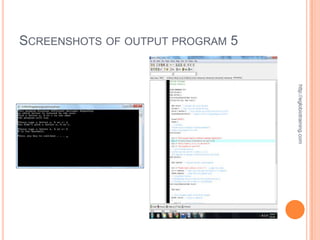
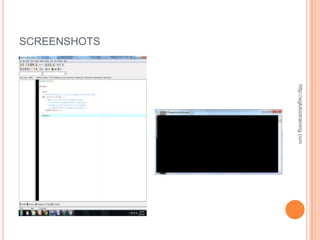
The document discusses looping statements in programming which allow a block of code to be repeatedly executed until a certain condition is reached. There are three main types of loops: for loops, while loops, and do-while loops. For loops initialize a variable, specify a condition, and update the variable each iteration. While loops continuously execute the code block as long as the condition is true. Do-while loops are similar to while loops but execute the code block at least once even if the condition is false.







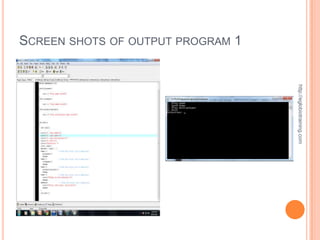


![EXPLANATION
#include <iostream>
- This tells the compiler to include files in using dev c++
of programming.
http://eglobiotraining.com
#include <stdlib.h>
- This tells the compiler to include files.
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- This starts the main function use in programming.
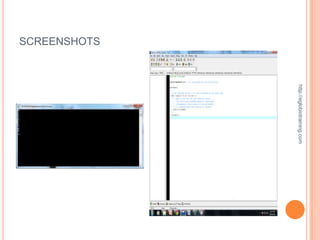
This 2nd example program that I did for the requirement
in programming will ask the user to select a number.
After entering the number, the programming software
which is the dev c++ program will print if the entered
number is equal to 1, 2 or 3. It will print different things
on the screen depending on which number the user
chose.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalrequirementinprogramming-121011012833-phpapp02/85/Final-requirement-in-programming-12-320.jpg)

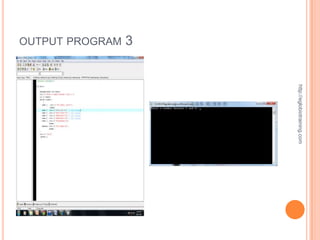

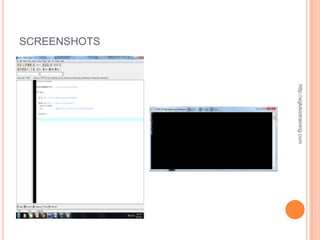
![ACTUAL SOURCE CODE OF PROGRAM 4
#include <iostream> void welcome()
#include <stdlib.h> {
cout << "This program displays different messages
dependingn";
using namespace std;
cout << "on which number is entered by the user.n";
http://eglobiotraining.com
void welcome();
cout << "Pick a number between 1 and 6 to see whatn";
int getInteger();
cout << "the program will say.nn";
void displayResponse(int choice);
} // end of welcome function
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
// getInteger asks the user for a number between 1 and 6.
{
// The integer is returned to where the function was called.
int choice; // declares the choice variable
int getInteger()
welcome(); // This calls the welcome function
{
choice = getInteger(); // calls getInteger and receives the
value for choice int response; // declares variable called response
displayResponse(choice); // passes choice to cout << "Please type a number between 1 and 6: "; //
displayResponse function prompt for number
cin >> response; // gets input from user and assigns it to
response
system("PAUSE");
return response; // sends back the response value
return 0;
} // end getInteger function
} // end main
// displayResponse function takes the int variable and uses it
// welcome function displays an opening message to
// explain the program to the user
// to determine which set of tasks will be performed.
void displayResponse(int choice)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalrequirementinprogramming-121011012833-phpapp02/85/Final-requirement-in-programming-16-320.jpg)

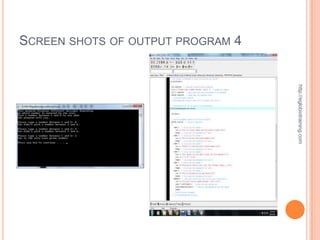

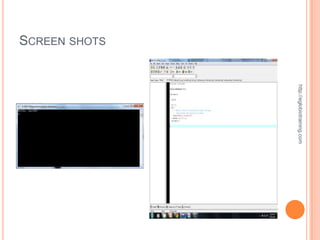
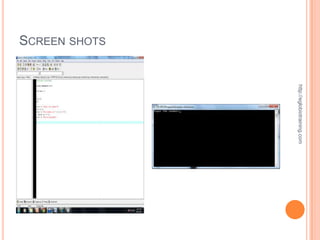
![ACTUAL SOURCE CODE OF PROGRAM 5
#include <iostream> void welcome()
#include <stdlib.h> {
cout << "This program displays different messages dependingn";
using namespace std; cout << "on which letter is entered by the user.n";
void welcome(); cout << "Pick a letter a, b or c to see whatn";
http://eglobiotraining.com
char getChar(); cout << "the program will say.nn";
void displayResponse(char choice); } // end of welcome function
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) // getChar asks the user for a letter a, b or c.
{ // The character is returned to where the function was called.
char choice; // declares the choice variable char getChar()
welcome(); // This calls the welcome function {
choice = getChar(); // calls getChar and returns the value for choice char response; // declares variable called response
displayResponse(choice); // passes choice to displayResponse function
cout << "Please type a letter a, b or c: "; // prompt for letter
system("PAUSE"); cin >> response; // gets input from user and assigns it to response
return 0; return response; // sends back the response value
} // end main } // end getChar function
// welcome function displays an opening message to // displayResponse function takes the char variable and uses it
// explain the program to the user // to determine which set of tasks will be performed.
void displayResponse(char choice)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalrequirementinprogramming-121011012833-phpapp02/85/Final-requirement-in-programming-20-320.jpg)