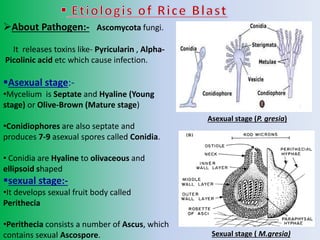
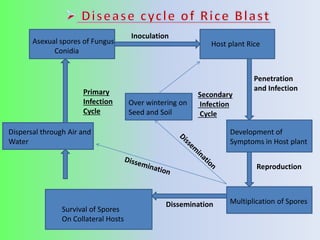
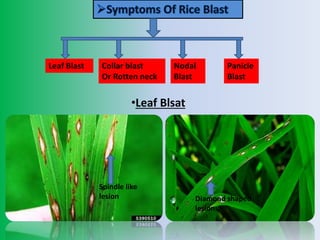
This document discusses the rice blast fungus, a fungal disease that is the most severe and infectious disease of rice plants. It first appeared in Japan in 1904 and India in 1913. The pathogen is a type of ascomycota fungi that releases toxins and has both asexual and sexual stages. It is spread by wind and seeds. The disease is managed through cultural practices like removing weeds, soil solarization, resistant varieties, and proper spacing. Biological controls include seed treatments with fungi like Pseudomonas fluorescence and Tricoderma viride. Chemical controls include seed treatments with fungicides and foliar sprays.