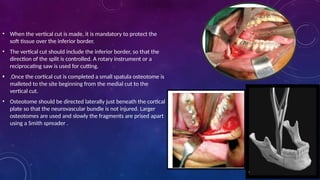
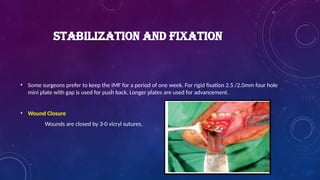
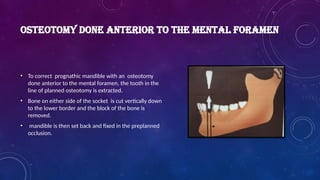
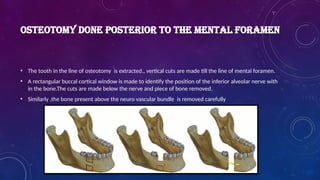
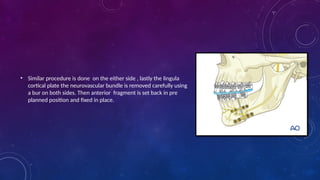
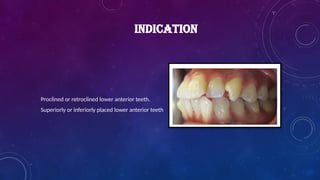
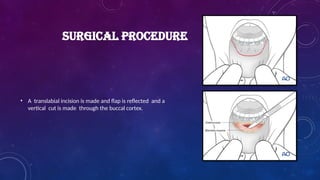
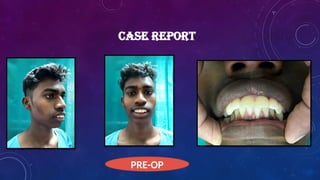
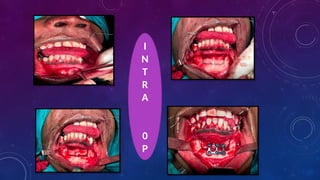
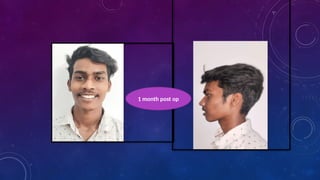
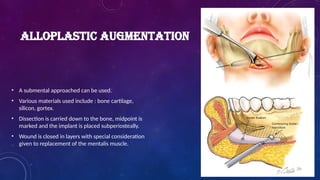
Introduction
Face forms the identity of an individual .Facial deformities invariably make an individual highly self conscious of this abnormal features . The appearance sometimes has a psychological impact on the individual.
Definition
• The word orthognathic comes from the Greek word “ORTHOS’’ meaning to straighten and ‘’ GNATHOS’’ meaning jaw.
• It involves ‘surgical manipulation of the elements of the facial skeleton to restore the proper anatomic and functional relationship in patients with dentofacial and skeletal deformities.
HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENTS
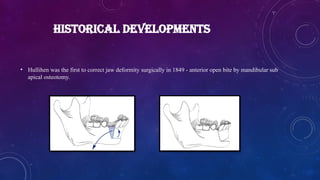
• Hullihen was the first to correct jaw deformity surgically in 1849 - anterior open bite by mandibular sub apical osteotomy.
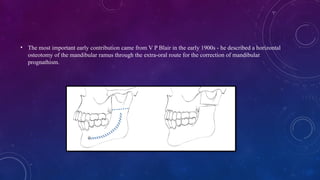
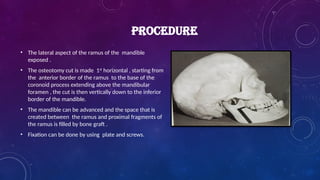
• The most important early contribution came from V P Blair in the early 1900s - he described a horizontal osteotomy of the mandibular ramus through the extra-oral route for the correction of mandibular prognathism.
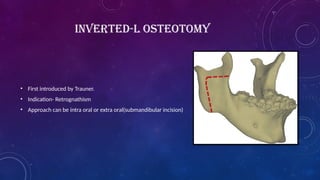
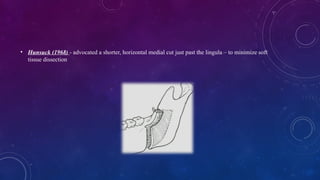
• Trauner 1955 described the inverted ‘L’ osteotomy of the ramus for the correction of mandibular prognathism.
