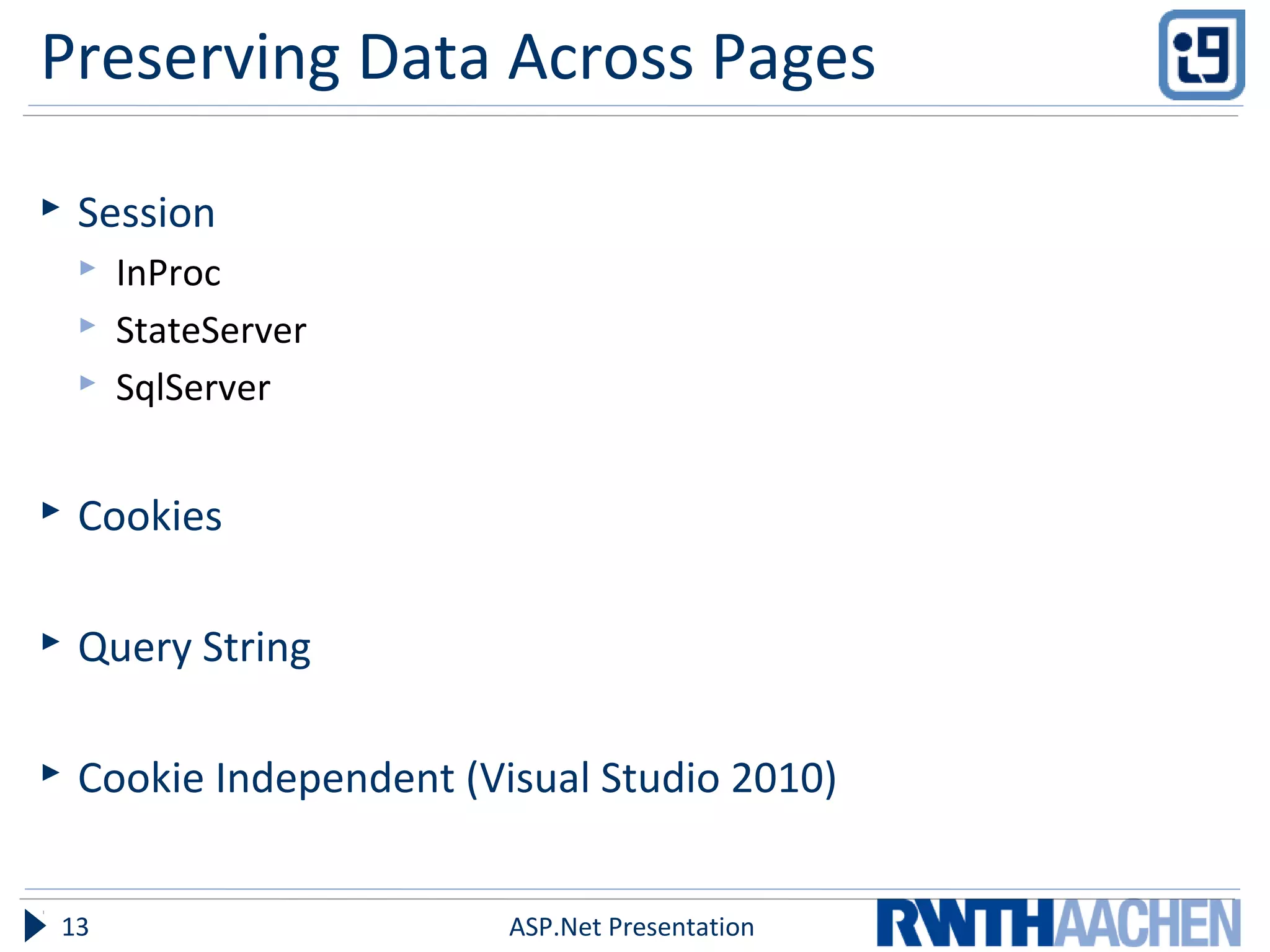
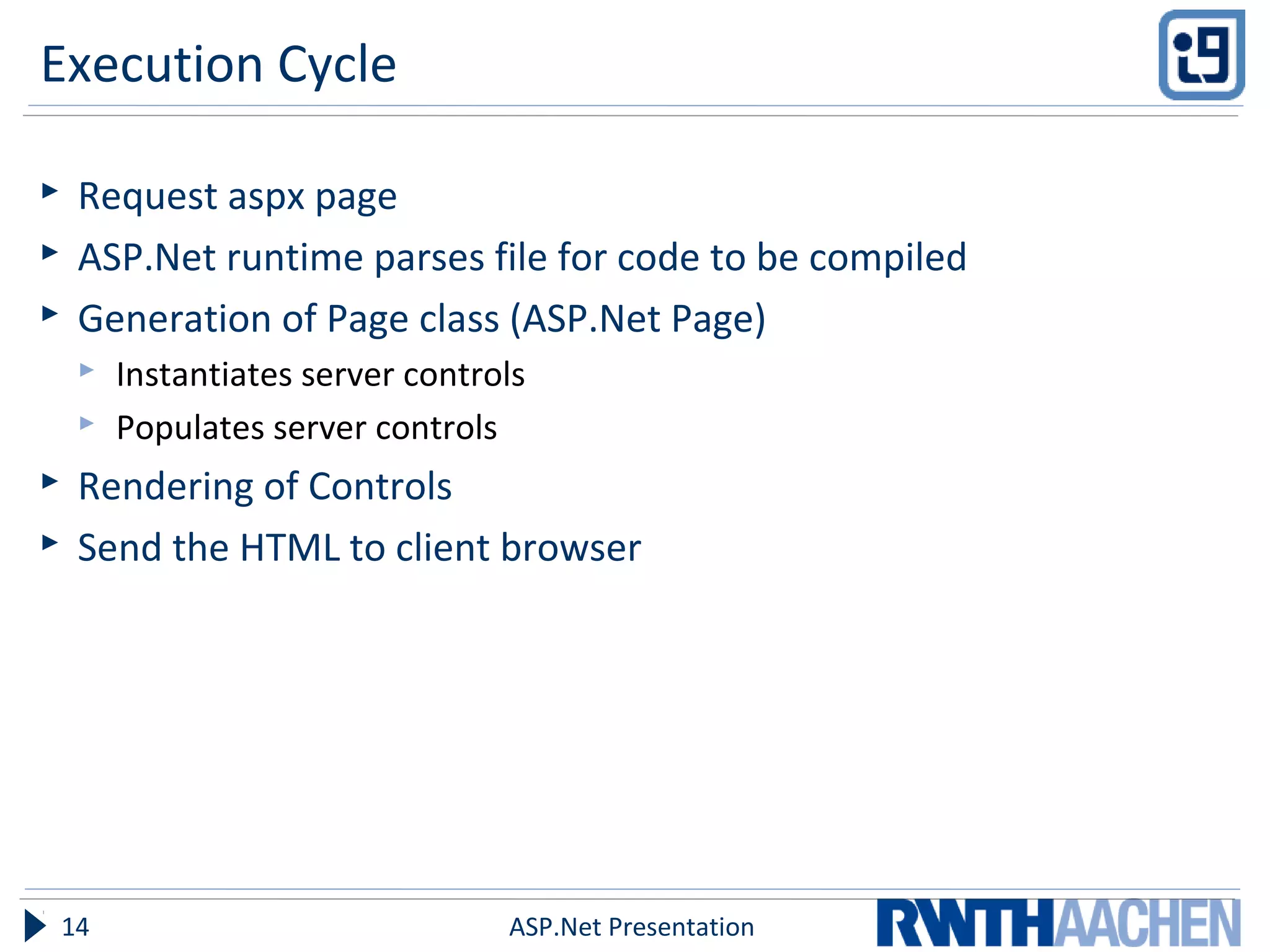
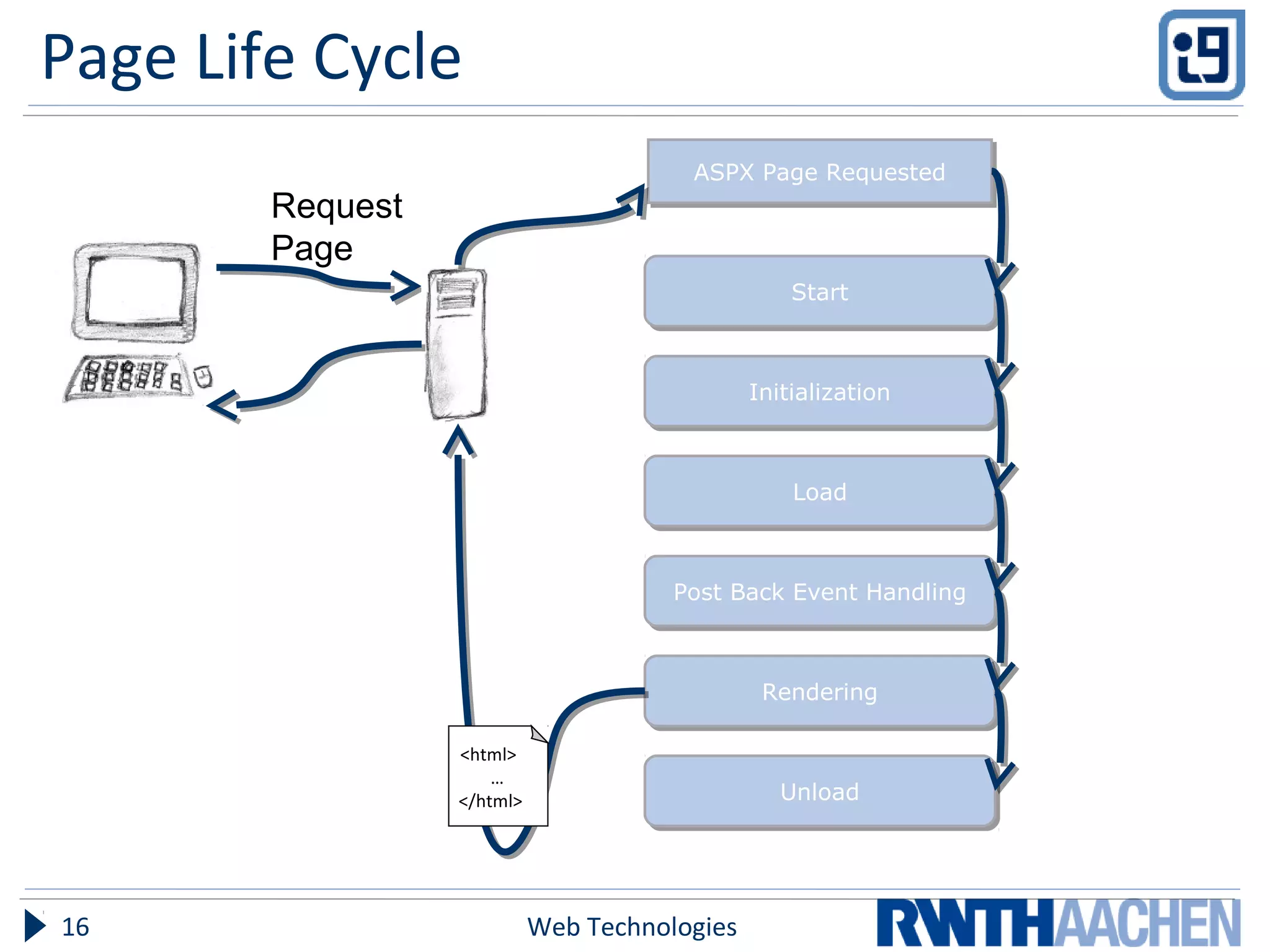
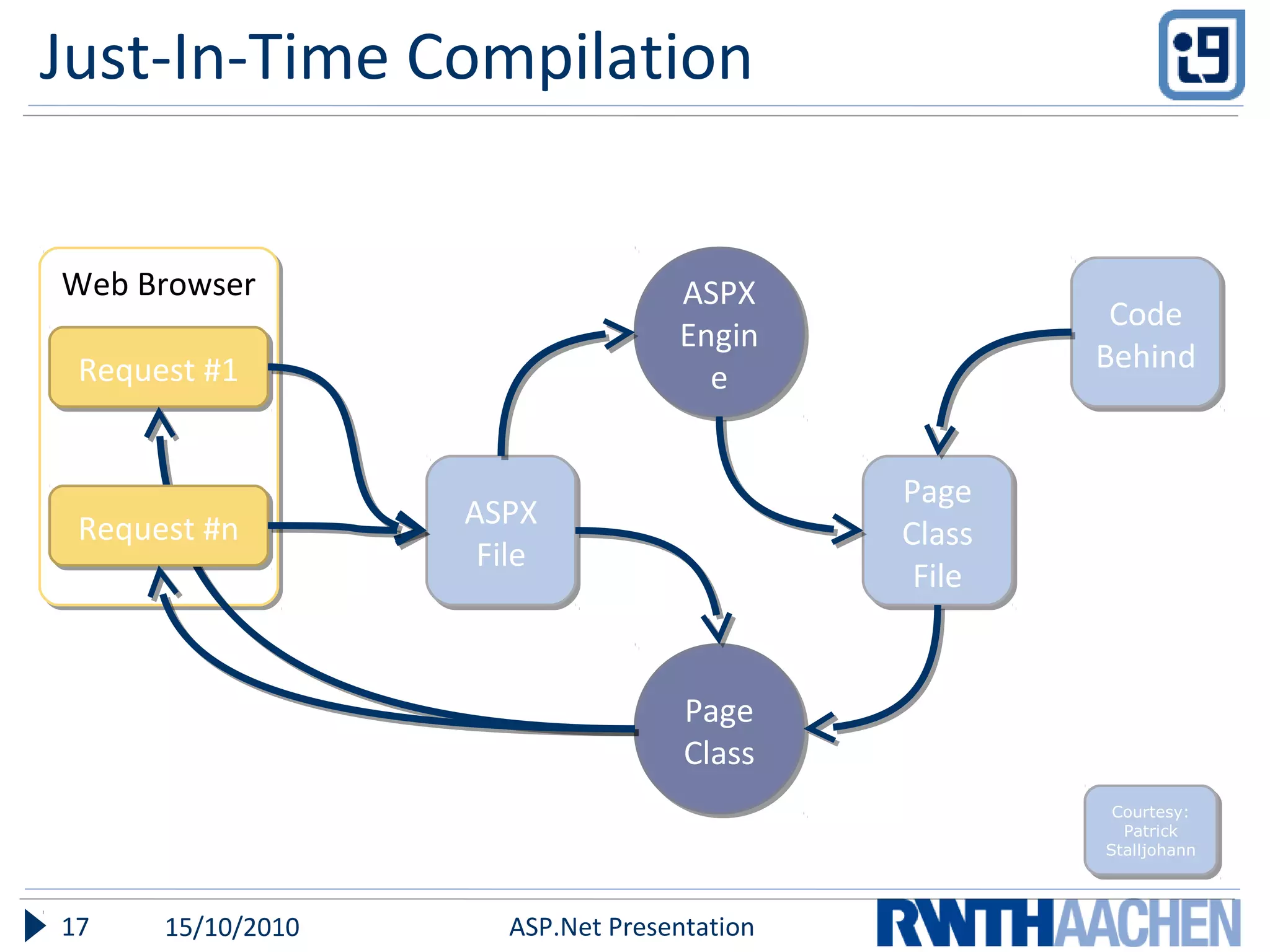
This document provides an overview of server-side ASP.NET technologies. It compares ASP.NET to PHP, discusses the problems with classic ASP that ASP.NET aimed to address, and outlines key ASP.NET concepts like the .NET framework, ASPX files and code-behind files, page lifecycle, controls, state management, and configuration files. The document also covers ASP.NET execution process, advantages over classic ASP, and references additional resources for further information.