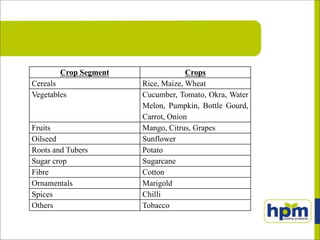
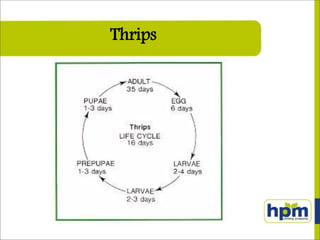
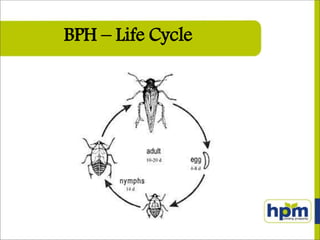
Imidacloprid is a systemic insecticide used to control various sucking pests across multiple crops including rice, cotton, and vegetables. It functions by blocking neuronal pathways in insects, leading to paralysis and death, and displays moderate toxicity to humans. Super Imida, a specific formulation, offers effective pest control with easy application while being compatible with fungicides and posing minimal risk to beneficial insect populations.









![• The MRL of SUPER IMIDA in Rice & Cotton seed oil has
already been fixed by Central Committee for Food Standards
[CCFS] as 0.05 ppm.
• SUPER IMIDA does not have any adverse effect on the
population of common natural enemies like Coccinella,
Chrysoperla, etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/superimidalarge-170429155028/85/Super-imida-large-10-320.jpg)

![RECOMMENDATIONS
Crop Name of the Pest Dosage / acre
[ml]
Dilution
in water
[Litres]
Cotton /
Bt-Cotton
Aphids, Jassids & Thrips
30-50
150-200
Rice
Brown Plant Hopper [BPH]
&
White backed Plant Hopper
[WBPH]
150-200](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/superimidalarge-170429155028/85/Super-imida-large-12-320.jpg)