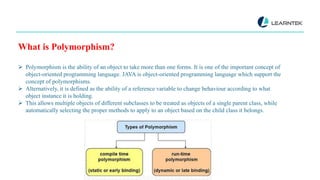
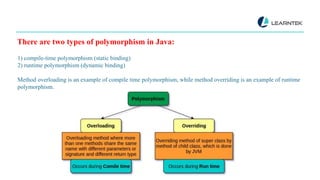
Polymorphism is the ability of an object to take more than one form and is a key concept in object-oriented programming, especially in Java, enabling different subclasses to be treated as objects of a single parent class. There are two types of polymorphism in Java: compile-time (static binding) through method overloading and runtime (dynamic binding) through method overriding. While polymorphism aids in code reuse and reduces coupling, it can also complicate implementation and impact performance.



![class Addition
{
static int add1 (int a,int b)
{
return a+b;
}
static int add1(int a,int b,int c)
{
return a+b+c;
}
}
class xyz
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(Addition.add1(13,13));
System.out.println(Addition.add1(9,9,9));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphisminjava-181210115949/85/Polymorphism-in-java-6-320.jpg)

![.
class xyz1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(Addition.add1(13,13));
System.out.println(Addition.add1(9.5,9.5));
}
}
Output:
26
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphisminjava-181210115949/85/Polymorphism-in-java-8-320.jpg)

![TIME FOR EXPERIMENT
class Overload2
{
public static void main (String args [])
{
Overload1 Obj = new Overload1();
double result;
Obj.do(20);
Obj.do(20, 30);
result = Obj.do(4.5);
System.out.println("Output is: " + result);
}
}
a: 20
a and b: 20,30
double a: 4.5
Output is: 20.25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphisminjava-181210115949/85/Polymorphism-in-java-10-320.jpg)


![public static void main(String args[])
{
dog obj = new dog();//creating object
obj.do();//calling method
}
}
Output:
Dog is eating food](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphisminjava-181210115949/85/Polymorphism-in-java-13-320.jpg)

![Copyright @ 2018 Learntek. All Rights Reserved. 15
class car extends Vehicle
{
public void run()
{
System.out.println("speed is faster than bike");
}
}
// Next, run() method will be called, depends on type of actual instance created on runtime
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Vehicle v1 = new bike();
v1.run();
Vehicle v2 = new car();
v2.run();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphisminjava-181210115949/85/Polymorphism-in-java-15-320.jpg)