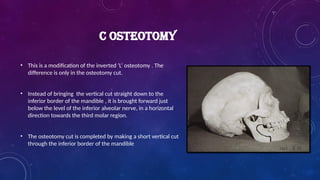
• Caldwell and colleagues modification of L osteotomy to C - osteotomy
• Hugo Obwegesser (1955) described the technique of intraoral sagittal split osteotomy for the correction of mandibular problems.
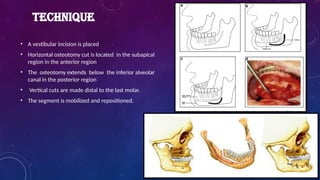
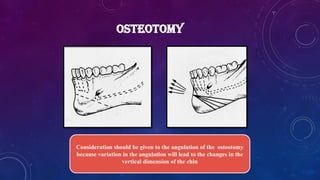
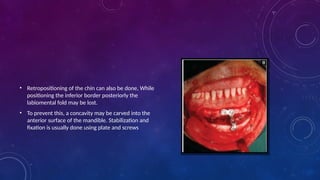
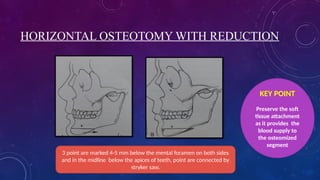
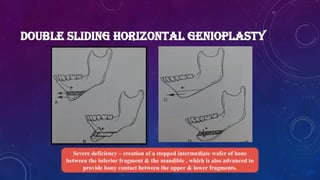
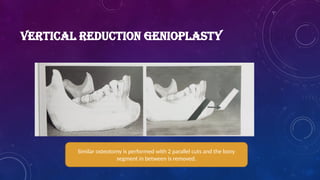
• Heinz Köle described the procedure of genioplasty 1968 and a technique to correct open bite.
• Burstone et al (1978 & 1980) gave an analysis for the assessment of dentofacial deformity using cephalometric radiographs " The cephalometric analysis for orthognathic surgery" (COGS).
• The latest developments in orthognathic surgery is the use of adjunct plastic surgical procedures like liposuction, lip correction.
Etiopathogenesis
CONGENITAL
• Genetic – Underlying genetic predisposition
• Syndromes –Apert’s and Crouzon’s syndrome
ACQUIRED
• Traumatic
• Others – neoplastic growth in the jaws, surgical resections etc.
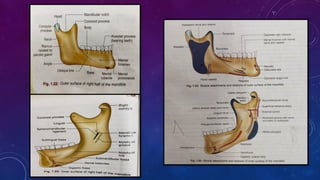
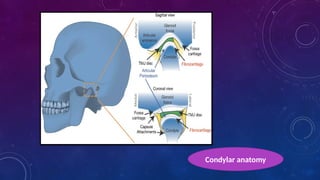
Anatomical position of the mandibular canal
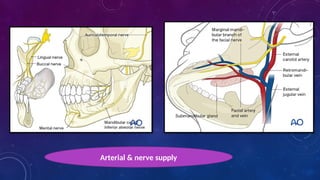
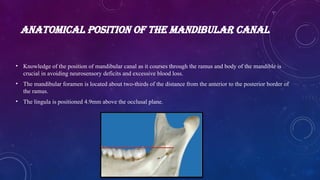
• Knowledge of the position of mandibular canal as it courses through the ramus and body of the mandible is crucial in avoiding neurosensory deficits and excessive blood loss.
• The mandibular foramen is located about two-thirds of the distance from the anterior to the posterior border of the ramus.
• The lingula is positioned 4.9mm above the occlusal plane.
Classification of IAN course by CARTER & KEEN
• Type 1: Nerve has a course near the apices of the teeth.
• Type2: The main trunk is low down in the body.
• Type 3: Has similar main trunk to type 2 with several smaller trunks to the molar teeth.
TIMING OF OSTEOTOMIES
• The treatment of dentofacial deformities is based on a careful co-ordination of orthodontics and surgeon.
• Early treatment using functional appliances and by orthodontic teeth movements may prevent functional and psychological problems, limit the deformity, shorten treatment time, improve results and obtain stability.
• As a rule it is better to wait till the skeletal growth is completed before doing orthognathic surgery.