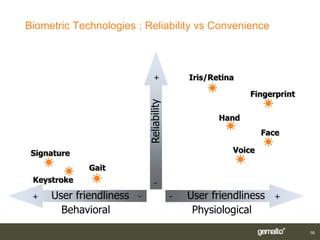
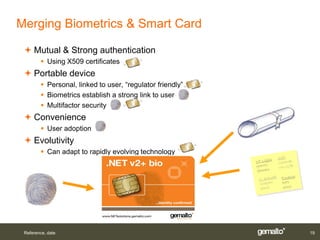
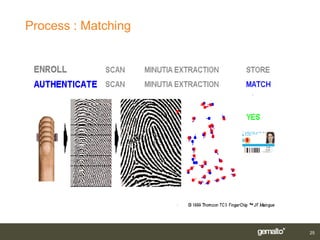
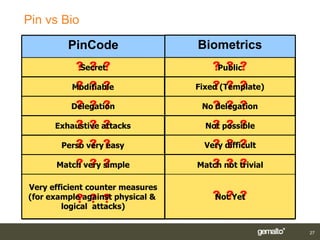
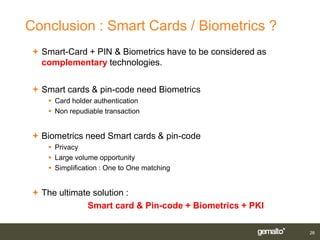
Gemalto introduced smart card and biometric authentication solutions. It discussed using fingerprints for biometric authentication on computers due to user acceptance and technology maturity. Combining biometrics with smart cards provides multifactor authentication with a portable device linked to the user, improving security and convenience. Existing implementations include matching biometrics on or off the smart card. Limitations include operating system support, but workarounds exist and the ultimate solution is a smart card using PKI with both a PIN and biometrics for authentication.