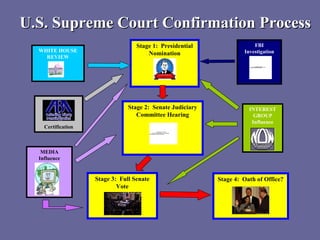
The document discusses the process and politics of nominating Supreme Court justices. It outlines the constitutional basis for nominations, which allows the President to nominate justices with Senate approval. It also lists factors that influence nominations, such as party affiliation and judicial philosophy. Additionally, it details the multi-step confirmation process involving the White House, FBI investigation, Senate hearings, and final Senate vote.