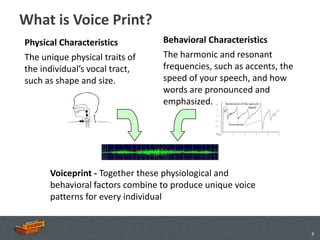
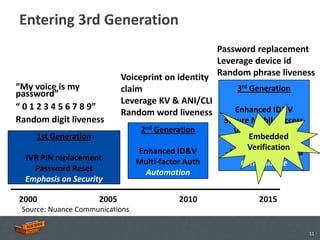
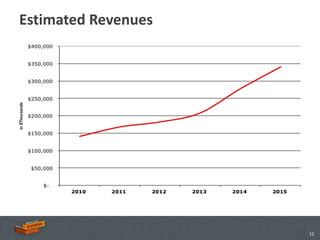
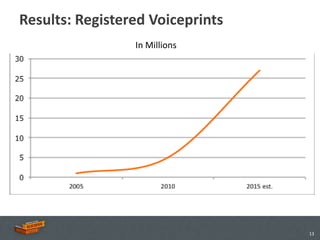
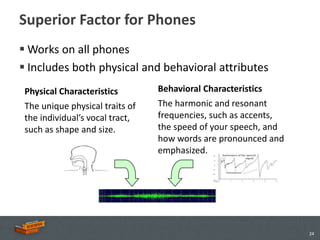
The document discusses the advancements and applications of voice biometrics, specifically focusing on speaker verification technology and its relevance for secure mobile transactions. It highlights the need for stronger authentication methods in an increasingly mobile and interconnected world, addressing issues like fraud protection and user authentication. Key points include the various components of voice biometrics, the importance of unique voice patterns, and the growing demand for secure mobile commerce solutions.