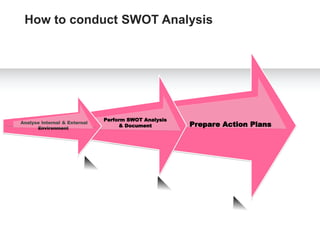
A SWOT analysis is a framework used to evaluate a company's or product's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It involves identifying internal factors (strengths and weaknesses) as well as external factors (opportunities and threats) that are important for achieving organizational success. The document outlines the key aspects of conducting a SWOT analysis, including establishing objectives, analyzing internal and external environments, brainstorming factors, prioritizing ideas, and developing action plans. The benefits of SWOT analysis include providing a decision-making tool, helping to set strategic objectives, and allowing companies to benchmark against competitors.